Hydrothermal preparation method of nano-ZnO cellulose composite material on basis of NaOH-urea solution and application
A composite material and cellulose technology, which is applied in the field of hydrothermal preparation of nano-ZnO cellulose composite materials, can solve the problems of difficult application, environmental pollution, and high cost of ionic liquids, and achieve good practicability, high removal efficiency, and hydrothermal synthesis. The effect of temperature reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1Z
[0026] The preparation of embodiment 1ZnO cellulose nanocomposite material (zinc acetate is zinc source)
[0027] Take 50g of NaOH / Urea aqueous solution (NaOH:Urea:H 2 The mass ratio of O is 7︰12︰81), add 2g of microcrystalline cellulose, stir rapidly until dissolved, add dropwise 30mL of 1mol / L Zn(CH 3 COO) 2 solution, after stirring and aging for 30min, with 2% H 2 SO 4 The pH value of the solution was adjusted to 9, transferred to a hydrothermal reaction kettle for 2 hours at 100°C, washed with distilled water for 3 times, dried in an oven at 70°C, and weighed to obtain a nano-ZnO cellulose composite material.
[0028] The prepared ZnO cellulose nanocomposites were characterized as follows:
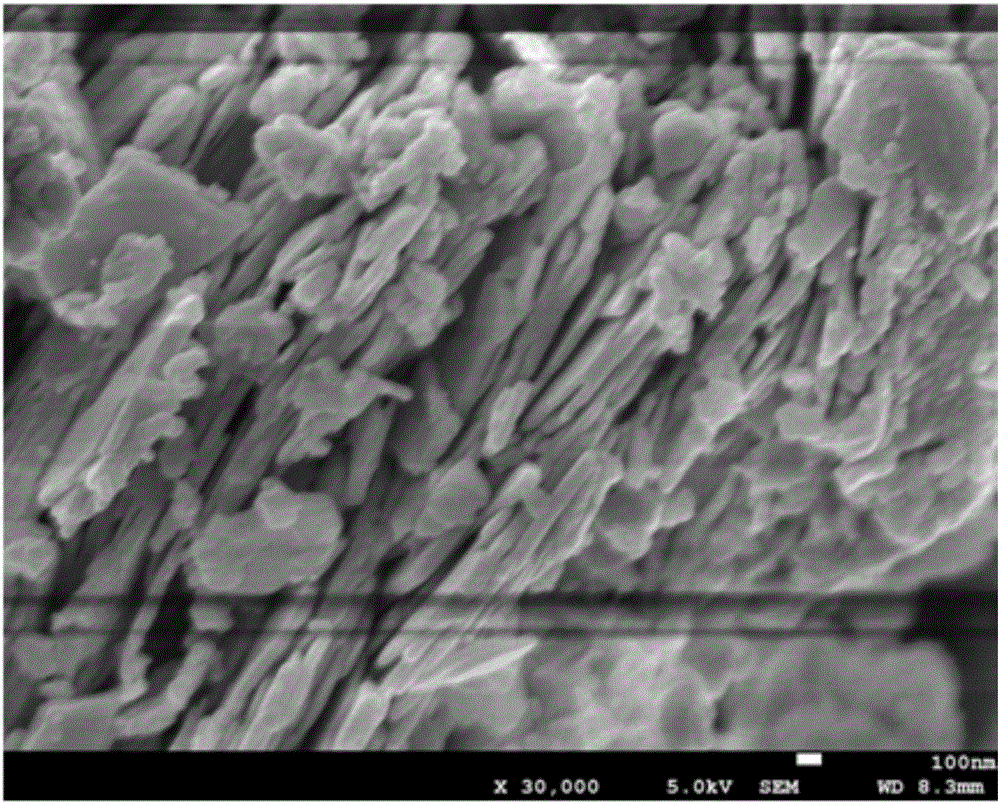
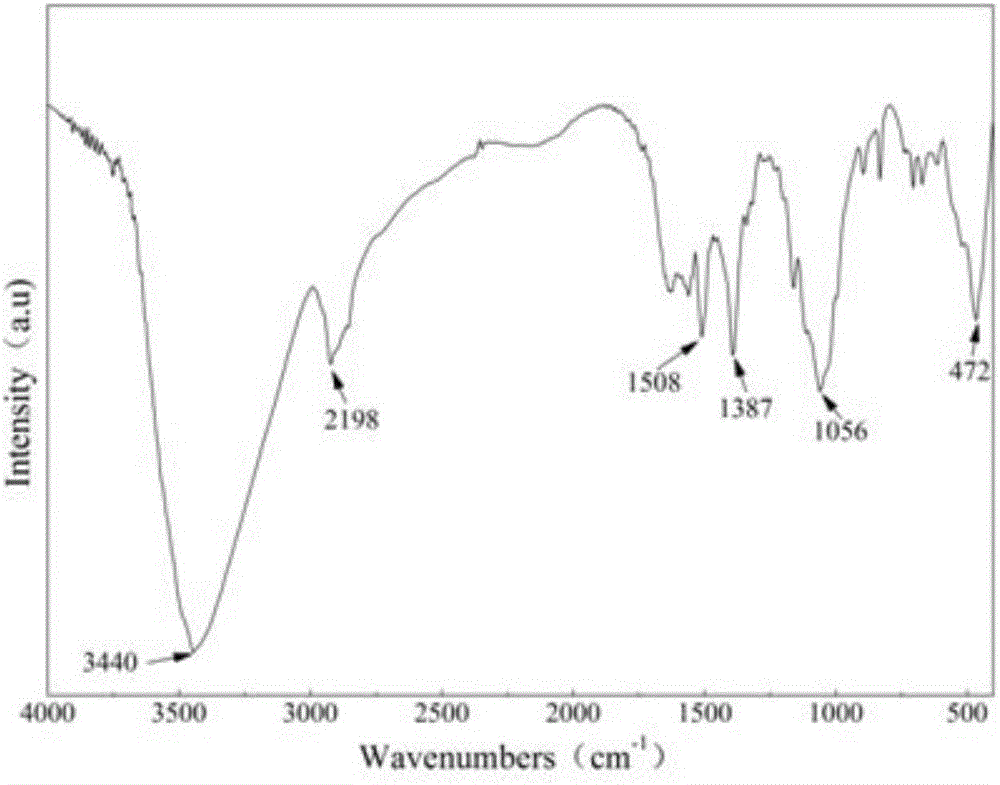
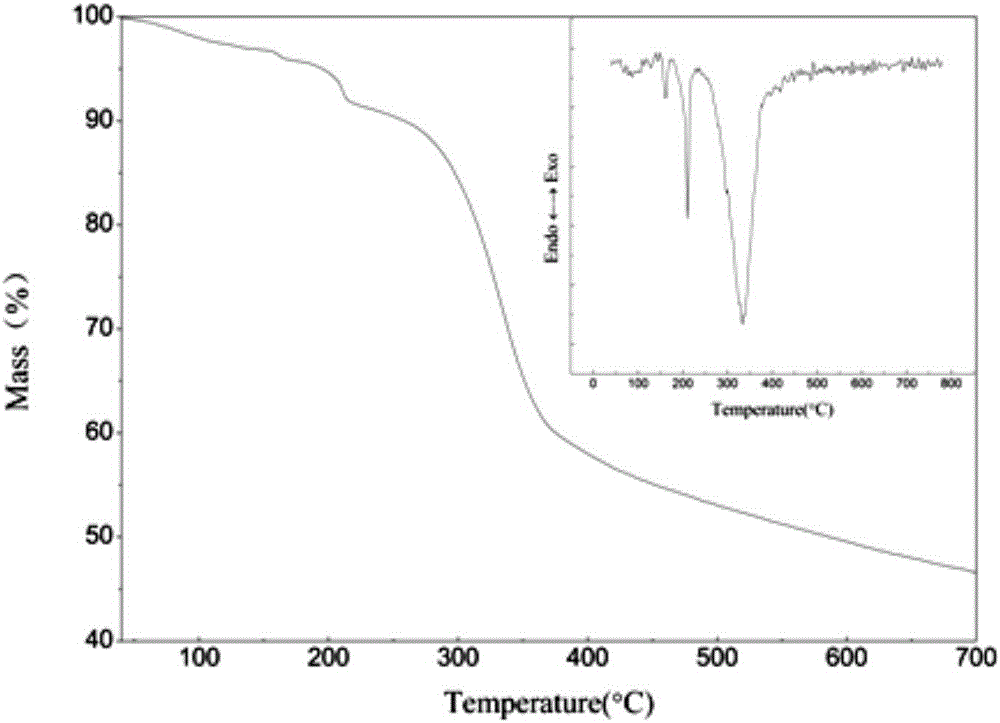
[0029] Electron microscope images of the prepared ZnO cellulose nanocomposites figure 1 As shown, the infrared image is shown as figure 2 As shown, TG as image 3 As shown, the XRD pattern is as Figure 4 . It can be seen from the electron microscope that ZnO gathers on the s...
Embodiment 2Z
[0030] Photodegradation performance of embodiment 2 ZnO cellulose nanocomposites to phenol wastewater
