Method for inducing differentiation of human skin-derived precursor cells into corneal endothelial-like cells
A technology of precursor cells and corneal endothelium, applied in the field of tissue engineering and ophthalmic repair, can solve the problems of not finding expanded functional corneal endothelial cells, lack of animal experiments, poor histocompatibility, etc., to achieve suitable clinical experiments and applications, High induction efficiency, immunogenicity and weak immunoreactivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1 Inducing the differentiation of human skin-derived precursor cells into corneal endothelial-like cells
[0048] 1. Cultivation of SKPs precursor cells derived from human skin:
[0049] Rinse and disinfect the skin tissue with penicillin-streptomycin, cut into 1mm×2mm tissue pieces, digest with Dispase enzyme at 4°C for 12-24h, remove the epidermis to obtain the dermis, digest with collagenase for 2-3h, and use fetal bovine serum Neutralize with DMEM, dissociate the cells, filter them with a cell mesh, inoculate the cells in a culture flask, add SKPs culture medium, and place at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultured in an incubator. After about 2-3 weeks, spherical suspension SKPs are formed, which are used to induce differentiation when passed to 2-4 passages. The culture observation results of SKPs cells are shown in figure 1 shown.
[0050] SKPs culture medium is DMEM / F12=3:1 basal medium, supplemented with 2% B27, 40ng / ml bFGF, 20ng / ml EGF, 1% green chain double antib...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2 Identification of corneal endothelial-like cells and corneal repair experiment
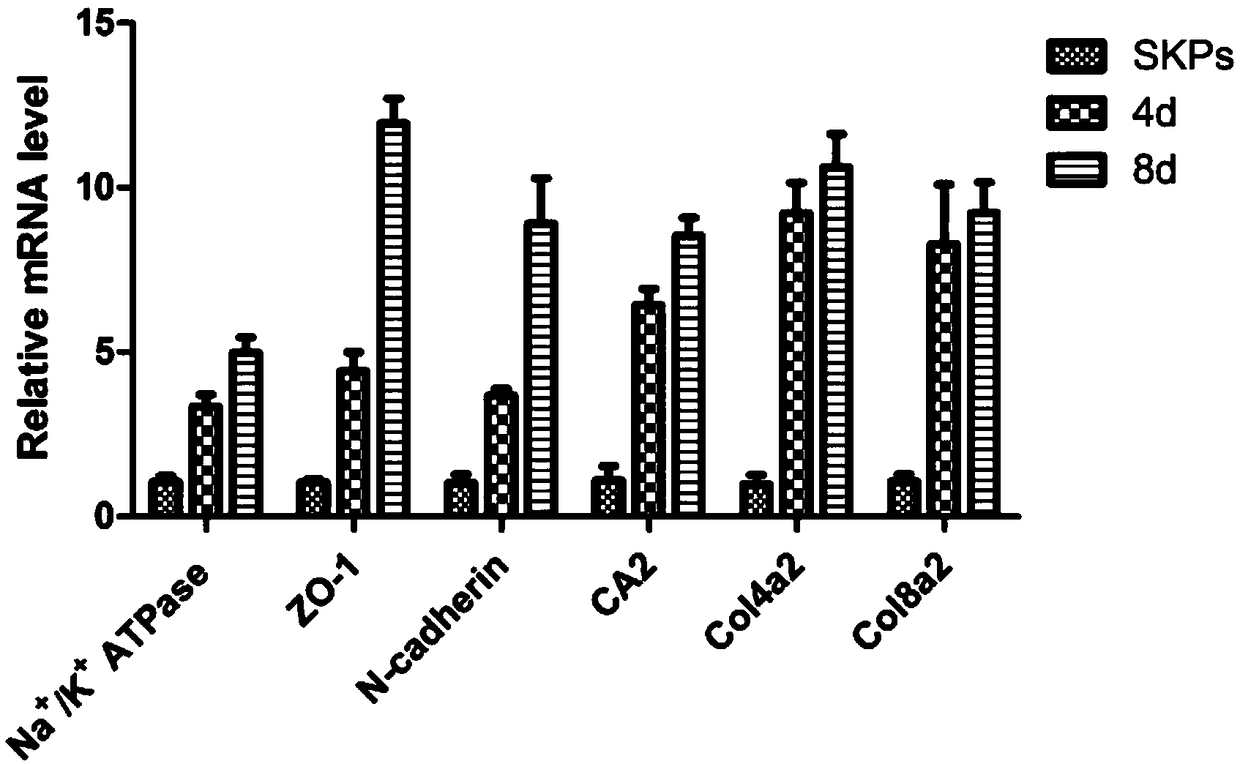
[0058] After 4 days of induction, part of the cells transformed into polygonal shapes, which gradually increased with time. After 8 days, polygonal cells accounted for the majority, forming tight connections with each other in a monolayer mosaic-like arrangement. Optical microscope observation, immunofluorescence, real-time quantitative PCR, Western Blotting confirmed that the induced cells had similar morphology and marker expression to human keratocytes. Corneal endothelial-like cells can be stably passaged for 3-4 passages, and can still maintain their morphology and the expression of various markers after passage. The optical microscope effect picture of SKPs induced to differentiate into corneal endothelial-like cells can be found in figure 2 shown. RT-PCR results and Westernblotting test results respectively refer to image 3 , Figure 4 .
[0059] Rabbit corneal endot...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com