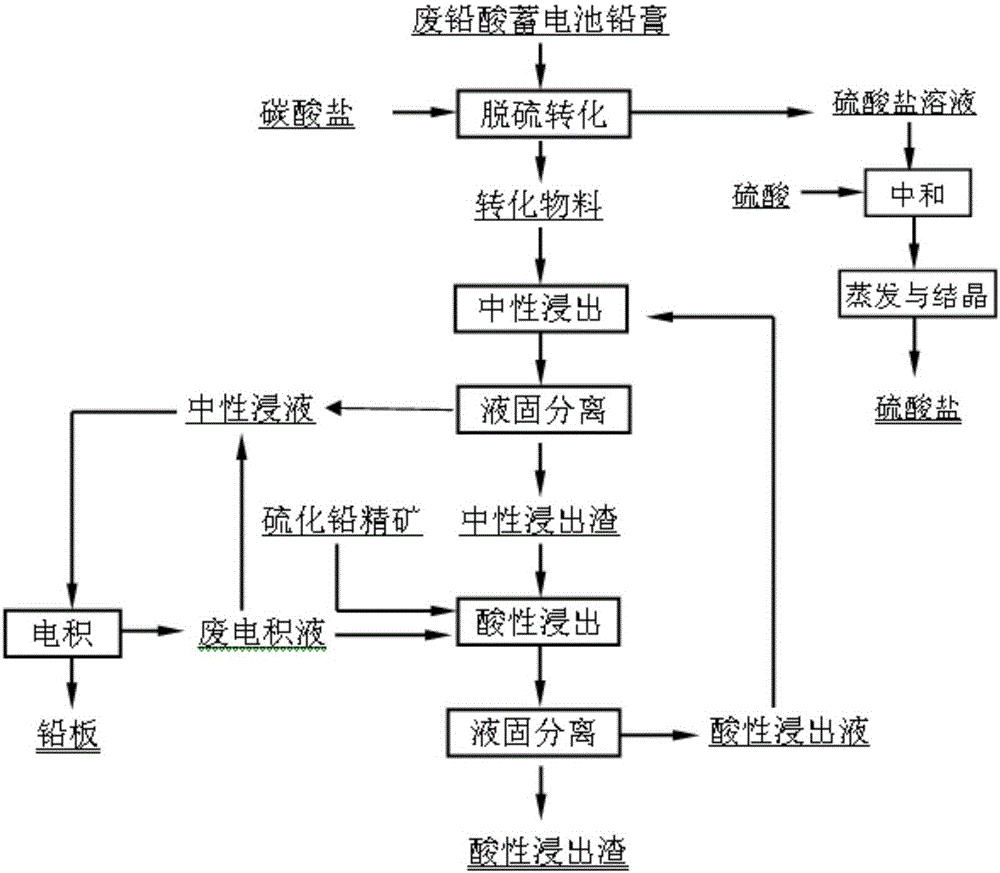
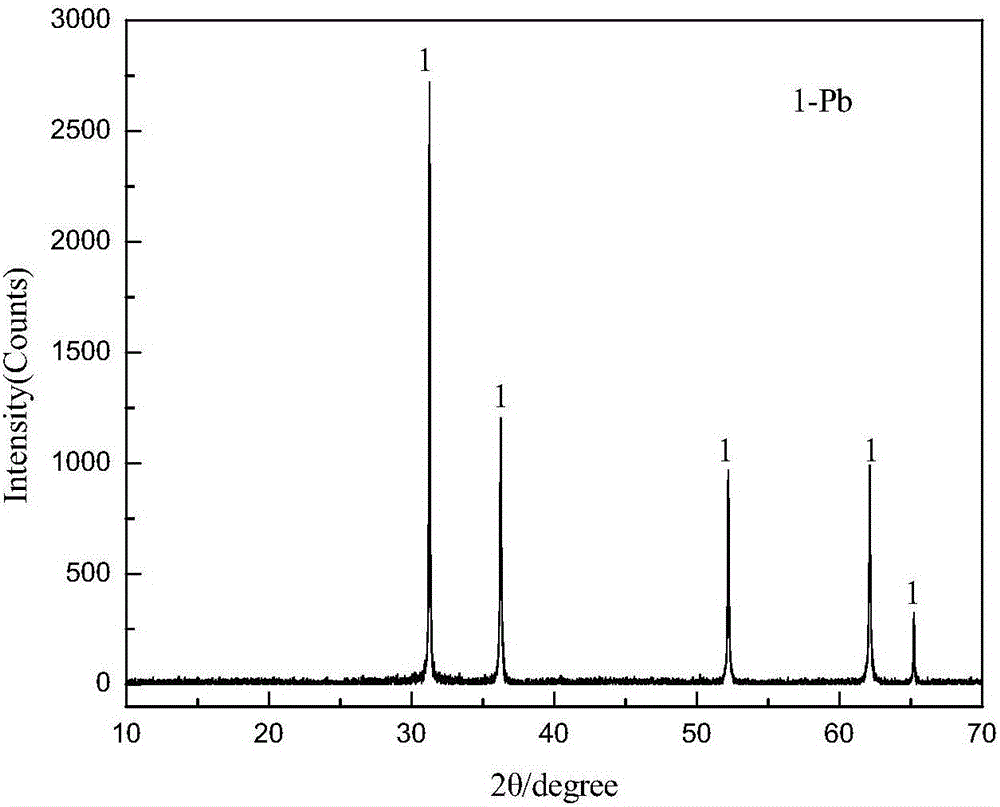
All-wet method for extracting lead from lead plaster and lead sulfide concentrate
A lead sulfide, all-wet technology, applied in the field of lead extraction, can solve problems such as environmental pollution, and achieve the effects of reducing use costs, good stability, and being beneficial to environmental protection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] The phases of the lead sulfate material used in the test are shown in Table 1, and the chemical composition of the lead sulfide concentrate is shown in Table 2.
[0059] Table 1 lead sulfate material lead phase analysis / %
[0060] Phase Pb / PbSO 4
Pb / PbO Pb / PbO 2
Pb T Pb
content / % 30.40 12.90 25.63 <1 72.90
[0061] Table 2 Chemical composition of lead sulfide concentrate
[0062] element Pb S Fe Ag Element / % 48.71 17.32 7.76 0.0057
[0063] Get lead sulfate material 200g (its lead material phase is as table 1), and the carbonate consumption in the carbonate solution of preparation is 1.3 times of theoretical amount, press material and carbonate solution in beaker by liquid-solid ratio 4:1mL / g Mix and mix in medium, stir at 200r / min, convert at a temperature of 85°C for 1.0h; filter and wash until no sulfate exists in the washing liquid. Take the material after desulfurization and conversion, ad...
Embodiment 2
[0065] The phases of the lead sulfate material used in the test are shown in Table 1, and the chemical composition of the lead sulfide concentrate is shown in Table 2.
[0066]Get lead sulfate material 400g (its lead phase is as table 1), and the carbonate consumption in the carbonate solution of preparation is 1.5 times of theoretical amount, by liquid-solid ratio 6:1mL / g material and carbonate solution are in beaker and put it into a water bath at a stirring speed of 200r / min, transform at a temperature of 25°C for 2.5h; filter and wash until no sulfate exists in the lotion. Take the desulfurized conversion material, add the material to the acidic leachate (containing 1.3mol / L of free methanesulfonic acid and 30g / L of lead methanesulfonate) according to the liquid-solid ratio of 5:1mL / g, and stir at a stirring speed of 400r / min. Leach at a temperature of 75°C for 2.5 hours, and obtain filter residue and neutral leachate after separation; lead sulfide concentrate is subjected...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com