Flame retardant additive, preparation method of flame retardant additive and lithium battery
A technology of flame retardant additives and flame retardants, which is applied in the field of electrochemistry and can solve the problems of low safety performance of lithium batteries
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0049] The invention also provides a preparation method of the flame retardant additive,
[0050] Method I includes the following steps:
[0051] (1) uniformly mixing the flame retardant, organic matter and water to obtain the first mixed solution, wherein the mass ratio of the flame retardant, organic matter and water is 1:1:998-1:1:98;
[0052] (2) Spray drying the first mixed solution to obtain a flame retardant additive whose shell is an organic shell, wherein the drying temperature is 100°C-150°C, and the injection rate is 5-25mL / min.
[0053] Method II includes the following steps:
[0054] (1) Tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) and water are mixed uniformly to obtain a second mixed solution, and cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) is added in the second mixed solution to prepare silicon dioxide. The prepared silica is sintered at high temperature to obtain hollow silica;
[0055] Wherein, the mass fraction of ethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) in the second mixed solution is ...
Embodiment 1
[0065] This example is used to illustrate the flame retardant additive prepared according to method I of the present invention.
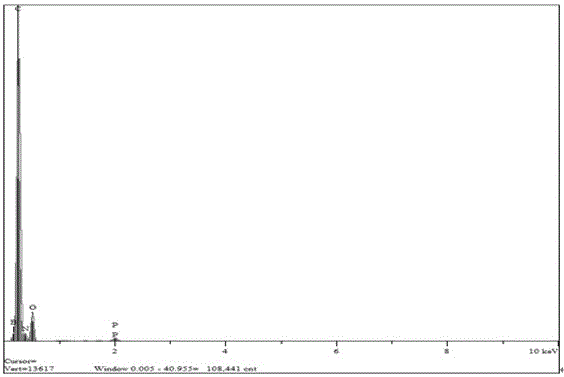
[0066] (1) 1g triphenyl phosphate (TPP), 1g polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and 998g water are mixed uniformly to obtain the first mixed solution;
[0067] (2) Spray-dry the first mixed solution, set the inlet temperature of the spray dryer to 150° C., and the injection rate to 10 mL / min to prepare the flame retardant additive.
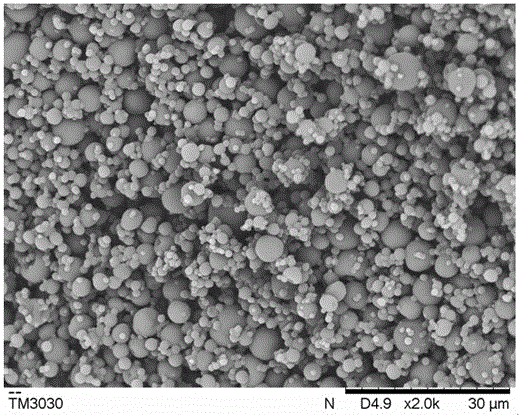
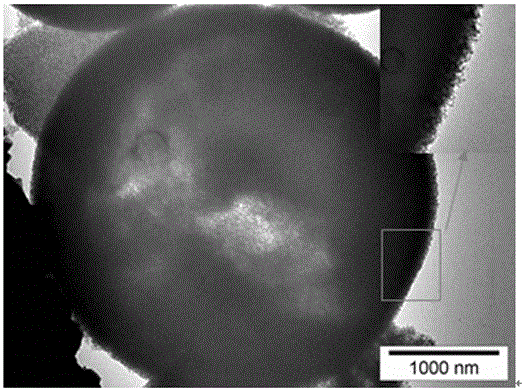
[0068] Since polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) is less soluble in water than triphenyl phosphate (TPP), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) will preferentially precipitate and become solid, covering the outer surface of triphenyl phosphate (TPP). A flame retardant additive that forms a core-shell structure with an outer shell of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) and an inner shell of triphenyl phosphate (TPP). The diameter of the core-shell structure is 0.2 μm-5 μm, and the thickness of the polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) shell 0.1μm-0.5μm.
[0069] fig...
Embodiment 2
[0074] This example is used to illustrate the flame retardant additive prepared according to method I of the present invention.
[0075] (1) Mix 1g triphenyl phosphate (TPP), 1g polyethylene oxide (PEO) and 500g water to obtain the first mixed solution;
[0076] (2) Spray-dry the first mixed solution, set the inlet temperature of the spray dryer to 120°C, and the injection rate to 15mL / min to prepare the flame retardant additive.
[0077] Since the solubility of polyethylene oxide (PEO) in water is lower than that of triphenyl phosphate (TPP), polyethylene oxide (PEO) will preferentially precipitate and become a solid state, covering the outer surface of triphenyl phosphate (TPP). A flame retardant additive that forms a core-shell structure with polyethylene oxide (PEO) as the outer shell and triphenyl phosphate (TPP) as the inner. The diameter of the core-shell structure is 0.5 μm-3 μm, and the thickness of the polyethylene oxide (PEO) shell is 0.1μm-1μm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com