SmFex alloy and preparation method thereof
A technology for alloys and alloying elements, which is applied to the preparation of SmFex alloys by a reduction diffusion method and the field of preparation thereof, can solve the problems of difficulty in accurately controlling the samarium content of mesh alloys, restricting the development of samarium iron-nitrogen permanent magnet materials, long production process flow, etc. The labor cost and the consumption of auxiliary materials are reduced, the washing time is shortened, and the distribution is uniform.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
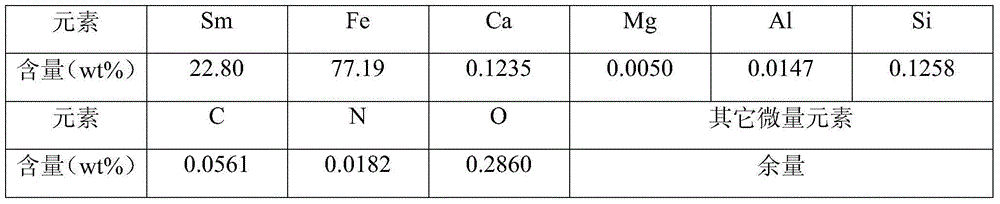
Embodiment 1
[0032] (1) Selection of raw materials: The raw materials are samarium oxide (purity greater than 99.95%), samarium chloride (purity greater than 99%), iron powder (purity greater than 99.5%, size is 200 mesh) and metal calcium particles (purity greater than 99.5%) , particle size is 2 ~ 5mm).
[0033] (2) Raw material pretreatment: vacuum dehydrate calcium chloride at 400° C. for 1.5 h.
[0034] (3) After mixing samarium chloride, samarium oxide, iron powder and calcium particles evenly, charge the furnace.
[0035] (4) Vacuumize, after washing the furnace with high-purity argon for 3 times, fill it with high-purity argon to 0.98 atmospheres;
[0036] (5) After raising the temperature to 750° C. for 1.5 hours, then raising the temperature to 1100° C. for 3 hours, then turning off the power and cooling to room temperature.
[0037] (6) The product is crushed to 50 mesh, washed with water to separate the samarium-iron alloy and the reducing slag.
[0038] (7) The product is v...
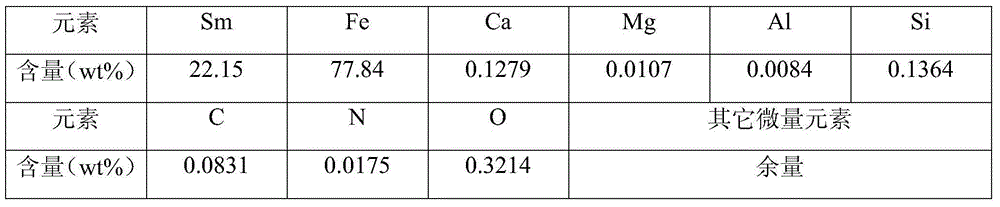
Embodiment 2
[0051] A SmFe 9.0 The preparation method of the base alloy material is basically the same as in Example 1, except that the ratio of samarium oxide and samarium chloride is as follows (the ratio of samarium oxide: samarium chloride is 8):
[0052] The raw material formula of table 4 embodiment 2
29.8g
Samarium chloride
3.7g
[0054] iron powder
88.3g
Calcium particles
14.5g
[0055] 2. Process conditions are shown in Table 5:
[0056] The processing condition of table 5 embodiment 2
[0057] Samarium chloride treatment temperature
400℃
processing time
1.5h
Mixing time
1.5h
Charging furnace temperature
60℃
Heating rate
15℃ / min
One-stage holding temperature
750℃
One stage constant temperature time
1.5h
Second stage holding temperature
1100℃
Two-stage constant temperature time
3h
Broken particle size
50...
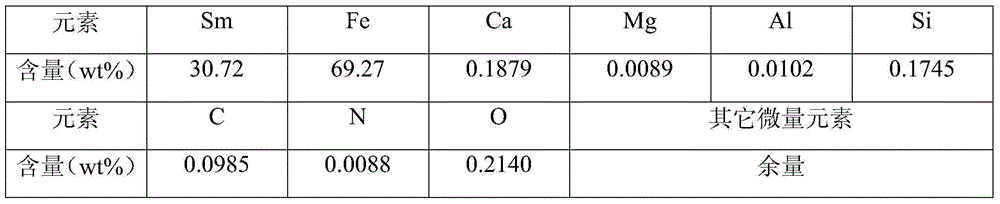
Embodiment 3
[0062] A SmFe 6 The preparation method of the basic alloy material is basically the same as that of Example 1, the difference is only to adjust the amount of Fe powder added and the process conditions:
[0063] The raw material formula of table 7 embodiment 3
[0064] Samarium oxide
29.8g
Samarium chloride
4.4g
iron powder
56.7g
Calcium particles
14.2g
[0065] 2. The process conditions are shown in Table 8:
[0066] The process condition of table 8 embodiment 3
[0067] Samarium chloride treatment temperature
400℃
processing time
1.5h
Mixing time
1.5h
Charging furnace temperature
60℃
Heating rate
15℃ / min
One-stage holding temperature
750℃
[0068] One stage constant temperature time
1.5h
Second stage holding temperature
1050℃
Two-stage constant temperature time
4h
Broken particle size
50 mesh
washing time
60min...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com