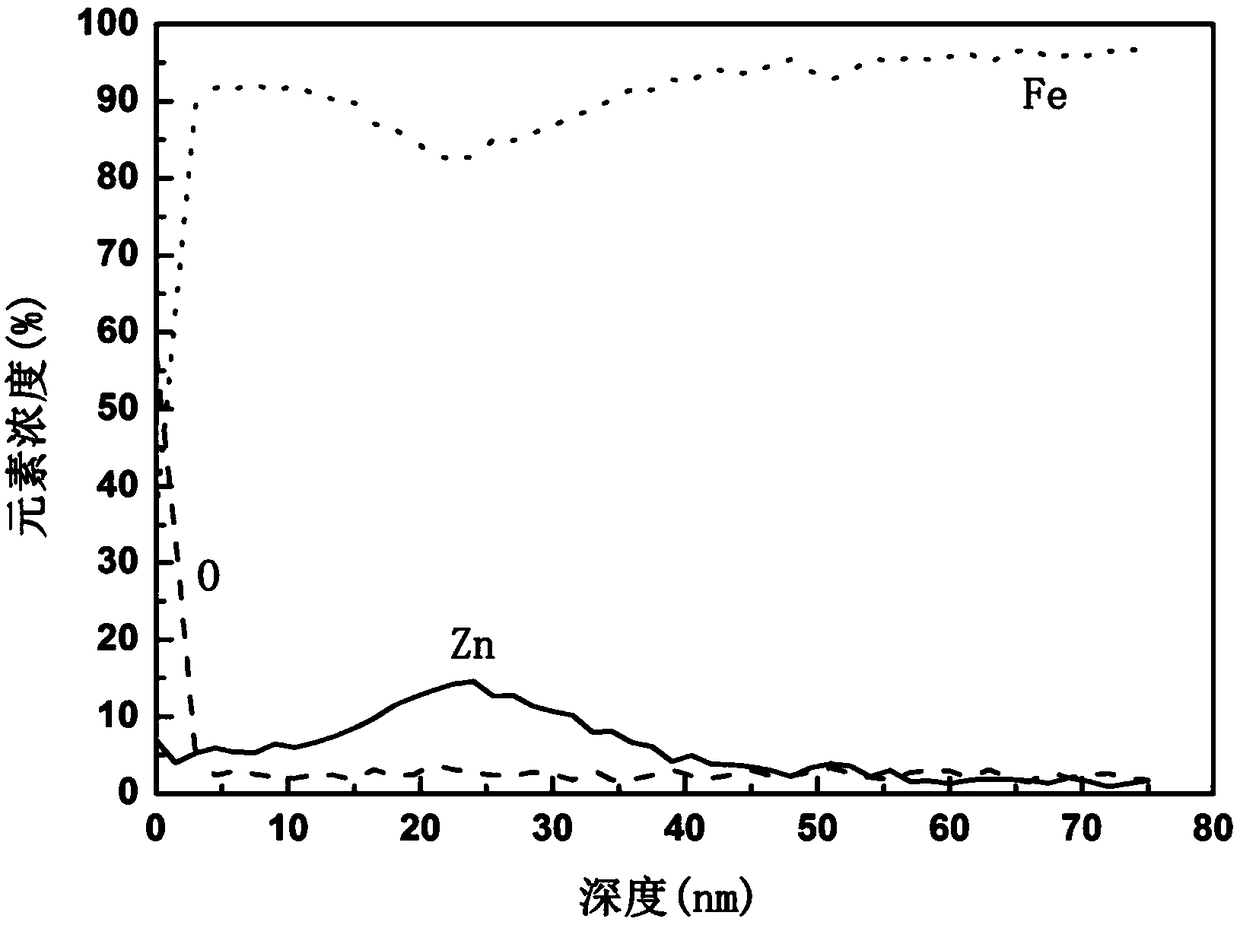
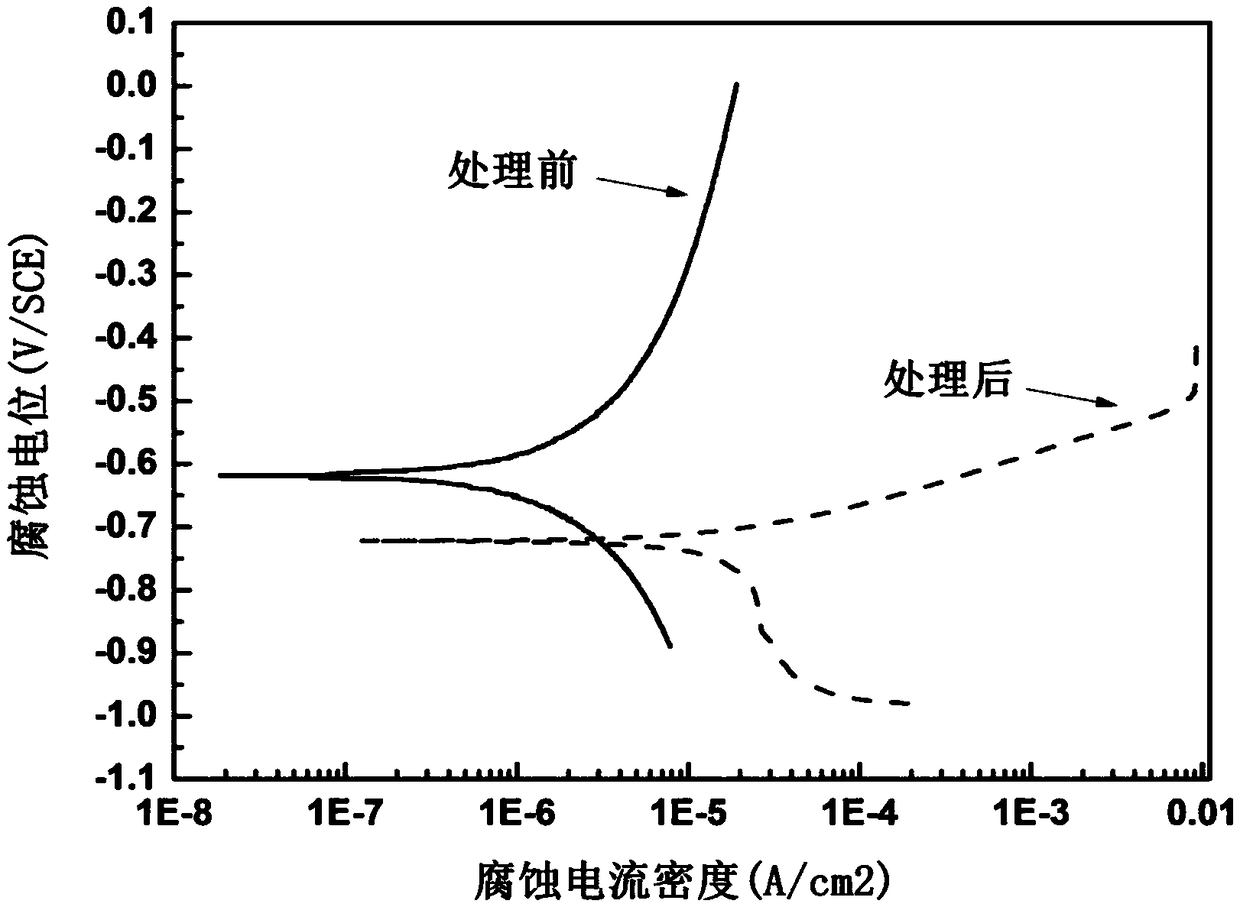
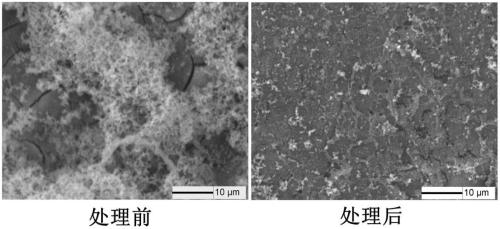
A method for surface modification of biodegradable iron and iron alloys by zinc ion implantation
A technology of biodegradation and ion implantation, applied in ion implantation plating, drug delivery, tissue regeneration, etc., can solve the problems of unreported, allergic and inflammatory reactions, insufficient binding force between the zinc film and the substrate, etc., to improve biological Compatibility, effect of increasing corrosion rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] The first step: substrate pretreatment:
[0036] After the biomedical pure iron substrate is ground and polished, it is ultrasonically cleaned with acetone and absolute ethanol for 15 minutes to prepare the substrate sample;
[0037] The second step: ion implantation to prepare zinc surface modification layer:
[0038] (A) Put the substrate sample prepared in the first step into an ion implanter to remove surface impurities by argon ion sputtering; wherein, the vacuum degree is 0.2×10 -3 Pa, energy 8k V, time 5min;
[0039] (B) The substrate sample treated with argon ions is doped with zinc element to obtain a sample with a zinc surface modification layer; the ion implanter selects the target material as a zinc target, and the parameters required for doping zinc element: vacuum Degree 2.0×10 -3 Pa, zinc dose 1×10 17 ions / cm 2 , voltage energy 40k V, current 1.5mA;
[0040] The third step: heat treatment of the film:
[0041] Put the sample with the zinc surface m...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The first step: substrate pretreatment:
[0052] After the biomedical iron alloy Fe-X (X = any one of Mn, Co, W, Si) alloy matrix is ground and polished, it is ultrasonically cleaned with acetone and absolute ethanol for 15 minutes to prepare the matrix sample;
