Totally biodegradable short fibre enhanced medical hydrogel body dressing and preparation method thereof
An all-biological, gel-based technology, applied in the medical field, can solve problems such as weak mechanical strength, and achieve the effects of low cost, improved mechanical properties, and low requirements for molding equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
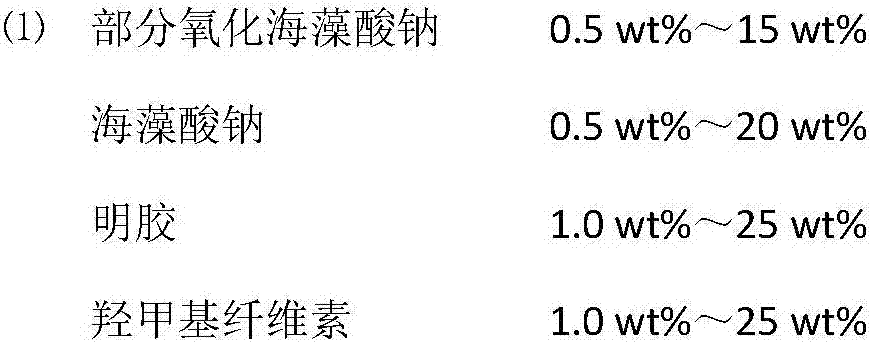
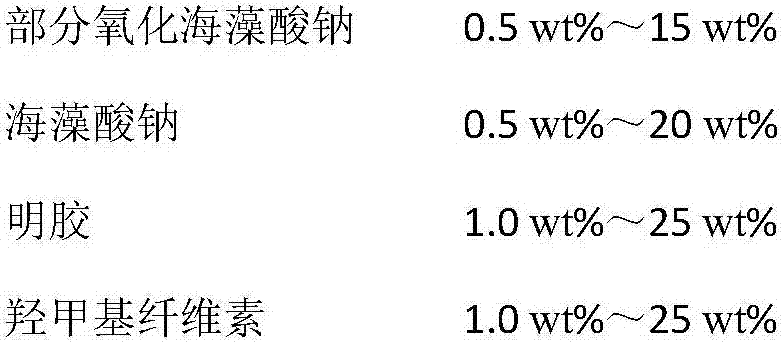
[0024] (1) Weigh 1.2g of sodium alginate and 1.2g of hydroxymethyl cellulose, add 97.6g of deionized water, stir evenly for wet spinning, control the diameter to 10μm-50μm, and the aspect ratio to 1:2-1.
[0025] (2) Use a balance to weigh 1.90g of sodium alginate and add it to 150g of deionized water, stir it with a magnetic force at 30°C to dissolve completely, add 1.76g of sodium periodate solid, and react in the dark for 48 hours, and the temperature is not higher than 30°C, then add 0.41g Ethylene glycol was used to terminate the reaction, and 500 g of ethanol and 3.0 g of sodium chloride were added to allow static sedimentation, suction filtration, and drying in a vacuum oven at 40°C for 48 hours.
[0026] (3) Add 1.2g of sodium alginate, 1.2g of hydroxymethyl cellulose, and 2.4g of gelatin into 85g of deionized water, and stir magnetically at 50°C until completely dissolved.
[0027] (4) Weigh 1.2g of 1,2-propanediol and 4.8g of glycerol, add the system obtained in step...
Embodiment 2
[0030] (1) Weigh 0.2g of sodium alginate and 2.4g of hydroxymethyl cellulose, add 97.4g of deionized water, stir evenly for wet spinning, control the diameter to 10μm-50μm, and the aspect ratio to 1:2-1.
[0031] (2) Add 0.2g of sodium alginate, 2.4g of hydroxymethyl cellulose, and 1.2g of gelatin into 78.5g of deionized water, and stir magnetically at 30°C until completely dissolved.
[0032] (3) Weigh 3g of 1,2-propanediol and 9g of glycerol, add the system obtained in step (3), and stir to dissolve completely. Weigh 1.2g of partially oxidized sodium alginate prepared in step (2) of case 1, and stir magnetically at room temperature until the partially oxidized sodium alginate is completely dissolved and the system is free of stratification. Weigh and add 5.0 g of short fiber, the length is about 50 μm, and the aspect ratio is 1:1, stir magnetically at room temperature, and mix well.
[0033] (4) Take 50g of the above-mentioned homogeneous system and pour it into a petri dis...
Embodiment 3
[0035] (1) Weigh 0.6g of sodium alginate and 1.8g of hydroxymethyl cellulose, add 97.6g of deionized water, stir evenly and perform wet spinning, control the diameter to 10μm-50μm, and the aspect ratio to 1:2-1.
[0036] (2) Add 0.6g of sodium alginate, 1.8g of hydroxymethyl cellulose, and 1.8g of gelatin into 81.62g of deionized water, and stir magnetically at 40°C until completely dissolved.
[0037] (3) Weigh 1.75g of 1,2-propanediol and 7.84g of glycerol, add the system obtained in step (3), and stir to dissolve completely. Weigh 0.6g of partially oxidized sodium alginate prepared in step (2) of case 1, and stir magnetically at room temperature until the partially oxidized sodium alginate is completely dissolved and the system is free of stratification. Weigh and add 1.0 g of short fiber, the length is about 20 μm, the aspect ratio is 2:1, magnetically stir at room temperature, and mix well.
[0038] (4) Take 50g of the above-mentioned homogeneous system and pour it int...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com