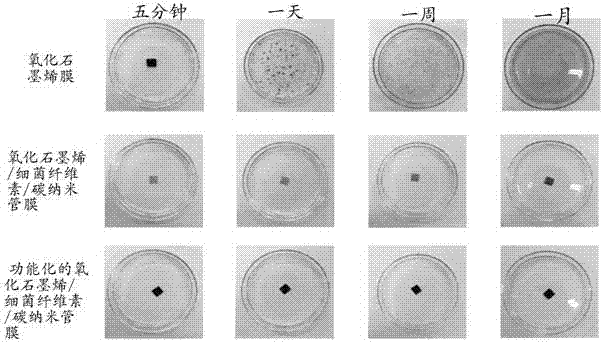
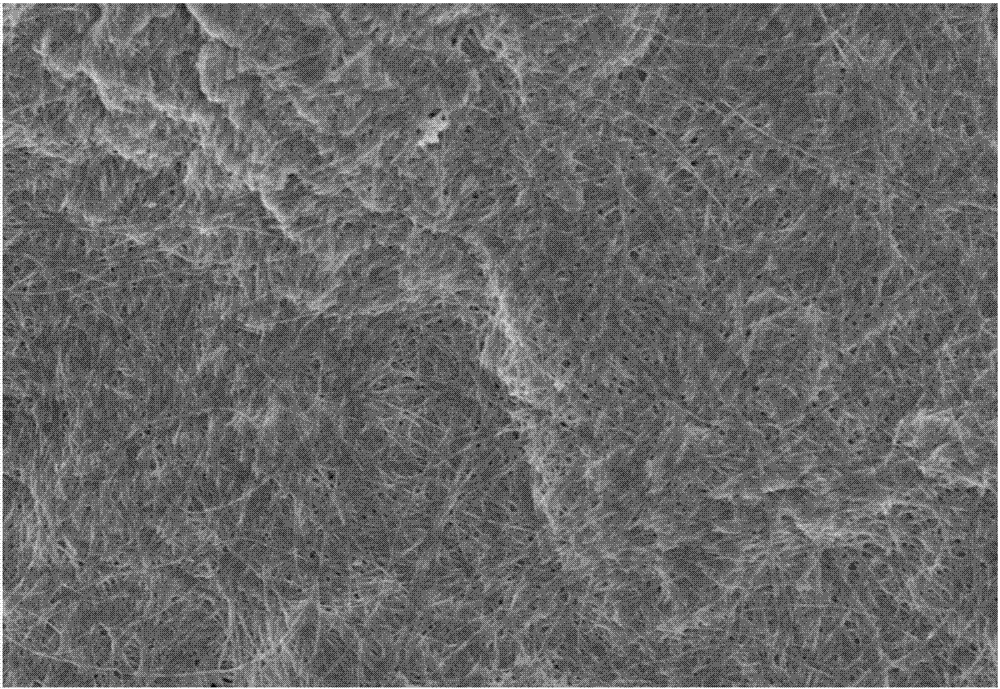
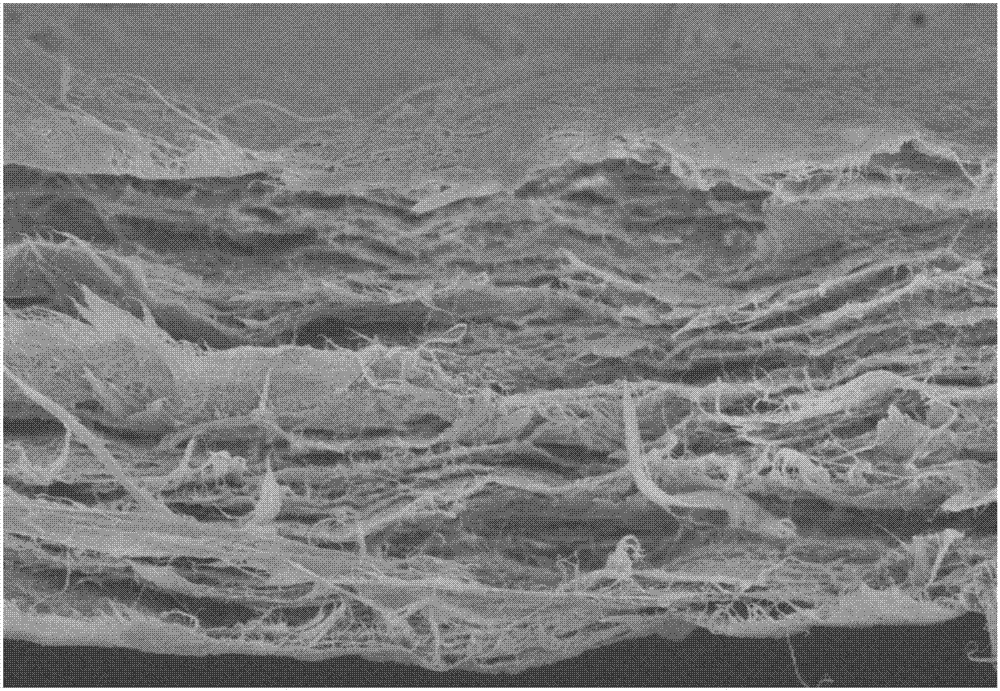
Preparation method and application of functionalized graphene oxide/bacterial cellulose/carbon nano tube composite membrane
A carbon nanotube composite and bacterial cellulose technology, applied in the field of graphene, can solve the problems of restricted application range and low flux of separation membrane
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0035] The invention provides a kind of preparation method of functionalized graphene oxide / bacterial cellulose / carbon nanotube composite film, comprising the following steps:
[0036] A) mixing the surface-functionalized bacterial cellulose solution with carbon nanotubes to obtain a first mixed solution;
[0037] B) The first mixed solution is mixed with the functionalized graphene oxide solution and then vacuum filtered to obtain a graphene / bacterial cellulose / carbon nanotube composite membrane.
[0038] In the invention, firstly, the bacterial cellulose solution with surface functionalization is mixed with carbon nanotubes to obtain the first mixed solution.
[0039] Wherein, the surface functionalized bacterial cellulose is prepared according to the following method:
[0040] adding the solution of the surface functionalization reagent to the bacterial cellulose solution, and stirring thoroughly to obtain a surface functionalized bacterial cellulose solution;
[0041] Th...
Embodiment 1
[0076] Disperse 0.5g of carbon nanotubes into 300mL, 30% (70mLH 2 (0+30mLNaClO) sodium hypochlorite solution, stirring continuously to make it fully dispersed in the NaClO solution, and reacting at 25°C for 12h. After the reaction is finished, it is filtered and washed repeatedly with water to obtain acidified carbon nanotubes.
