Nanofiber capable of providing slow controlled release of medicines after pulse and preparation method of nanofiber
A technology of nanofibers and drugs, applied in the field of materials science, can solve problems such as poor effects, and achieve the effect of clear juxtaposition structure, simple preparation process, and smooth fiber surface
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Example 1: Implementation of electrospinning process and preparation of side-by-side nanofibers
[0029] Co-dissolve 2 g of paracetamol and 7 g of polyvinylpyrrolidone K60 in 100 ml of absolute ethanol to prepare a side-by-side working fluid of fiber bundles.
[0030] Co-dissolve 4 g of the drug acetaminophen and 20 g of the fiber-forming polymer ethylcellulose in 100 ml of absolute ethanol to prepare the working fluid on one side of the main fiber bundle.
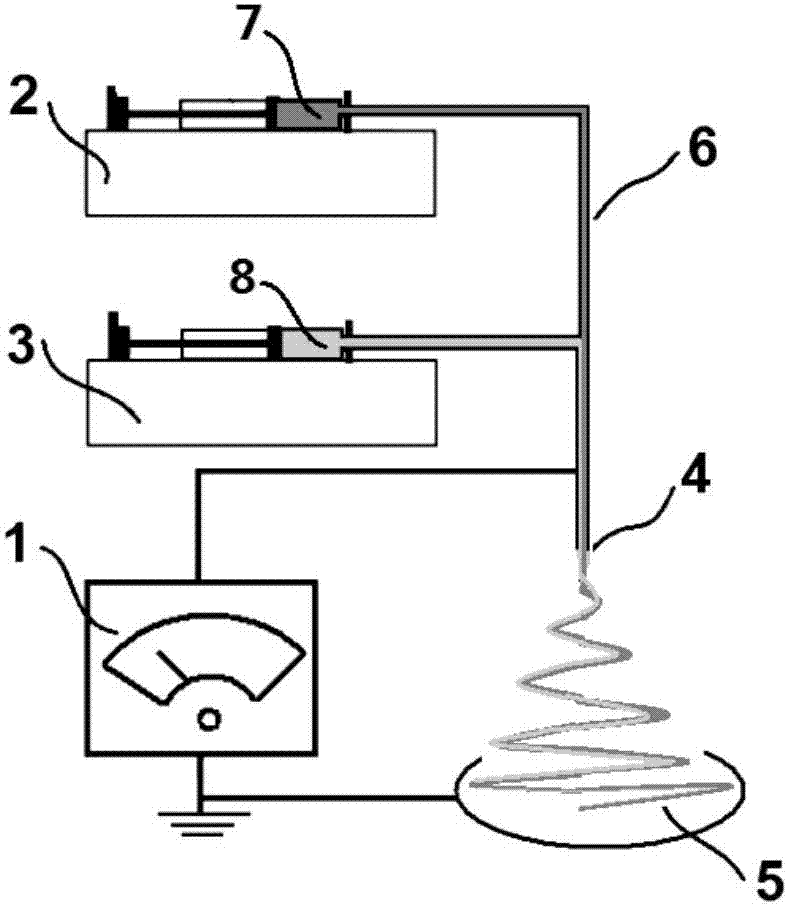
[0031] Put the above two kinds of working fluids into the corresponding syringes 7 and 8 respectively, install them on the respective syringe pumps 2 and 3, and connect them to the two inlets of the parallel spinning head 4, connect the high-pressure spinning head 4 and the high-pressure generator 1.
