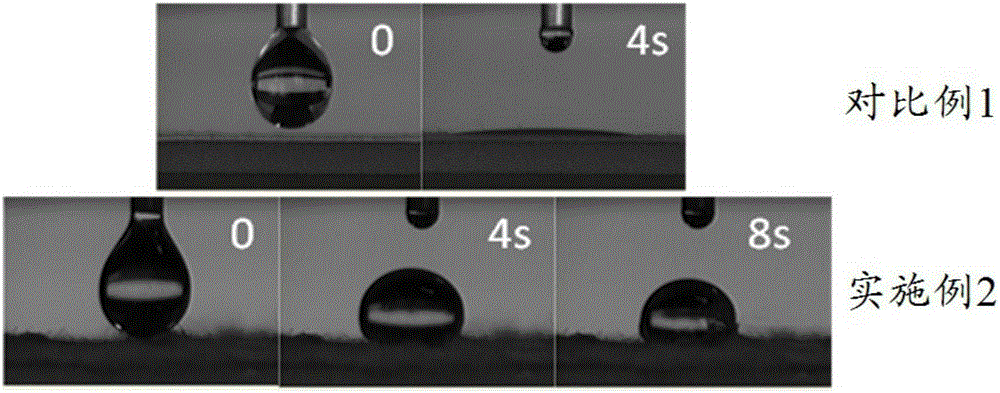
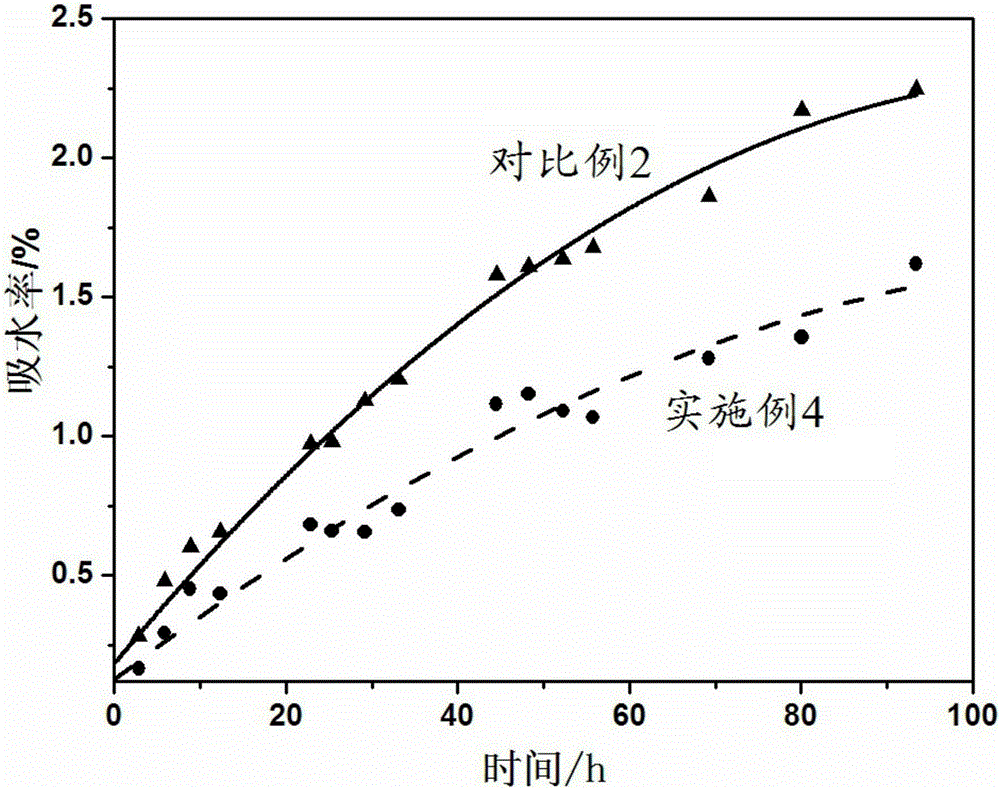
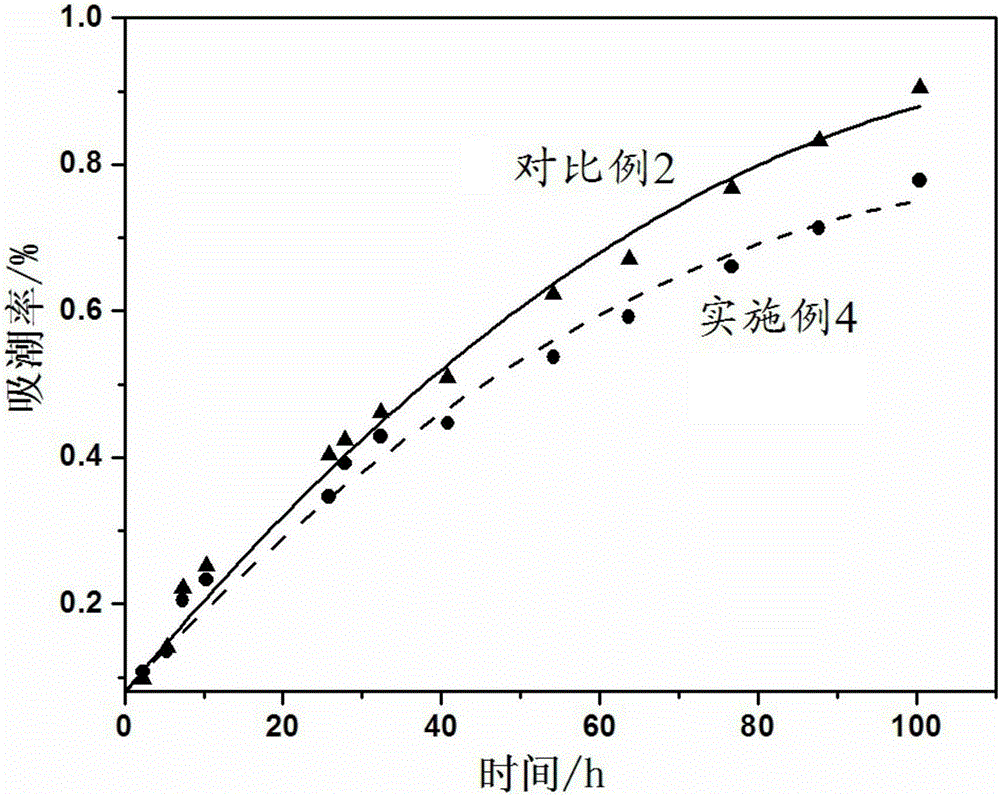
Cellulose fiber modification method, modified cellulose fibers and application
A cellulose fiber modification technology, applied in the field of cellulose fiber modification and modified cellulose fiber, can solve the problems of unconsidered chemical bonding interface force, high production cost, strong toxicity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Example 1 Ring-opening polymerization of styrene oxide
[0076] Weigh 20.5g of styrene oxide and 0.576g of potassium tert-butoxide initiator into a pre-dried reactor with a volume of 100mL, put in a magnet, fill it with nitrogen and exhaust oxygen for 10 minutes, seal it, and place it at a constant temperature of 95°C Anionic ring-opening polymerization was carried out by heating in a water bath for 24 hours. Then the temperature was lowered to 60° C., 2 g of methanol was added, and the reaction was terminated by stirring for 10 minutes.
Embodiment 2
[0077] Example 2 Preparation of styrene oxide grafted modified cellulose fibers
[0078] Dry the wood fiber in vacuum at 80°C for 24h, and then continue vacuum drying at 100°C for about 2h to reach a constant weight. Weigh 27.0 g of the above-mentioned dry wood fiber, add it to an ethanol solution of sodium ethoxide (which contains 4.1 g of sodium ethoxide and 54.0 g of ethanol), stir at room temperature for 24 hours, and vacuumize at 65 ° C to remove ethanol and the trace moisture, and then vacuum-dried at 100°C for 2 hours. Under nitrogen environment, take 25.0g of sodium alkoxide pretreated and