Method for identifying differential marker of IC50 dose of vitamin C for RAW264.7 and K562 cells
A technology of RAW264.7 and vitamins, applied in the field of 1HNMR metabolomics analysis technology, can solve the problems of unclear biological significance of metabolite changes, unknown metabolite changes, and unknown biological significance, and achieve reliable data preprocessing Fast, easy-to-use effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0084] (2) Preparation of cell extract:
[0085] Preparation of vitamin C group cell extract: RAW264.7 or K562 cells in the corresponding vitamin C IC 50 Cultivate at a certain dose, add cold methanol after culturing to quench cell metabolism, then use methanol chloroform water extraction method for ultrasonic crushing and extraction, and collect the water phase;
[0086] Preparation of the cell extract of the blank group: culture RAW264.7 or K562 cells, add cold methanol after culture to quench the cell metabolism, and then use methanol chloroform water extraction method for ultrasonic crushing and extraction, and collect the water phase;
[0087] In the process of preparing cell extracts, for the tissue structure and components of RAW264.7 or K562 cells, in order to ensure that as much metabolite information as possible can be obtained from vitamin C group cells and blank group cells, the extraction reagent is preferably selected It is a mixed solvent of methanol, chloroform ...
Embodiment 1
[0140] 1. Method principle
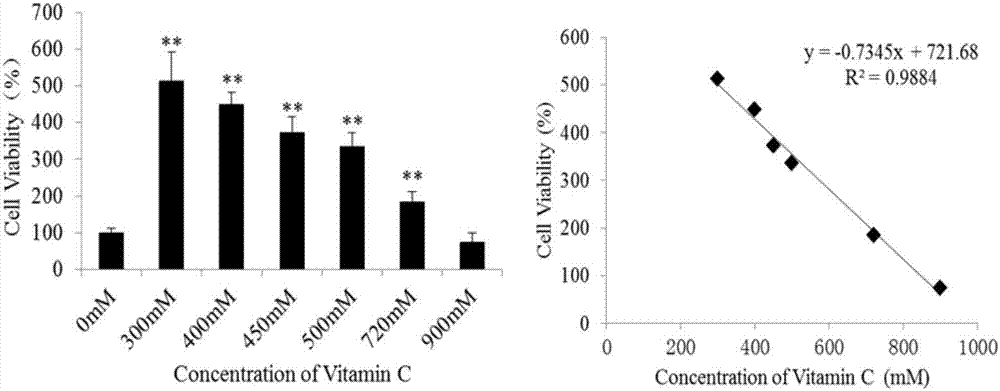
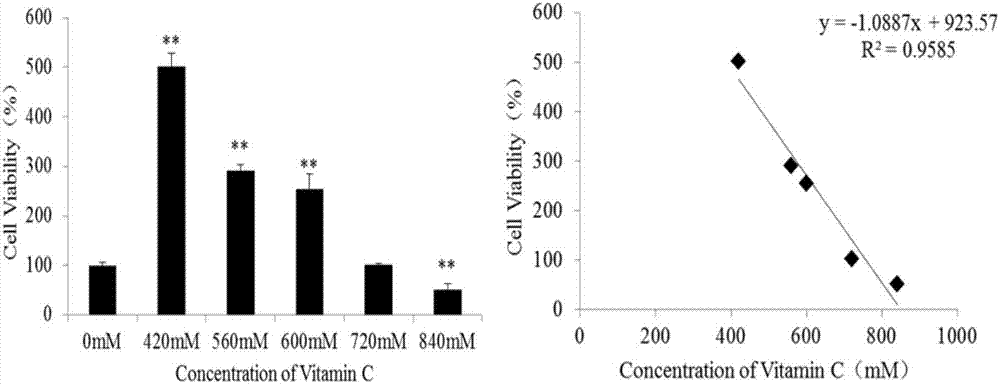
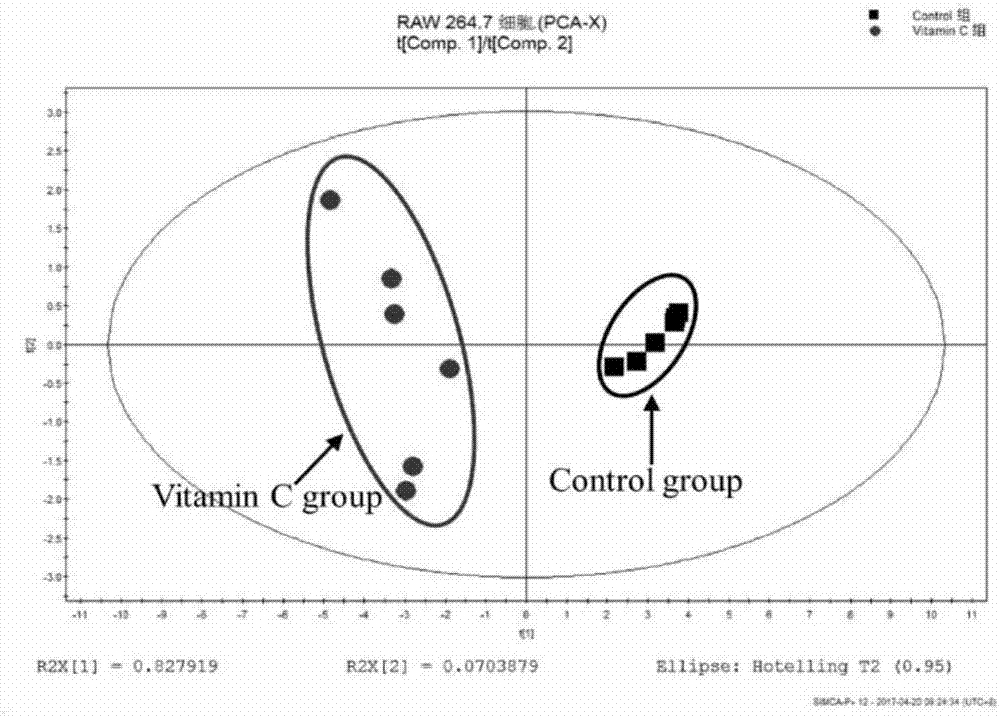
[0141] High-concentration doses of vitamin C will affect the metabolic level of cells after acting on cells, and change the types and concentrations of intracellular metabolites. 1 H NMR technology can identify the differential metabolites after vitamin C treatment and the control group, and then use metabolomics analysis technology to analyze the obtained data with PCA, PLS-DA, OPLS-DA and other techniques to find differential metabolism thing. Qualitative analysis was performed through the Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) and the Biological Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Database (BMRB) to determine the species names of the differential metabolites. The identified differential metabolites were imported into the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) database and MetaboAnalyst (MetPA) for pathway enrichment analysis.
[0142] 2. Instruments and materials
[0143] Instruments and equipment:
[0144] Stat Fax-2000 microplate reader American ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com