Streptomyces thermoviolaceus chitinase, as well as preparation method and application of streptomyces thermoviolaceus chitinase
A technology of chitinase and Streptomyces violaceum, applied in the field of chitinase, can solve the problems of increased production cost of chitosan oligosaccharides and large amount of enzymes, and achieve the effect of improved efficiency and efficient secretion and expression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Example 1 Codon optimization and total gene synthesis of chitinase gene
[0038] On the premise of not changing the amino acid sequence, using the preferred codon of Pichia pastoris, the chitinase (GH19 family) of Streptomyces thermoviolets was artificially designed (as shown in the sequence SEQ ID NO.1, GenBank accession number: BAA88833 ) coding gene, see SEQ ID NO.2 for the specific nucleotide sequence. The optimized nucleotide sequence has the highest homology of 78% with the original coding gene sequence (as shown in sequence SEQ ID NO.3, GenBank accession number: AB016842.1). The optimized gene sequence was entrusted to Sankon for full synthesis, and the synthesized gene sequence was named chitinase gene stchi19.
Embodiment 2
[0039] The expression vector construction of embodiment 2 chitinase gene stchi19
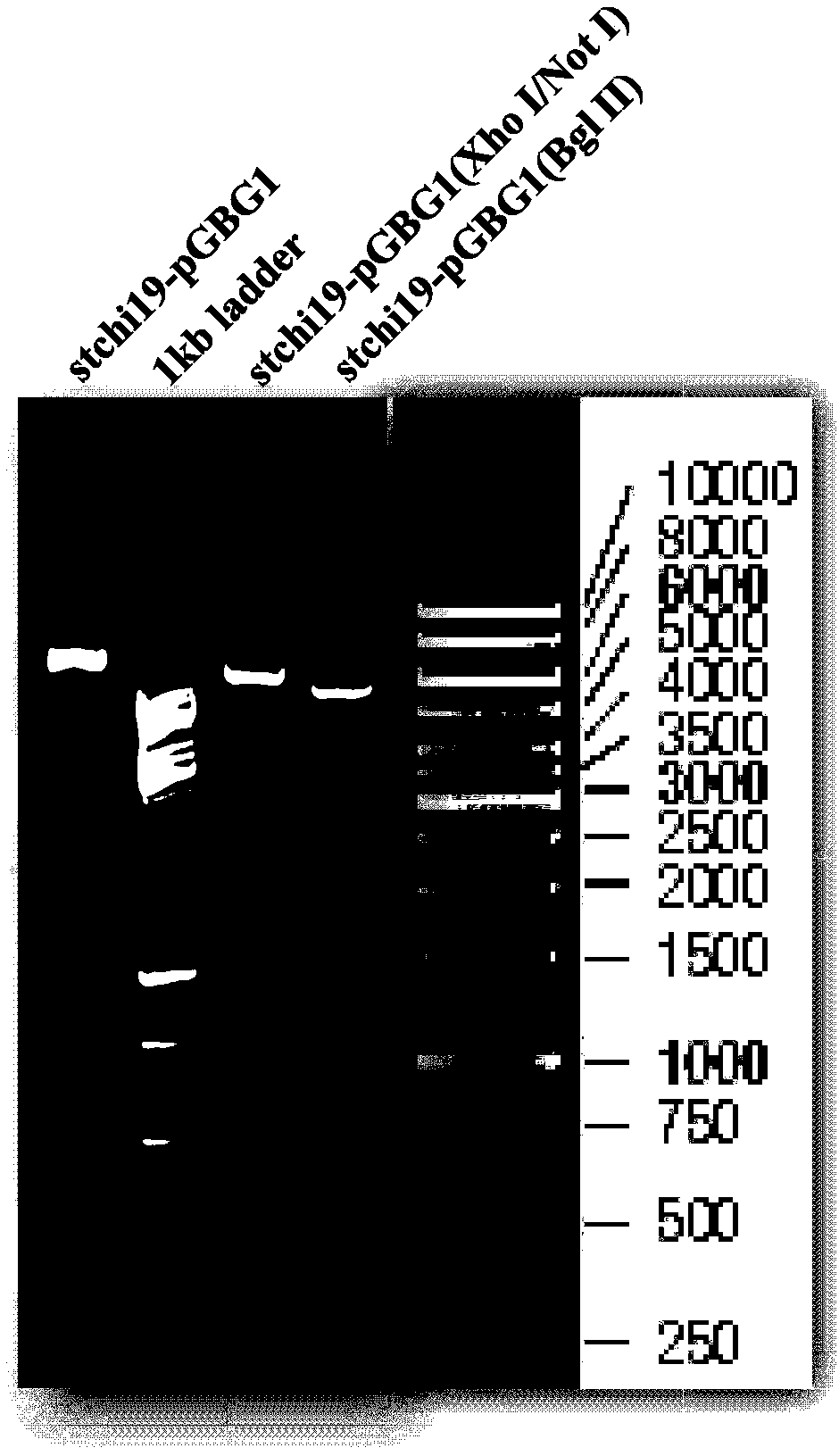
[0040] First, use restriction endonucleases Xho I and Not I to double-enzyme digest the cloning vector containing chitinase gene stchi19 to obtain the target gene fragment, and use the same endonuclease to double-enzyme digest the expression vector pGBG1, recover large fragments. The two recovered products were connected to obtain a recombinant vector named stchi19-pGBG1. In order to confirm that the target chitinase gene has been constructed into the vector, we used Xho I / Not I and Bgl II to carry out double and single digestion of the recombinant vector respectively, and performed agarose gel electrophoresis on the product. The results are as follows: figure 1 Shown: After double enzyme digestion, the target gene fragment appeared between 500bp-750bp, which was consistent with the 690bp fragment of stchi19; after Bgl II digestion, the expected two fragments appeared, followed by the large fra...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3 Screening of Chitinase Pichia Pichia Engineering Bacteria and Preparation of Chitinase
[0042] After the obtained recombinant plasmid stchi19-pGBG1 was linearized by the restriction endonuclease BglII, gel electrophoresis was used to separate and excise the nucleotide fragment containing the gene of interest (such as figure 2 shown in the larger fragment), electroporation introduced into Pichia pastoris GS115, and the recombinant obtained by screening on the histidine auxotrophic MD plate was spread on the BMMY agar plate containing colloidal chitosan (0.5%) for cultivation , from which the monoclonal strain with the largest hydrolytic circle was screened out. A single colony of the screened monoclonal strain was inoculated in 200 mL of BMGY medium, cultured at 30°C and 250 rpm for 48 hours, the supernatant was discarded by centrifugation, and an equal amount of BMMY was added to induce expression. After 24 hours, add methanol to a final concentration of 1%...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com