Epitaxial wafer of light-emitting diode and growing method thereof
A technology of light-emitting diodes and growth methods, which is applied in the field of epitaxial wafers of light-emitting diodes and their growth, can solve problems such as LED luminous efficiency needs to be improved, and achieve the effect of improving luminous efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
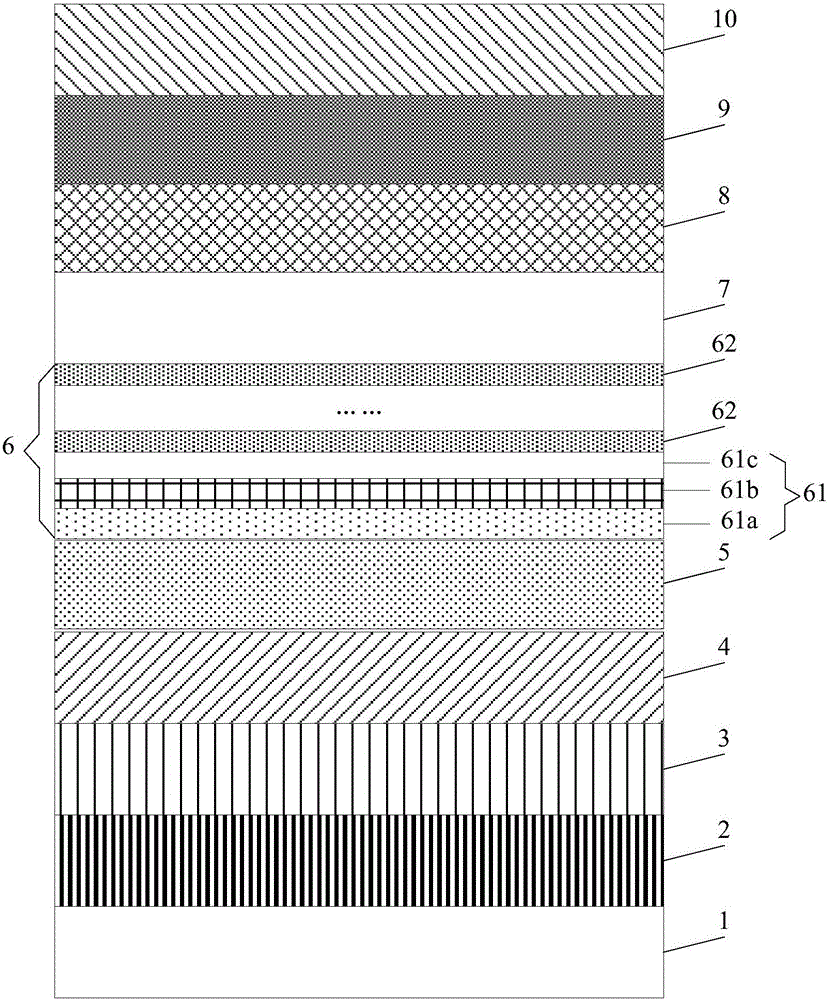
[0034] An embodiment of the present invention provides an epitaxial wafer of a light emitting diode, see figure 1 , the epitaxial wafer includes a sapphire substrate 1, and a buffer layer 2, an undoped GaN layer 3, an N-type GaN layer 4, a shallow well layer 5, a multi-quantum well layer 6, a low-temperature P Type GaN layer 7, P-type electron blocking layer 8, high-temperature P-type GaN layer 9, and P-type contact layer 10.
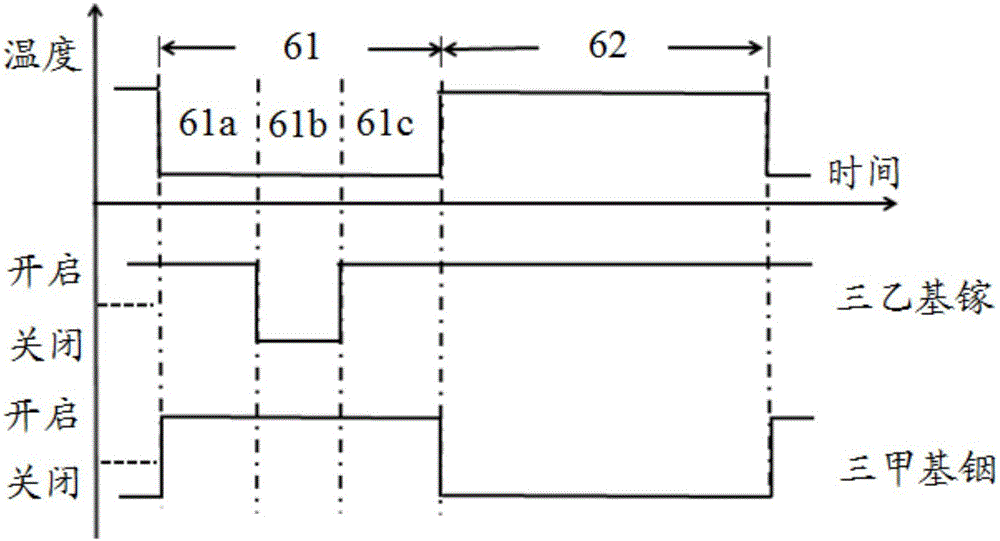
[0035] In this embodiment, the multiple quantum well layer 6 includes alternately stacked quantum well layers 61 and quantum barrier layers 62 . The quantum barrier layer 62 is a GaN layer; the quantum well layer 61 includes sequentially stacked In x Ga 1-x N layer 61a, InN layer 61b, In y Ga 1-y In the N layer 61c, 0.4z Ga 1-z N layer and GaN layer, 0<z<0.1. The P-type electron blocking layer 9 is an AlGaN layer.
