Method for removing zirconium, zinc and chromium in red mud
A red mud removal rate technology, applied in the field of zinc and chromium, and zirconium removal in red mud, can solve the problems of low pH value of solution, heavy metal removal from red mud, poor selectivity, etc., and achieve high pH value of waste liquid, heavy metal removal The effect of high removal rate and low drug consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
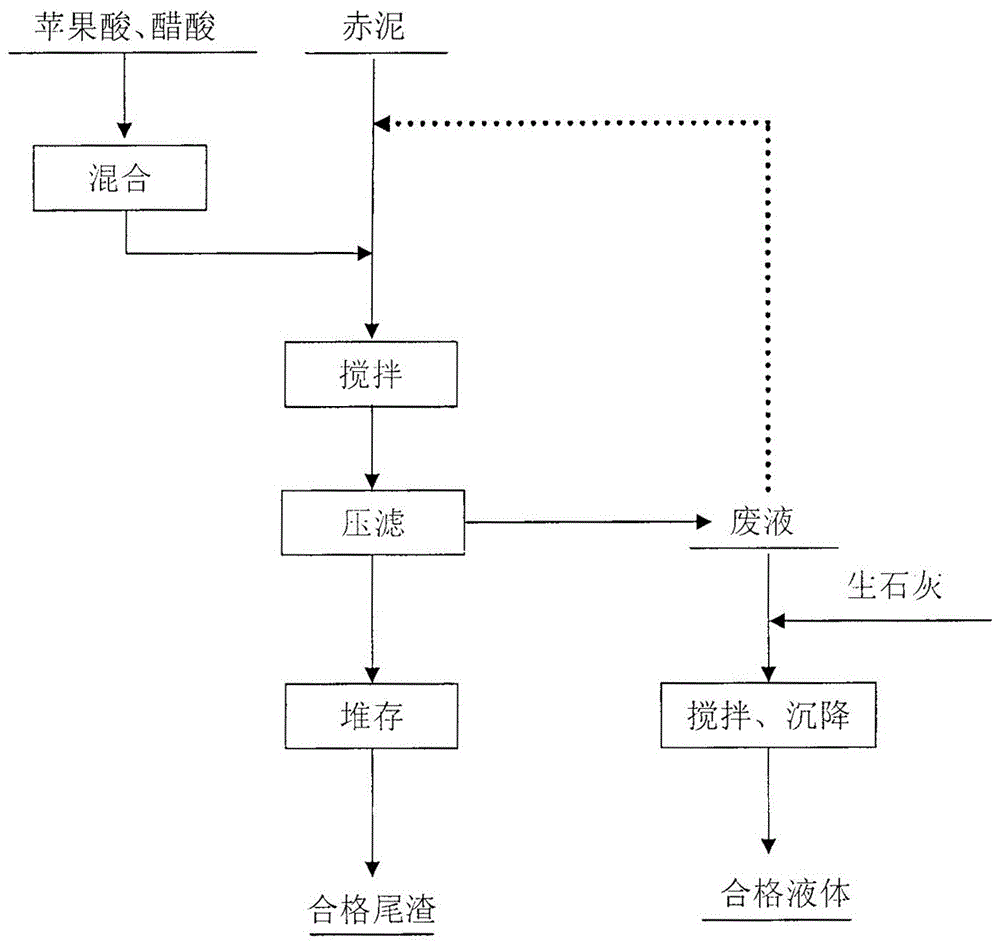
[0024] Add the malic acid solid into the acetic acid solution at a mass percentage of 5%~10%, stir for 120~140min at a temperature of 30°C and a stirring intensity of 300r / min, and obtain a mixed acid after stirring and dissolving completely; Mix the mud with the mixed acid, stir and dissolve under the condition that the mass ratio of liquid to solid is 2~8:1. The dissolution process is 40℃, stirring time 120~210min and stirring intensity 100r / min. After the stirring is completed, the slurry Press filtration to obtain waste liquid and tailings. The removal rate of zirconium is 99.5%, the removal rate of zinc is greater than 99%, and the removal rate of chromium is greater than 99%. The tailings can be directly transported by belt to the tailings dam for storage, and after natural air drying The obtained qualified tailings can be used to prepare construction materials and also be used as a soil conditioner. The waste liquid can be used to return to dissolve the next batch of re...
Embodiment 2
[0026] Add the malic acid solid into the acetic acid solution at a mass percentage of 10%~15%, stir for 140~160min at a temperature of 40°C and a stirring intensity of 400r / min, and obtain a mixed acid after stirring and dissolving completely. Then mix the red mud with the mixed acid, stir and dissolve under the condition that the liquid-solid mass ratio is 8~14:1. After the end, the slurry is press-filtered to obtain waste liquid and tailings. The removal rate of zirconium is 99.7%, the removal rate of zinc is greater than 99.2%, and the removal rate of chromium is greater than 99.3%. The tailings can be directly transported to the tailings dam through the belt for storage. Qualified tailings can be obtained after natural air drying, which can be used to prepare building materials, and can also be used as a soil conditioner. The waste liquid can be used to return to dissolve the next batch of red mud. The dissolution process is that the volume ratio of the waste liquid to the...
Embodiment 3
[0028]The malic acid solid is added to the acetic acid solution at a mass percentage of 15%~20%, stirred for 160~180min at a temperature of 20~40°C and a stirring intensity of 450r / min, and the mixed acid is obtained after stirring and dissolving completely. Then mix the red mud with the mixed acid, stir and dissolve under the condition that the liquid-solid mass ratio is 14~20:1. After the end, the slurry is press-filtered to obtain waste liquid and tailings. The removal rate of zirconium is 99.9%, the removal rate of zinc is greater than 99.5%, and the removal rate of chromium is greater than 99.5%. The tailings can be directly transported to the tailings dam through the belt for storage. Qualified tailings can be obtained after natural air drying, which can be used to prepare building materials, and can also be used as a soil conditioner. The waste liquid can be used to return to dissolve the next batch of red mud. The dissolution process is that the volume ratio of the was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com