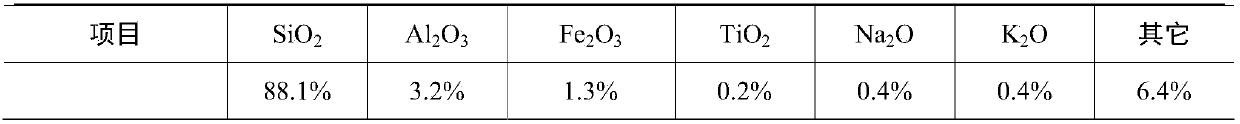
High-ethylene-selectivity catalyst for preparation of low carbon olefins from methanol
A low-carbon olefin and catalyst technology, applied in the field of special catalysts, can solve problems such as difficult operating conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
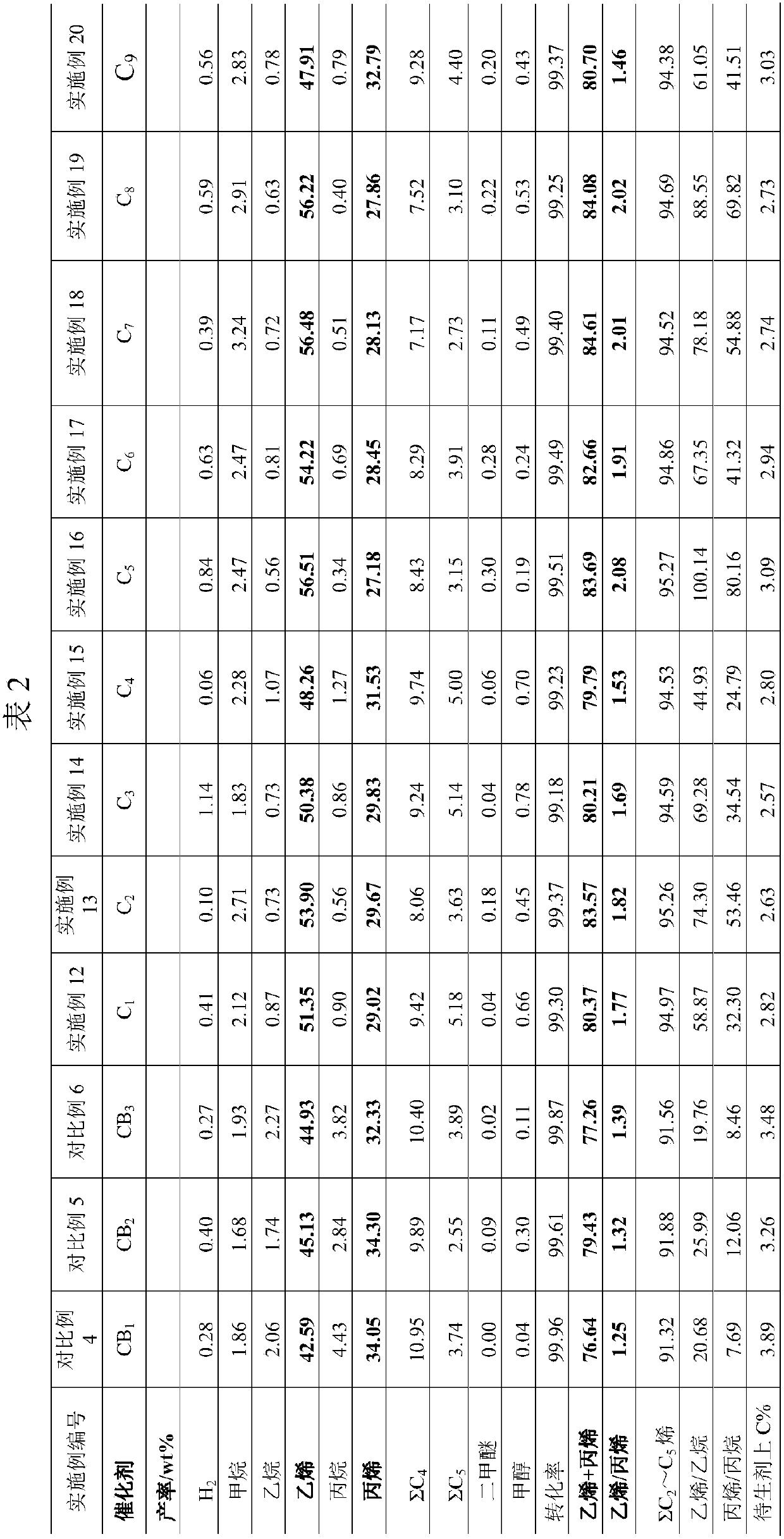
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0063] Put de-cationic water and 10 kg of conventional SAPO molecular sieve (dry basis) into the stirred tank, beating and dispersing into a slurry with a solid content of 25% by weight. Sequentially add a zinc acetate aqueous solution containing 0.273 kg of ZnO and 0.54 kg of P to the slurry 2 O 5 Concentrated phosphoric acid, stir and disperse uniformly, heat up to 55°C and keep the temperature constant for 45 minutes, and then flash dry the mixed slurry. The dried product was calcined at 550°C for 60 minutes to obtain 2.5 wt% Zn modifier (calculated as ZnO) and 5.0 wt% P modifier (calculated as P 2 O 5 Calculated) modified silicon aluminum phosphate (SAPO) molecular sieve KSAPO-01.
Embodiment 2
[0065] Put de-cationic water and 10 kg of conventional SAPO molecular sieve (dry basis) into the stirred tank, beating and dispersing into a slurry with a solid content of 25% by weight. Sequentially add a zinc nitrate aqueous solution containing 0.43 kg ZnO and 0.268 kg P to the slurry 2 O 5 Stir and disperse the ammonium dihydrogen phosphate uniformly, raise the temperature to 55°C and keep the temperature constant for 45 minutes, and then flash dry the mixed slurry. The dried product was calcined at 550°C for 60 minutes to obtain 4.0 wt% Zn modifier (calculated as ZnO) and 2.5 wt% P modifier (calculated as P 2 O 5 Calculated) modified silicon aluminum phosphate (SAPO) molecular sieve KSAPO-02.
Embodiment 3
[0068] Take 5 kg (dry basis) of diatomaceous earth (as non-cohesive inorganic oxide or inorganic hydroxide (E)), be beaten with deionized water and dispersed into a slurry with a solid content of 30% by weight, and pumped into a ball mill for grinding , Until the particle size of more than 90% of the solid matter in the slurry <5.5μm.
[0069] Put 1.8 kg of decationized water, 0.05 kg (dry basis) acidic silica sol (as an inorganic binder), 0.4 kg (dry basis) modified silicon aluminum phosphate (SAPO) molecular sieve KSAPO-01, 0.1 kg in the stirred tank. (Dry basis) diatomaceous earth, 0.25 kg (dry basis) kaolin, 0.02 kg (dry basis) Zn(NO 3 ) 2 .6H 2 O and 0.1 kg (dry basis) pseudo-boehmite (as a binder), beating and dispersing for 120 minutes. Add 0.13 kg of concentrated phosphoric acid and continue beating for 60 minutes. Then, the obtained slurry was spray-dried at an inlet temperature of 500°C and an exhaust gas temperature of 180°C to prepare a molecular sieve KSAPO-01 conta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com