[0031] Get the phenol solution of 100mL 50mg / L in the 250mL quartz beaker, add the ZnO / cellulose composite material 0.1g that obtains in the embodiment 1, add the hydrogen peroxide of 0.01g30% after stirring on the magnetic stirrer, under ultraviolet light and Under sunlight, samples were taken every half hour to analyze the concentration of phenol in the solution, and the solution was stirred for 6 hours. After 6 hours, the removal rate of phenol was 66.36%.
[0032] The concentration of phenol was obtained by measuring the absorbance at 235 nm with a UV-visible spectrophotometer according to the phenol standard curve.
[0033] The formula for calculating the removal rate of phenol is:
[0034] In the formula, C 0 and C are the concentration of phenol solution before and after photodegradation respectively;
[0035] The removal rate of phenol is as follows Figure 5 s...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Take 50g of NaOH / Urea aqueous solution (NaOH:Urea:H 2 The mass ratio of O is 7︰12︰81), add 4g microcrystalline cellulose, stir rapidly until dissolved, add 1mol / L ZnCl dropwise 2 , after stirring and aging for 30min, with 2% H2 SO 4 The pH value of the solution was adjusted to 9, transferred to a hydrothermal reaction kettle for 2 hours at 100°C, washed with distilled water for 3 times, dried in an oven at 70°C, and weighed to obtain a nano-ZnO cellulose composite material.
[0038] Electron microscope images of the prepared ZnO cellulose nanocomposites Image 6 As shown, the infrared image is shown as Figure 7 As shown, the XRD pattern is as Figure 8 shown, from Image 6 It can be seen that due to the addition of more cellulose, the cellulose dissolution is not sufficient, and some cellulose microfibrils exist, and the generated ZnO is wrapped on the surface of the cellulose microfibrils. The dissolved and regenerated cellulose particles are small, and fluffy Zn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com