dried fibers into a pre-dried reaction bottle, repeat vacuuming / nitrogen 3 times, remove the air, seal, and inject 10.0g of dehydrated and dried fibers with a syringe. Styrene was added to the above reactor, nitrogen gas was passed for 10 minutes, mechanically stirred at room temperature for 8 hours, so that the styrene oxide monomer was uniformly distributed on the fiber, and then ...
Embodiment 3
[0079] Example 3 Preparation of styrene oxide-allyl glycidyl ether grafted modified cellulose fibers
[0080]Dry the wood fiber in vacuum at 80°C for 24h, and then continue vacuum drying at 100°C for about 2h to reach a constant weight. Weigh 30.0 g of the above-mentioned dry wood fiber, add it to an ethanol solution of potassium ethylate (which contains 4.5 g potassium ethylate and 60.0 g ethanol), stir at room temperature for 24 hours, and vacuumize at 65 ° C to remove ethanol and carried trace moisture, and then vacuum-dried at 100°C for 2 hours. Under nitrogen environment, take 25.0g of pretreated and dried fiber by potassium alkoxide into a pre-dried reaction bottle, repeat vacuuming / nitrogen three times, remove the air, seal it, and put 7.5g of dehydrated and dried styrene oxide Mix well with 2.5g allyl glycidyl ether, then add the above-mentioned epoxy monomer mixture into the above-mentioned reactor with a syringe, feed nitrogen for 10min, and mechanically stir for 10...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| contact angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of grafting | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight distribution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com