[0032] The speed of injecting the parallel solution into the parallel spinning head 4 is controlled respectively by two syringe pumps 2 and 3, the parallel flow rate is 1.0 mL / h, the distance between the fiber receiv...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: Structural and Morphological Characterization of Slow Controlled Release Nanofibers After Drug Pulse
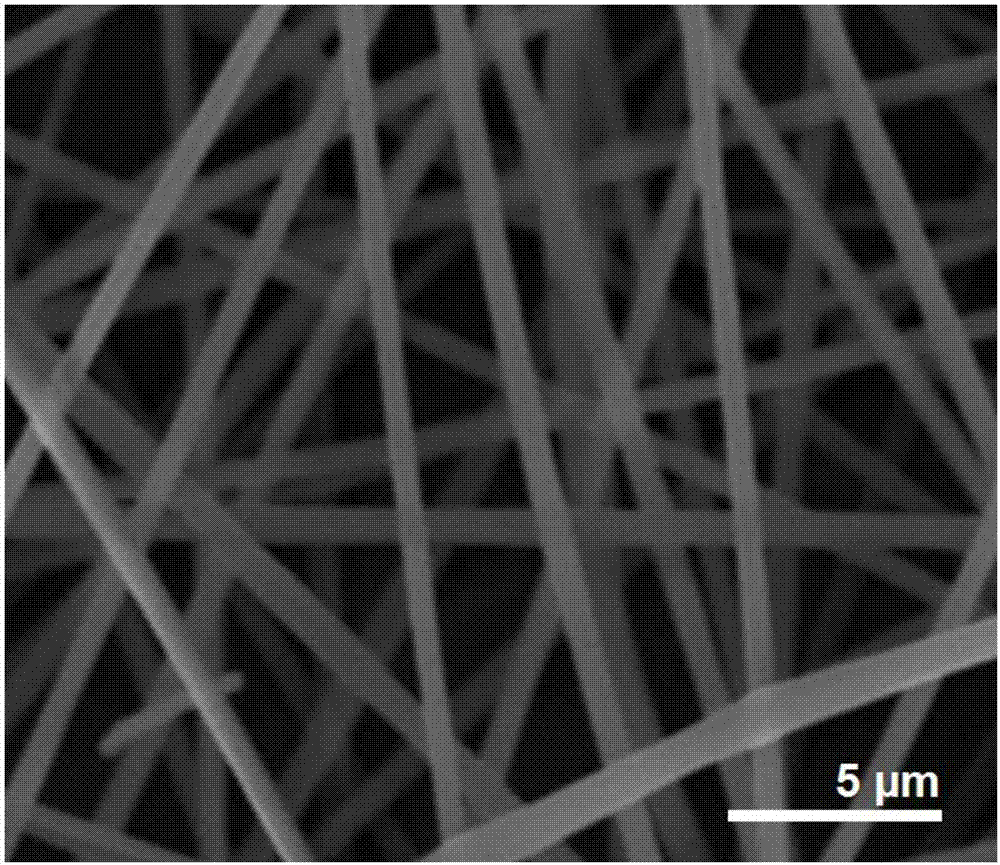
[0036] Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) was used to observe the surface of the fiber prepared in Example 1 after spraying gold, and the results were as follows image 3 shown. The prepared fiber exhibits a good linear state, no beading structure occurs, the fiber surface is smooth, and the fiber accumulation is uniform. The diameter is 720 ± 150 nm, the distribution is relatively uniform, and the diameter distribution is relatively concentrated.
[0037] The internal structure of the prepared fiber was observed by high-resolution transmission electron microscope (TEM), and the results were as follows: Figure 4 As shown, the bilateral side-by-side structural features of nanofibers are clear. The internal structure of the fiber is as Figure 5 As shown, the drug 33 is evenly distributed on both sides of the Jonas nanofibers. One side 1...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3: Drug controlled release function analysis of slow controlled release nanofibers after drug pulse
[0039] According to the 2015 edition of Chinese Pharmacopoeia Appendix ⅩD Release Test Method 2, the RCZ-8A intelligent dissolution tester was used to conduct the in vitro dissolution test on the drug-loaded nanofibers obtained above. The control speed was 50rpm, the temperature was 37±0.1°C, and the dissolution medium was 900 mL pH7.0 phosphate buffer solution to investigate the drug release performance of nanofibers in vitro. Sampling 5mL at the scheduled time, filtered through a 0.22 µm microporous membrane to obtain the eluate sample, and immediately replenished with the same volume of isothermal fresh medium. After proper dilution of the sample, ultraviolet measurement was carried out at λ = 258 nm using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer, and the dissolution amount and cumulative dissolution percentage of the drug paracetamol were calculated, repeated 6 times. Th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com