Micro-display OLED device and manufacturing method thereof
A micro-display and device technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electric solid-state devices, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve problems such as improving yield rate, simplifying process, and improving yield rate, so as to improve yield rate, simplify process, improve performance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
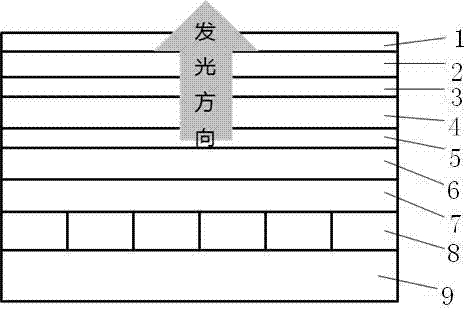
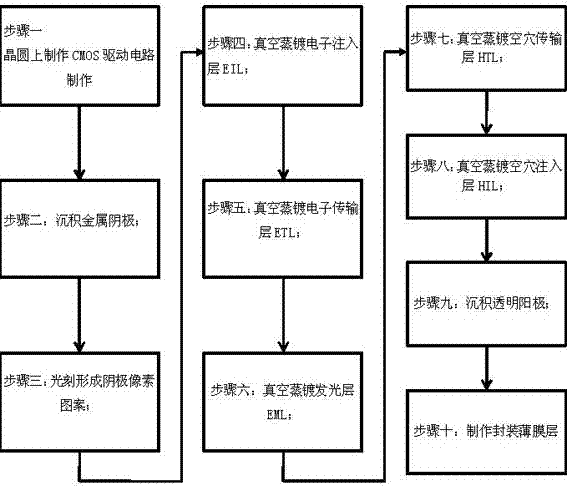
[0028] Embodiment one Figure 4 Shown is the device structure of the single-color (such as a certain display color such as green, blue or yellow) or white silicon-based micro-display OLED described in the present invention, and a protective glass is added outside the thin-film encapsulation layer. Among them, the cathode is metal Al, and the small squares in the cathode in the figure indicate the pixel pattern. Both the cathode coating and the cathode pixel pattern are manufactured in the integrated circuit wafer foundry using the standard CMOS process; the light-emitting layer EML emits the required green, blue , yellow or white organic light-emitting material layer; the anode is the most commonly used ITO transparent conductive oxide in the flat panel display industry, which not only has good light transmission and conductivity, but also has a high work function, and is easy to integrate with the hole injection layer, etc. Organic materials achieve the best energy level matc...
Embodiment 2
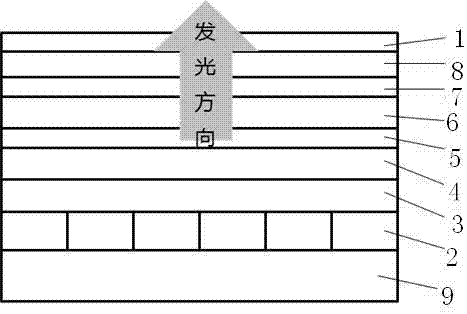
[0029] Embodiment two Figure 5 Shown is the device structure of the full-color silicon-based micro-display OLED of the present invention, in which a color filter film CF and a protective glass are added outside the thin film encapsulation layer. The cathode is metal Mg, and the small squares on the cathode in the figure indicate the pixel pattern. Both the cathode coating and the cathode pixel pattern are manufactured in the integrated circuit wafer foundry using a standard CMOS process; the light-emitting layer EML is an organic light-emitting material layer that emits white light ; The anode is the most commonly used ITO transparent conductive oxide in the flat panel display industry. It not only has good light transmission and conductivity, but also has a high work function, and is easy to achieve the best energy level matching with organic materials such as hole injection layers. , in order to reduce the driving voltage of OLED and improve the luminous performance, the IT...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com