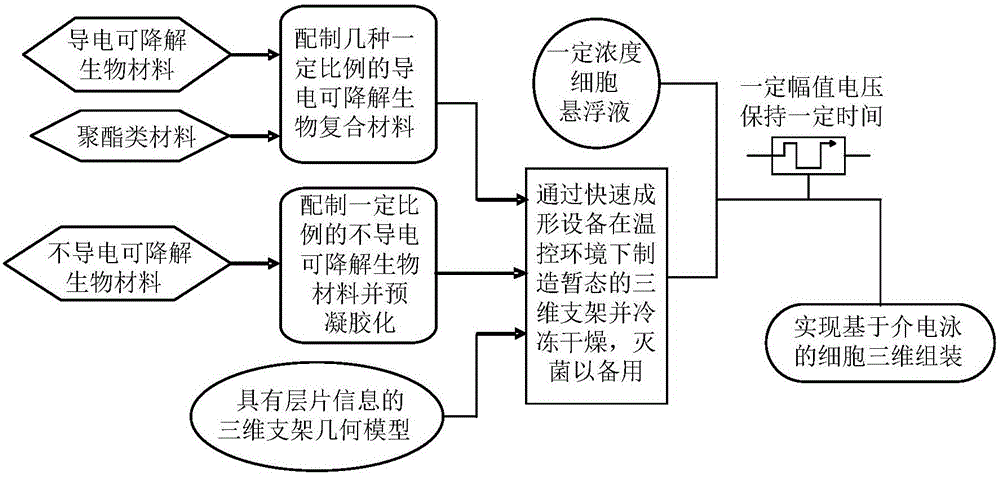
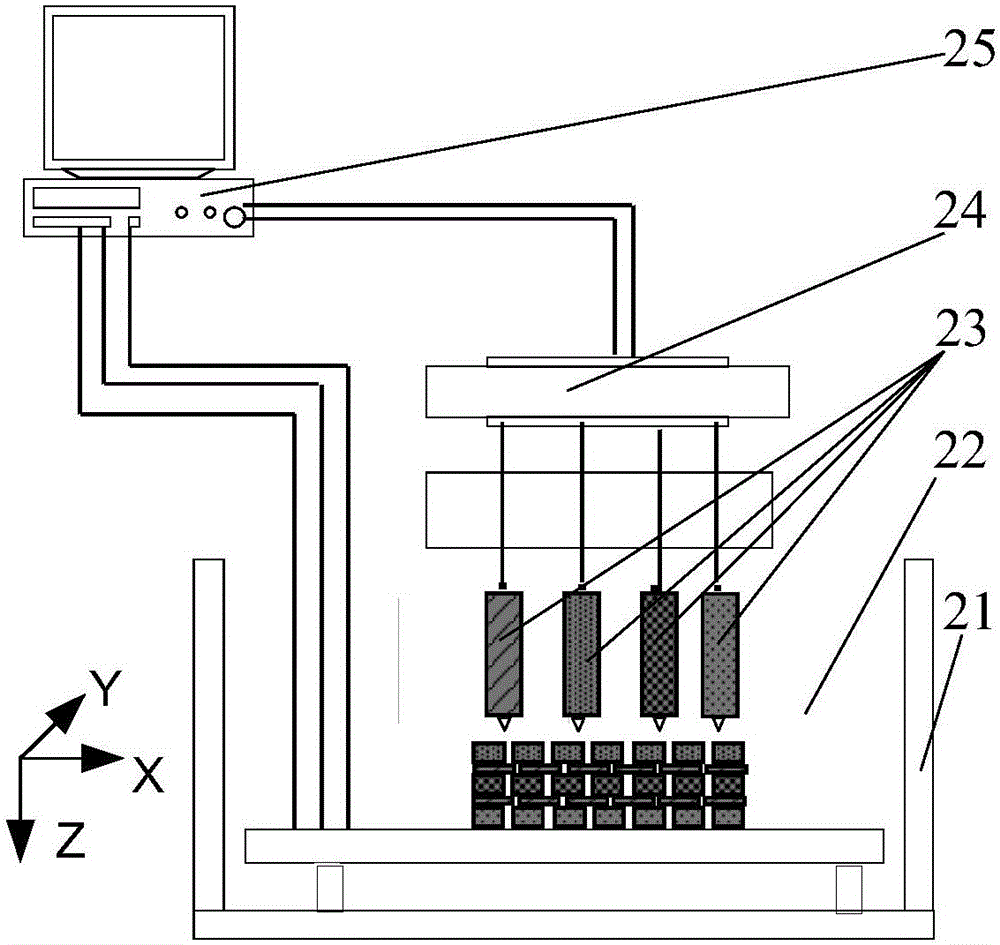
Three-dimensional cell assembly method based on dielectrophoresis adsorption principle
A three-dimensional assembly and dielectrophoresis technology, used in tissue regeneration, medical science, prosthesis, etc., to achieve the effect of high structural strength and precise control of cell distribution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1: Manufacturing a three-dimensional cartilaginous tissue structure by this method. Prepare gelatin into an aqueous solution with a concentration of 100g / L, which is called material A; dilute 50% glutaraldehyde with sterilized phosphate buffer solution 50 times to form a 1% glutaraldehyde solution, and filter it through a 0.22 μm filter membrane for later use. Call it material B; take the concentration as 1×10 6 / mL chondrocyte suspension 100mL spare, referred to as material C; the magnesium oxide-free particles wrapped by polypyrrole or poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-polystyrenesulfonic acid and polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer (50:50) is prepared into a sol solution, and its weight and volume percentage concentration is 8%, which is called material D; material A and material D are respectively loaded into the material cavity and equipped with a nozzle; according to the pre-designed structure and definition planning Pathway, the above mixture is stacke...
Embodiment 2
[0024] Example 2: Manufacture a three-dimensional structure of bone-cartilage tissue by this method. Prepare gelatin into an aqueous solution with a concentration of 100g / L, which is called material A; dilute 50% glutaraldehyde with sterilized phosphate buffer solution 50 times to form a 1% glutaraldehyde solution, and filter it through a 0.22 μm filter membrane for later use. Call it material B; take the concentration as 5×10 6 / mL chondrocyte suspension 100mL spare, called material C1; the concentration is 1×10 6 / mL osteoblast suspension 100mL spare, called material C2; the magnesium oxide-free particles wrapped by polypyrrole or poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-polystyrenesulfonic acid were copolymerized with polylactic acid-glycolic acid Material (50:50) is prepared into a sol solution, and its weight and volume percentage concentration is 8%, which is called material D; material A and material D are respectively loaded into the material cavity and equipped with a nozzle...
Embodiment 3
[0025] Example 3: The liver tissue-like three-dimensional structure of hepatic parenchymal cells-hepatic stromal cells-vascular endothelial cells was produced by this method. Prepare gelatin into an aqueous solution with a concentration of 100g / L, which is called material A; dilute 50% glutaraldehyde with sterilized phosphate buffer solution 50 times to form a 1% glutaraldehyde solution, and filter it through a 0.22 μm filter membrane for later use. Call it material B; take the concentration as 1×10 7 / mL liver parenchymal cell suspension 100mL spare, called material C1; the concentration is 2×10 6 / mL liver stromal cell suspension 100mL spare, called material C2; take the concentration of 5 × 10 6 / mL vascular endothelial cell suspension 100mL spare, called material C3; the magnesium oxide-free particles wrapped by polypyrrole or poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-polystyrenesulfonic acid and polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymerized Material (50:50) is prepared into a sol ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Layer thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com