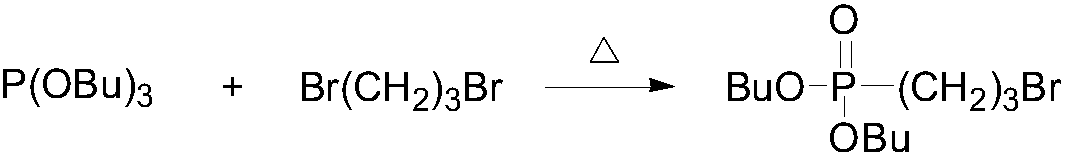A phosphoric acid-based modified cellulose adsorbent and its preparation method and application in rare earth recovery
A cellulose and phosphoric acid-based technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, other chemical processes, improvement of process efficiency, etc., can solve problems such as hindering industrial application, high ammonia nitrogen wastewater environment, high synthesis cost, etc., and achieve good separation and enrichment effect , high separation and enrichment efficiency, and reduced processing costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 Preparation of a phosphoric acid-based modified cellulose adsorbent (P-OCS)
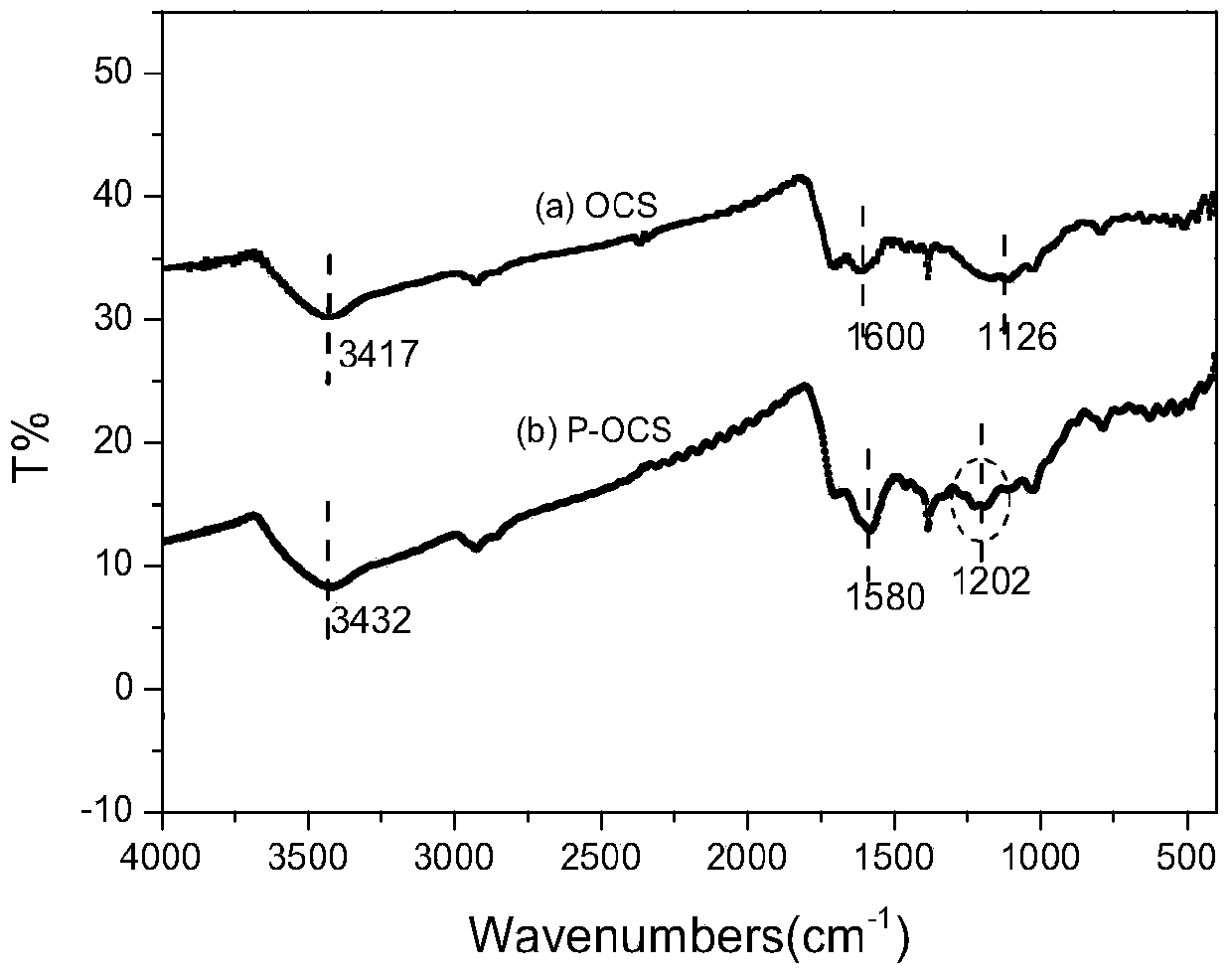
[0032] 1) Using straw as raw material, first wash the straw with water to remove impurities such as sludge on the surface, put it in a constant temperature drying box to dry at 50°C, take it out and pulverize it into powder, then add 20g of straw powder to 80mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, and put it in a water bath Heating, controlling the temperature at about 80°C, stirring for 12 hours and filtering, using 0.1mol / L NaHCO 3 Wash, then wash with deionized water until neutral, filter again, put it in a constant temperature drying oven, dry at 60°C for 24 hours, grind and sieve, and finally get a powder with a particle size of 100–150 μm, which is sulfuric acid acidification The straw, denoted as OCS, provides raw materials for the synthesis of adsorbents.
