Artificial cultivation method for wild agaricus campestris and application
A reed mushroom and artificial technology, applied in the field of artificial cultivation of wild reed mushrooms to obtain fruiting bodies, can solve the problems of extinction, reduction and aggravation of wild reed mushroom yield and quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Embodiment 1 strain separation
[0058] The present invention adopts the tissue separation method to obtain strains, selects some fruiting bodies of wild mushrooms with normal color and no damage by diseases and insect pests, removes surface debris, and wipes them with 75% alcohol. Cut the fruiting bodies longitudinally into two, take mung bean-sized tissue pieces at the junction of the stipe and cap, quickly insert the tissue pieces into a PDA plate with tweezers, and culture them in the dark for 10-15 days in a constant temperature incubator at 29°C.
Embodiment 2
[0059] Embodiment 2 Morphology, molecular biology identification
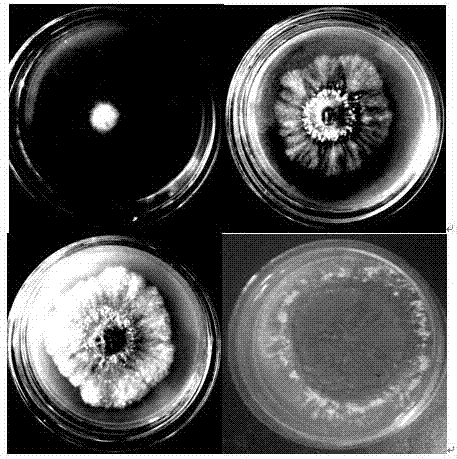
[0060] (1) Observation of colony morphology and structure: Observe its growth on the plate every other week, and take pictures to record the color and growth of mycelium.
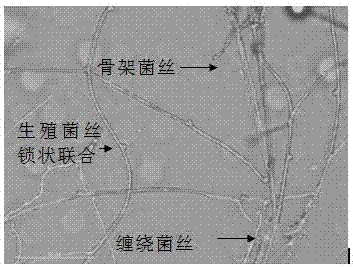
[0061] (2) Insert culture: insert culture, after the mycelium climbs to the cover glass, take it out and make a temporary mount, and observe the structure, type, branch, etc. of the mycelium under an optical microscope.
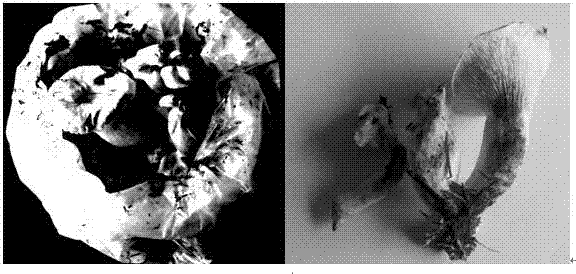
[0062] (3) Observation of the morphological characteristics of the fruiting bodies: records of cap size, color, shape, gills, stipe, etc.
[0063] 3 ITS identification process
[0064] (1) Cultivation of experimental materials
[0065] Take wild reed mushroom colonies that grow vigorously on the plate, transfer them to the prepared liquid medium in a clean bench aseptically, and culture them in the dark at 29°C. Mycelium can grow in about 15 days.
[0066] (2) Genomic DNA extraction reagents
[0067] ①Pick an appropriat...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Example 3 Screening of suitable temperature for mycelium growth
[0085] The PDA comprehensive medium was cultured at 5 different temperatures of 14°C, 19°C, 24°C, 29°C, and 34°C. Each temperature treatment was repeated 5 times, the diameter of mycelium was measured with a vernier caliper, and the average value was taken, and the growth of mycelium, color of mycelium and characteristics of colonies were recorded.
[0086] 1. Preparation of plate culture medium
[0087] Wash the petri dishes and sterilize under high pressure at 121°C and 0.10-0.12Mpa for 30 minutes before use. Turn on the ultra-clean table ultraviolet lamp, sterilize for 20 minutes, pour the melted PDA culture medium into a petri dish (volume is 20ml), cover and cool.
[0088] 2. Inoculation operation
[0089] Wait for the PDA medium to solidify before inoculating. Turn on the ultraviolet lamp for sterilization, and turn off the ultraviolet lamp after 20 minutes. Aseptically pick a 5mm square bacter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com