A method for preparing aluminum-based rare earth alloys by electrolysis near room temperature
A rare earth alloy and electrolysis technology, which is applied in the field of preparing aluminum-based rare earth alloys by electrolysis in a near room temperature environment, can solve the problems of incomplete exchange reaction, complex synthesis process, no application advantages, etc., and achieves low cost, shortened process flow, and reduced production. cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
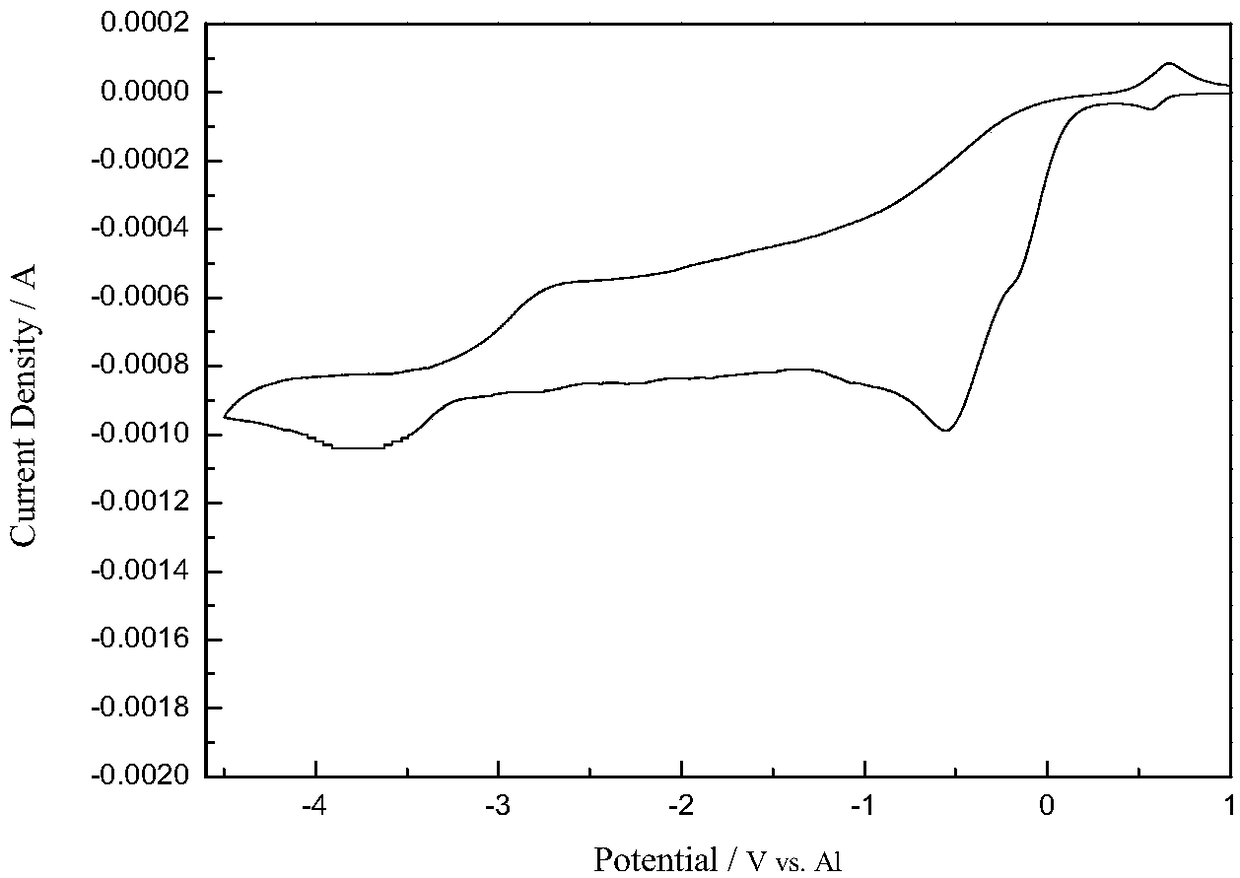
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0067] The raw materials for preparing the electrolyte are neodymium chloride and aluminum chloride-based ethylene carbonate ionic liquid, wherein the ionic liquid accounts for 98% of the total mass of the electrolyte, and the neodymium chloride accounts for 2% of the total mass of the electrolyte. Continuously feed inert gas into the electrolytic cell to discharge the air and water vapor in it, then add the ionic liquid into the electrolytic cell, then add neodymium chloride, stir and mix in the electrolytic cell to form an electrolyte system, and control the temperature of the electrolyte system to 55°C. The graphite rod is used as the anode, the aluminum sheet is used as the cathode, and the electrolysis voltage is -3.2V (vs Al). After 30 minutes of electrolysis, a feeding operation of neodymium chloride is carried out, and the mass of neodymium chloride is 1% of the total mass of the initial electrolyte, and 0.05% of the total mass of the initial electrolyte is added with N...
Embodiment 2
[0069] The raw materials for preparing the electrolyte are neodymium chloride and aluminum chloride-based ethylene carbonate ionic liquid, wherein the ionic liquid accounts for 97% of the total mass of the electrolyte, and the neodymium chloride accounts for 3% of the total mass of the electrolyte. Continuously feed inert gas into the electrolytic cell to discharge the air and water vapor in it, then add the ionic liquid into the electrolytic cell, then add neodymium chloride, stir and mix in the electrolytic cell to form an electrolyte system, and control the temperature of the electrolyte system to 65°C. The graphite rod is used as the anode, the aluminum sheet is used as the cathode, and the electrolysis voltage is -3.3V (vs Al). After 30 minutes of electrolysis, a feeding operation of neodymium chloride is carried out. The mass of neodymium chloride is 1% of the total mass of the initial electrolyte; after 60 minutes of electrolysis, the substrate and the sediment are colle...
Embodiment 3
[0071] The raw materials for preparing the electrolyte are neodymium chloride and aluminum chloride ethylene carbonate ionic liquid, wherein the ionic liquid accounts for 96% of the total mass of the electrolyte, and the neodymium chloride accounts for 4% of the total mass of the electrolyte. Continuously feed inert gas into the electrolytic cell to discharge the air and water vapor in it, then add the ionic liquid into the electrolytic cell, then add neodymium chloride, stir and mix in the electrolytic cell to form an electrolyte system, and control the temperature of the electrolyte system to 75°C. The tungsten rod is used as the anode, the aluminum sheet is used as the cathode, and the electrolysis voltage is -3.5V (vs Al). After 30 minutes of electrolysis, a feeding operation of neodymium chloride is carried out. The mass of neodymium chloride is 1% of the total mass of the initial electrolyte, and dimethyl carbonate of 0.5% of the total mass of the initial electrolyte is a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com