[0033] 2) Weigh 60.5g of 1,3-dibromopropane and 25g of tributyl phosphite, add them into a three-necked round-bottomed flask,...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2 Preparation of a phosphate-based cellulose adsorbent (P-OCS)
[0039] 1) Weigh 60.5g of 1,3-dibromopropane and add it to 25g of tributyl phosphite in a three-neck round-bottomed flask, stir, react at 140°C for 20h, and steam under reduced pressure at 115°C to obtain a colorless transparent liquid , to obtain the intermediate product I.
[0040] 2) Add 35 mL of DMF, add 1 g of sulfuric acid acidified straw OCS and 0.35 g of NaH under nitrogen protection, stir in an ice-water bath for 1 h, remove the ice-water bath, heat up to 40 ° C for 4 h, add 1 g of intermediate product I, mix and stir at room temperature for 24 h , filtered with suction, washed several times with 1mol / L HCl and distilled water, and dried to obtain the intermediate product II.
[0041] 3) In the nitrogen protection system, mix the intermediate product II with 20 mL of ethanol, add 1 mL of 4.9 mol / L KOH solution, stir and reflux at 75 ° C for 24 h, filter with suction, wash with 1 mol / L HCl ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] Example 3 Separation effect of a phosphoric acid-based modified cellulose adsorbent (P-OCS) on scandium in mixed rare earth metal ion solutions at different acidities
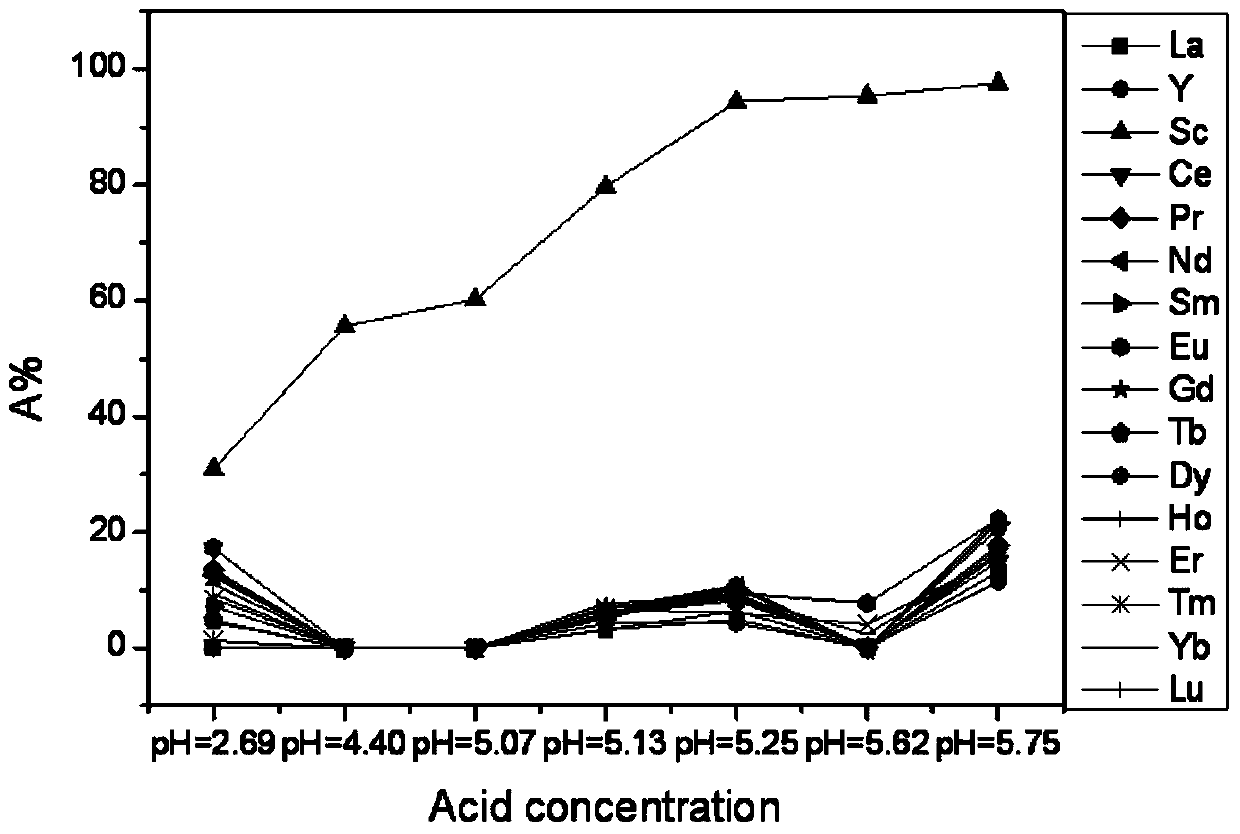
[0044] Take 100mL of solutions containing 20ppm of Sc, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, Lu, Y ions respectively, adjust the acidity of the solutions, and then add 100mg phosphoric acid-based modified cellulose adsorbent, shock adsorption for 24h, measure the concentration of each ion in the solution, such as figure 2 It can be seen from the figure that as the pH value increases, the adsorption rate of P-OCS to scandium gradually increases. When pH=5.25-5.75, the adsorption rate of P-OCS to scandium can reach nearly 100%. And it basically does not adsorb other rare earth metal ions except scandium, and the adsorption rates are all less than 20%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com