[0077] First, according to the mass ratio of polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride (PDDA) to bacterial cellulose of 1:10, polydiallyldimethylammonium chloride (PDDA) was added to 1 mg / mL of bacteria In the cellulose solution, the surface of bacterial cellulose is functionalized to make the surface positively charged; then according to the mass ratio of bacterial cellulose to acidified carbon nanotubes of 20:1, the acidified carbon nanotubes are added to the above functional In the acidified bacterial cellulose solution, the acidified carbon nanotubes are negatively charged, and the negatively charged carbon nanotubes are combined with the positively c...
Embodiment 2
[0103] First, take a certain amount of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and dissolve it in deionized water to form a 0.5 mg / mL CTAB solution; then add the CTAB solution to the bacterial cellulose solution with a concentration of 1 mg / mL . Wherein, the mass ratio of CTAB to the bacterial cellulose solution is 1:10; then the acidified carbon nanotubes are added to the bacterial cellulose solution, wherein the mass of the acidified carbon nanotubes prepared by the bacterial cellulose and Example 1 The ratio is 30:1, and fully stirred to obtain the first mixed solution.
[0104] Then, trishydroxymethylaminomethane was dissolved in deionized water to form a 1mol / L solution (Tris solution); then dilute hydrochloric acid with pH=6 was added to the solution to adjust the pH of the solution to 8.5 to obtain Tris-HCl Buffer solution; adding dopamine into the above buffer solution and stirring thoroughly, wherein the concentration of dopamine is 10 mg / mL. The above-mentioned Tris-...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com