Pretreatment and quantitative analysis method for rapid determination of pesticide residue in tea
A technology for rapid determination of pesticide residues, applied in the direction of measuring devices, analysis materials, material separation, etc., can solve the problems of long time-consuming and cumbersome detection methods, achieve good pigment removal, improve separation efficiency, and have wide application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] A pretreatment method for rapid determination of pesticide residues in tea,
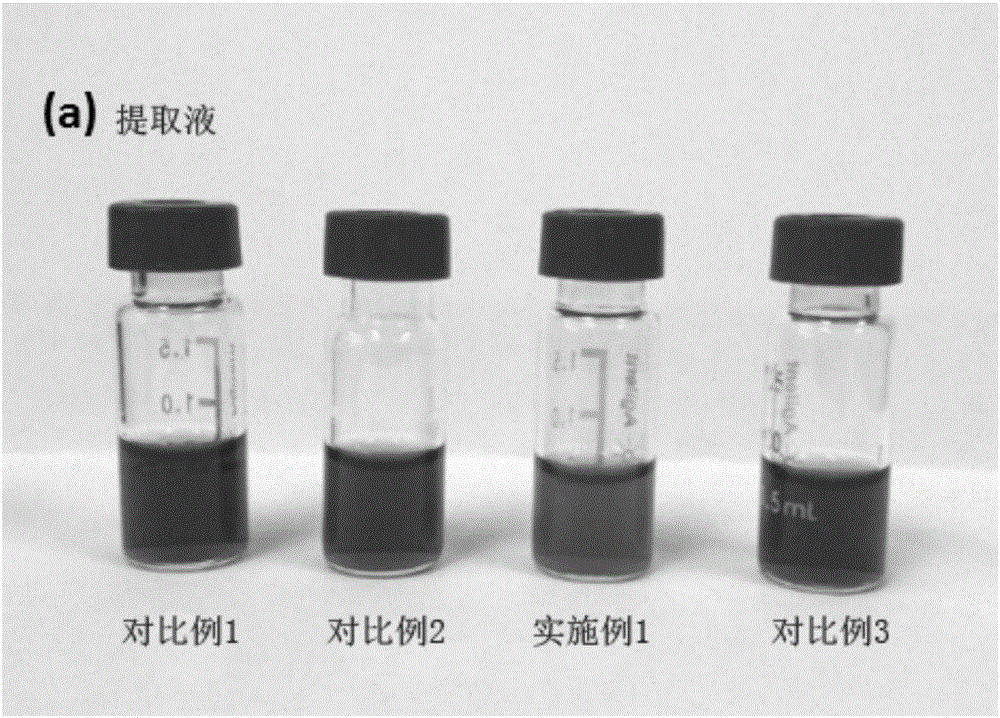
[0038] 1) Extraction steps: Weigh 4.0g of homogenized tea samples into a 50mL centrifuge tube, add 10mL of pure water to soak for 30min, then add 20mL of acetonitrile, vortex for 1min; then add 4.0g of NaOAc and vortex for 1min, then Min speed centrifugation 5min, acetonitrile and water phase separation, the gained supernatant acetonitrile layer is the tea extract (such as Figure 1a shown);
[0039] 2) purification step: get 1mL tea extract in embodiment 1, add the magnesium sulfate (MgSO 4 ), vortexed for 1 min and then centrifuged, the supernatant collected was the tea purification solution ( Figure 1b ), which can be used as a test solution for rapid determination of pesticide residues in tea.
[0040] Compared with the traditional QuEChERS extraction method, comparative examples 1-3 are as follows:
Embodiment 2
[0051] A pretreatment method for rapid determination of pesticide residues in tea, the purification steps are as follows:
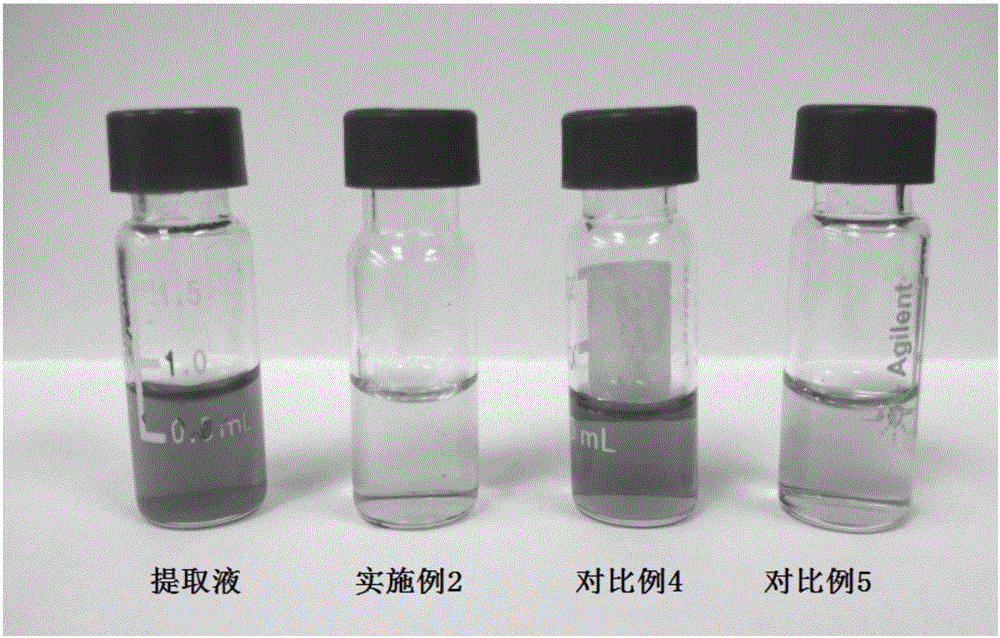
[0052] Get the 1mL tealeaves extract in embodiment 1, add the magnesium sulfate (MgSO 4 ), vortexed for 1 min and then centrifuged, the supernatant collected was the tea purification solution ( figure 2 ), which can be used as a test solution for rapid determination of pesticide residues in tea.
[0053] Compared with the traditional QuEChERS purification method, the comparative examples 4-5 are as follows:
Embodiment 3
[0062] At present, there are many types of pesticides used in the tea planting process. The present invention establishes a general-purpose detection method for rapid determination of pesticide residues in tea leaves. In this example, 69 commonly used pesticides (including organophosphorus, organochlorine, organic nitrogen, pyrethroids, phenylpyrazoles, etc.) for the investigation of this method. In order to obtain higher selectivity and sensitivity, this embodiment uses the standard solution of pesticides to optimize the precursor ions, product ions, and collision energy of pesticides in the GC-MS / MS analysis of this detection method. Two ion pairs were optimized for qualitative and quantitative analysis respectively, and the optimized results are shown in Table 3.
[0063] Table 3. Retention time, qualitative and quantitative transitions and collision voltage of 69 pesticides
[0064]
[0065]
[0066]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com