[0053] The second step: ion implantation to prepare zinc surface modification layer:
[0054] (A) Put the substrate sample prepared in the first step into an ion implanter to remove surface impurities by argon ion sputtering; wherein, the degree of vacuum is 0.1×10 -3 Pa, energy 12k V, time 10min;
[0055] (B) The substrate sample treated with argon ions is doped with zinc element to obtain a sample with a zinc surface modification layer; the ion implanter selects the target material as a zinc target, and the parameters required for doping zinc element: vacuum Degree 2.0×10 -3 Pa, zinc dose 2×10 17 ions / cm 2 , voltage energy 40k V, current 2mA;
[0056] The third step: heat treatment of the film:
[00...
Embodiment 3
[0060] The first step: substrate pretreatment:
[0061] After the biomedical iron alloy Fe-Mn-Si alloy substrate was ground and polished, it was ultrasonically cleaned with acetone and absolute ethanol for 15 minutes to obtain a substrate sample;
[0062] The second step: ion implantation to prepare zinc surface modification layer:
[0063] (A) Put the substrate sample prepared in the first step into an ion implanter to remove surface impurities by argon ion sputtering; wherein, the degree of vacuum is 0.25×10 -3 Pa, energy 12k V, time 10min;
[0064] (B) The substrate sample treated with argon ions is doped with zinc element to obtain a sample with a zinc surface modification layer; the ion implanter selects the target material as a zinc target, and the parameters required for doping zinc element: vacuum Degree 2.0×10 -3 Pa, zinc dose 3×10 17 ions / cm 2 , voltage energy 60k V, current 1mA;
[0065] The third step: heat treatment of the film:
[0066] Put the sample with...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com