[0036] Optionally, the thickness of the InN layer 61b may be 0.5-0.9 nm.
[0037] Optionally, In x Ga 1-x The thickness of the N ...
Embodiment 2
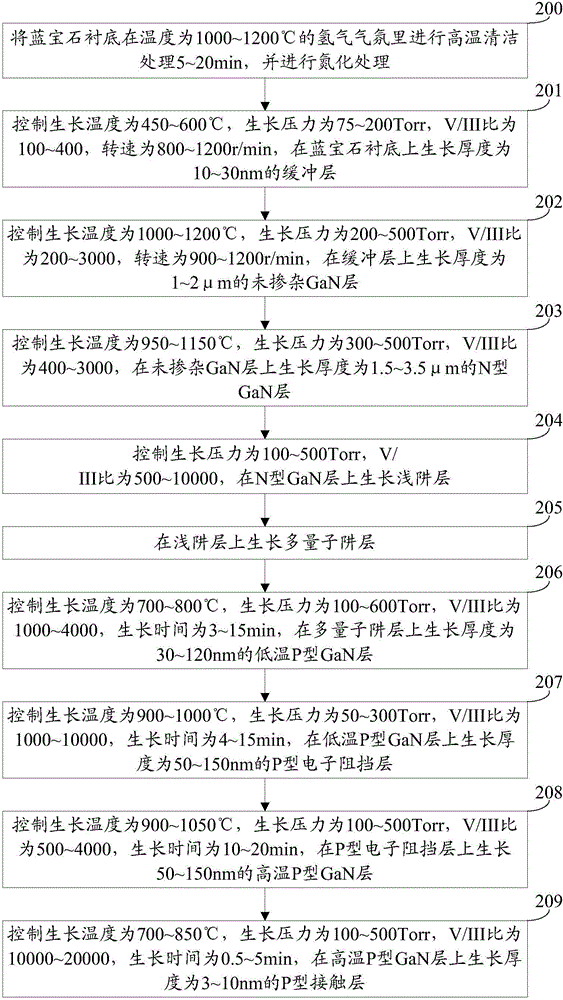
[0054] An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for growing an epitaxial wafer of a light emitting diode, which is suitable for growing the epitaxial wafer of a light emitting diode provided in Embodiment 1, see figure 2 , the growth method includes:
[0055] Step 200: Perform high-temperature cleaning treatment on the sapphire substrate in a hydrogen atmosphere at a temperature of 1000-1200° C. for 5-20 minutes, and perform nitriding treatment.
[0056] In this example, nitrogen (N 2 ) or hydrogen (H 2 ) as carrier gas, trimethylgallium (TMGa), triethylgallium (TEGa), trimethylaluminum (TMAl), trimethylindium (TMIn) and ammonia (NH3) as Ga, Al, In And N source, use silane (SiH4) and dimagnesium (CP2Mg) as N and P type dopants respectively.
[0057] Step 201: Control the growth temperature to 450-600° C., the growth pressure to 75-200 Torr, the V / III ratio to 100-400, and the rotation speed to 800-1200 r / min, and grow a buffer layer with a thickness of 10-3...
Embodiment 3
[0088] An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for growing an epitaxial wafer of a light-emitting diode. The difference between the growth method and the growth method provided in Embodiment 2 lies in that the thickness of each layer in the quantum well layer is different. Specifically, the thickness of the InN layer is 0.6-0.8nm, and the InN layer x Ga 1-x The thickness of N layer is 1~1.5nm, In y Ga 1-y The thickness of the N layer is 2-2.5 nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com