A method for preparing single-layer molybdenum disulfide quantum dots based on electronic dynamic regulation
A single-layer molybdenum disulfide, electronic dynamic control technology, applied in the field of femtosecond laser applications, can solve the problems of time-consuming, low efficiency, loss of semiconductor characteristics, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing yield and enhancing absorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
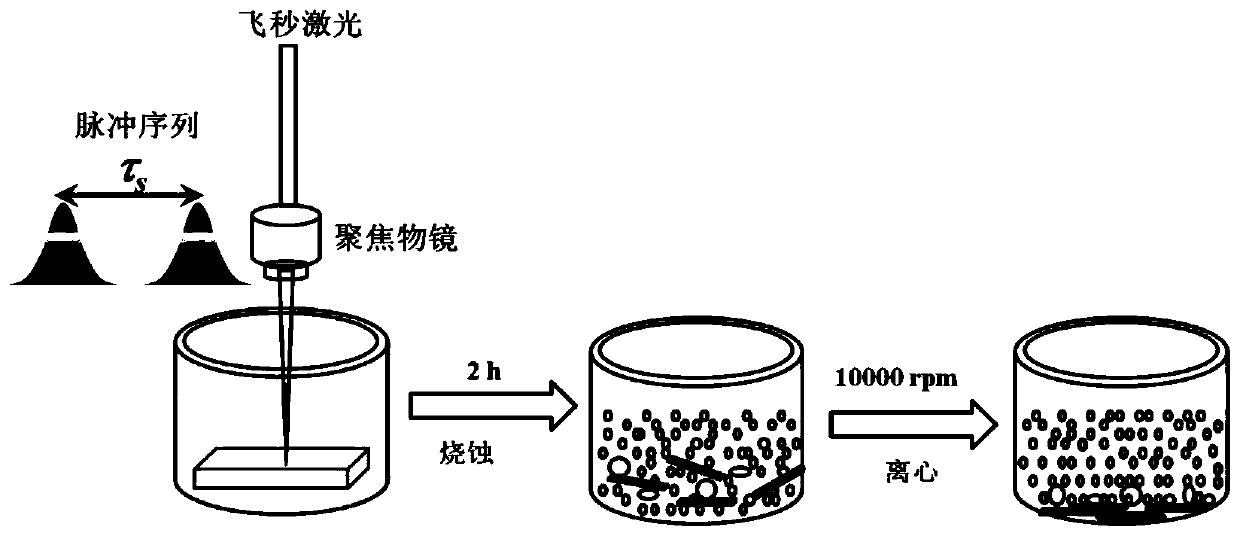
[0031] Using femtosecond laser time-domain shaping pulse sequence to regulate electronic dynamics to realize a fast and green method for preparing single-layer molybdenum disulfide quantum dots, the specific steps are as follows:
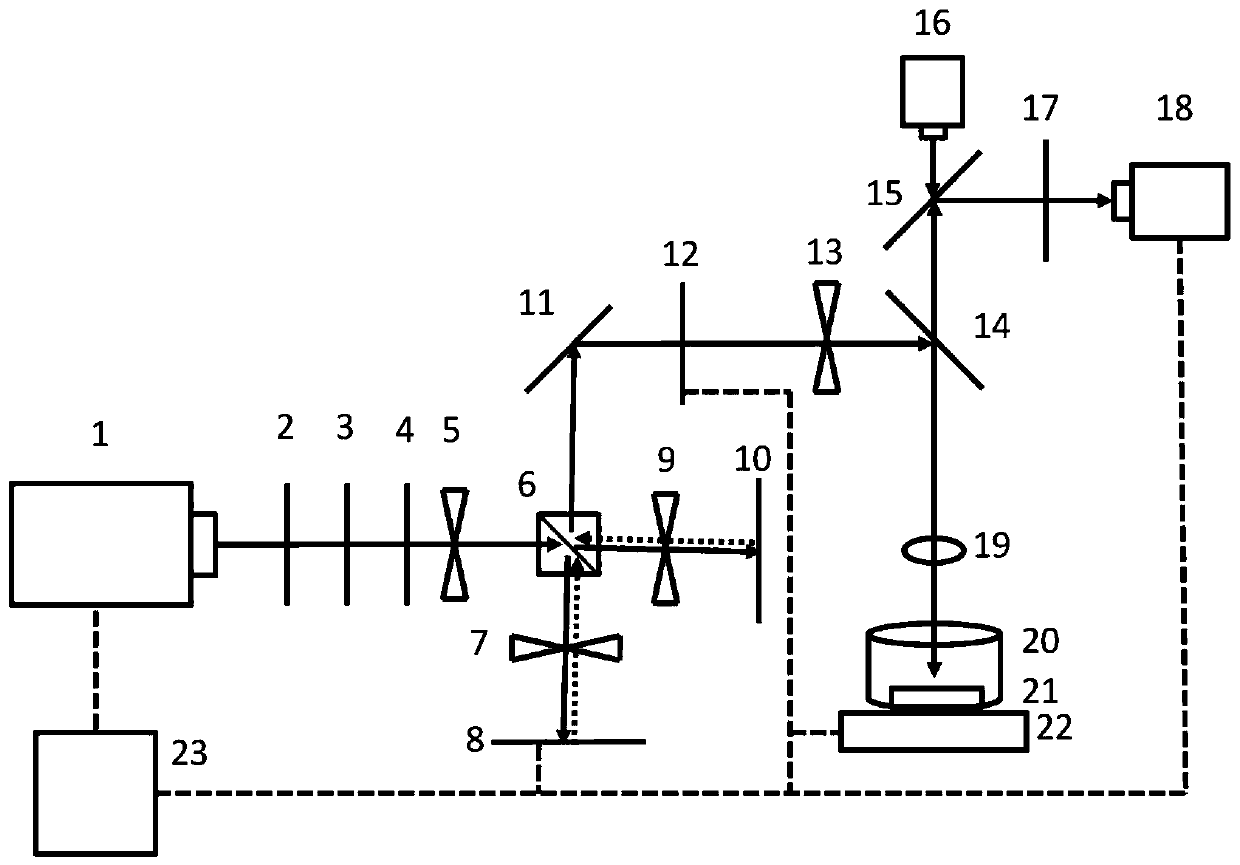
[0032] Step 1. Through the basic method of femtosecond pulse time-domain shaping, the traditional femtosecond laser pulse is modulated in the time domain into a femtosecond laser pulse sequence including two sub-pulses.
[0033] Step 2. Place the bulk molybdenum disulfide target on the bottom of the glass vessel, add 5ml of distilled water to immerse the surface of the material for about 3mm, and then focus the femtosecond laser pulse sequence modulated in step 1 on the molybdenum disulfide target and water. At the interface, the material is ablated by adjusting the energy of the femtosecond laser pulse sequence, the delay between sub-pulses, and the laser scanning speed and scanning interval.
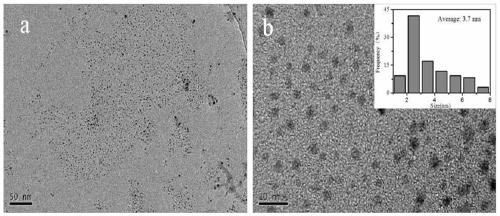
[0034] Step 3: Put the molybdenum disulfide suspension...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com