Combined treatment system and method for boron-containing radioactive waste liquid of nuclear power plant
A radioactive waste liquid and treatment system technology, applied in radioactive purification, nuclear engineering, etc., to achieve the effects of reduced radiation dose, good removal effect, and high operational flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
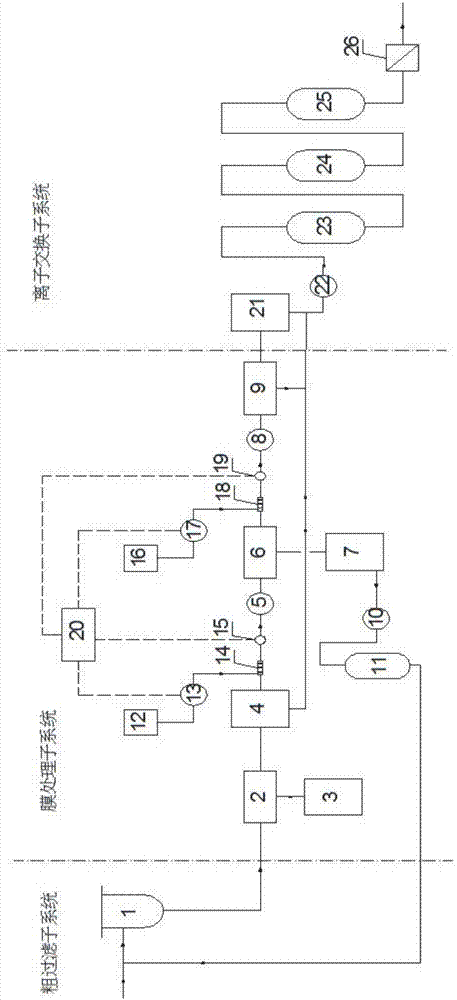
[0050] The waste liquid to be treated enters from the coarse filtration subsystem, and after passing through the filter 1, the particulate radioactive substances are removed.
[0051] Then the waste liquid flows into the membrane separation subsystem, first passes through the ultrafiltration treatment device 2, intercepts colloidal radioactive substances, and the formed concentrated liquid is discharged to the ultrafiltration concentrated liquid tank 3, and the permeate is discharged to the reverse osmosis raw water tank 4. The waste liquid in the reverse osmosis raw water tank enters the first-stage reverse osmosis membrane module 6 through the first booster pump 5, and then the concentrated liquid is discharged to the reverse osmosis concentrated liquid tank 7, and the permeate enters the second stage through the second booster pump 8 Reverse osmosis membrane module 9. The concentrated liquid of the second-stage reverse osmosis membrane module is returned to the reverse osmo...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Example 2: Removal of radioactivity and boron
[0055] For the boron-containing radioactive waste liquid produced by the normal operation of nuclear power plants, the activity concentration is ~10 6 Bq / L, boron concentration ~ 500ppm, according to the process of Example 1, all subsystems are put into operation, and the ion exchange bed is filled with Na-type cation resin.
[0056] After treatment, the radioactivity concentration of the waste liquid can be lower than 100Bq / L, meeting the emission limit requirements of coastal and inland nuclear power plants in GB 6249 (Regulations on Environmental Radiation Protection of Nuclear Power Plants). The concentration of boron in the effluent is less than 100ppm, and can be less than 0.5ppm after being diluted by the water discharged from the cooling tower of the power plant.
Embodiment 3
[0057] Embodiment 3: remove radioactivity
[0058] For some coastal nuclear power plants, the boron recovery system has been installed, and when there is no requirement for the boron concentration discharged into seawater, the reverse osmosis treatment device can be bypassed. The waste liquid treatment process is as follows: filter, ultrafiltration treatment device, first ion exchange bed, second ion exchange bed, third ion exchange bed and crushed resin filter. After the above treatment sequence, the radioactivity concentration of the waste liquid can also be lower than 100Bq / L, meeting the discharge limit requirements of coastal and inland nuclear power plants in GB 6249 (Regulations on Environmental Radiation Protection of Nuclear Power Plants). However, the boron concentration in the waste liquid remains at the original level.
[0059] The main advantage of this treatment is that no boron-containing concentrate will be produced, and no drying / solidification treatment is r...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com