Application of mpla in the preparation of drugs for the prevention and treatment of intestinal damage caused by ionizing radiation
A technology of ionizing radiation and intestinal damage, applied in the field of medicine, to increase the survival time, reduce the apoptosis of intestinal crypt cells, and achieve the effect of safe and convenient medication
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
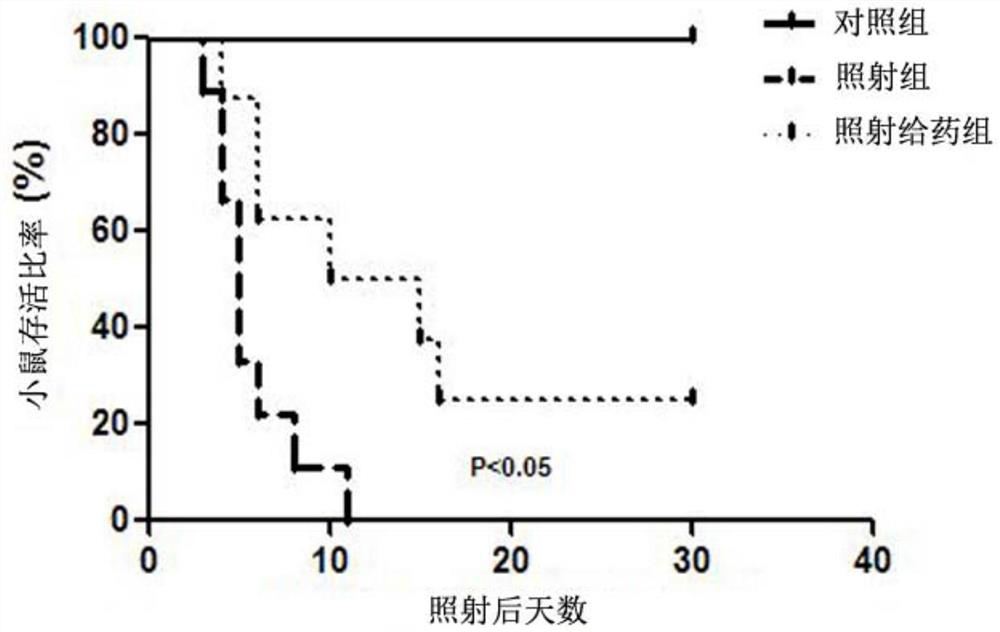
[0030] Firstly, a mouse model of radiation-induced intestinal injury was established. Female C57BL / 6 mice aged 6-8 weeks were selected and randomly divided into three groups: the irradiation group (15Gy) with 8 mice and the MPLA administration group (15Gy+MPLA) 12 hours before irradiation. )8 rats and 8 rats in the control group; 60 Coγ-rays were irradiated to the abdomen of mice once, and the absorbed dose of mice was 15Gy. MPLA (1 μg / mouse in 0.1 ml saline) or saline (0.1 ml / mouse) was delivered to the corresponding groups by intragastric administration. Mice (saline or MPLA pretreated) were observed and recorded every morning and evening for 30 days after radiation exposure. The activity of the mice in the irradiation group decreased significantly one day after irradiation, and the food intake decreased significantly, while the activity of the mice in the MPLA-administered group before irradiation was significantly better than that of the irradiation control group. The su...
Embodiment 2
[0032] (1) The radiation-induced intestinal injury mouse model is the same as that in Example 1;
[0033](2) Feeding of mice: Place the mice in a cage with daily change of litter at 25±1°C to ensure sufficient water and food.
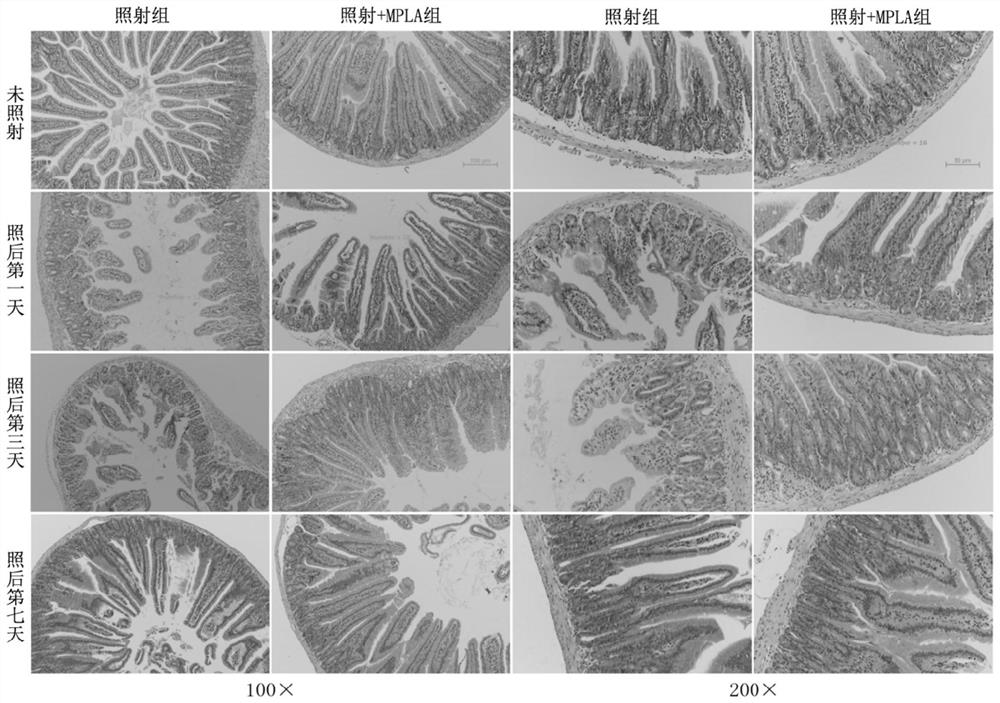
[0034] (3) Female C57BL / 6 mice aged 6-8 weeks were selected and randomly divided into two groups: 8 mice in the irradiation group (15Gy) and 8 mice in the MPLA administration group (15Gy+MPLA) 12 hours before irradiation. MPLA (1 μg / mouse in 0.1 ml saline) or saline (0.1 ml / mouse) was delivered to the corresponding groups by intragastric administration. At different time points after radiation exposure (1 day, 3 days, 7 days), the mice were sacrificed, and the small intestine tissues were taken, fixed, embedded in wax blocks, sectioned and stained with HE. as attached figure 2 As shown, ionizing radiation obviously caused the breakage and shedding of small intestinal villi in mice; the MPLA administration group before irradiation (irradiation + MPLA)...
Embodiment 3
[0036] (1) The radiation-induced intestinal injury mouse model is the same as that in Example 1;
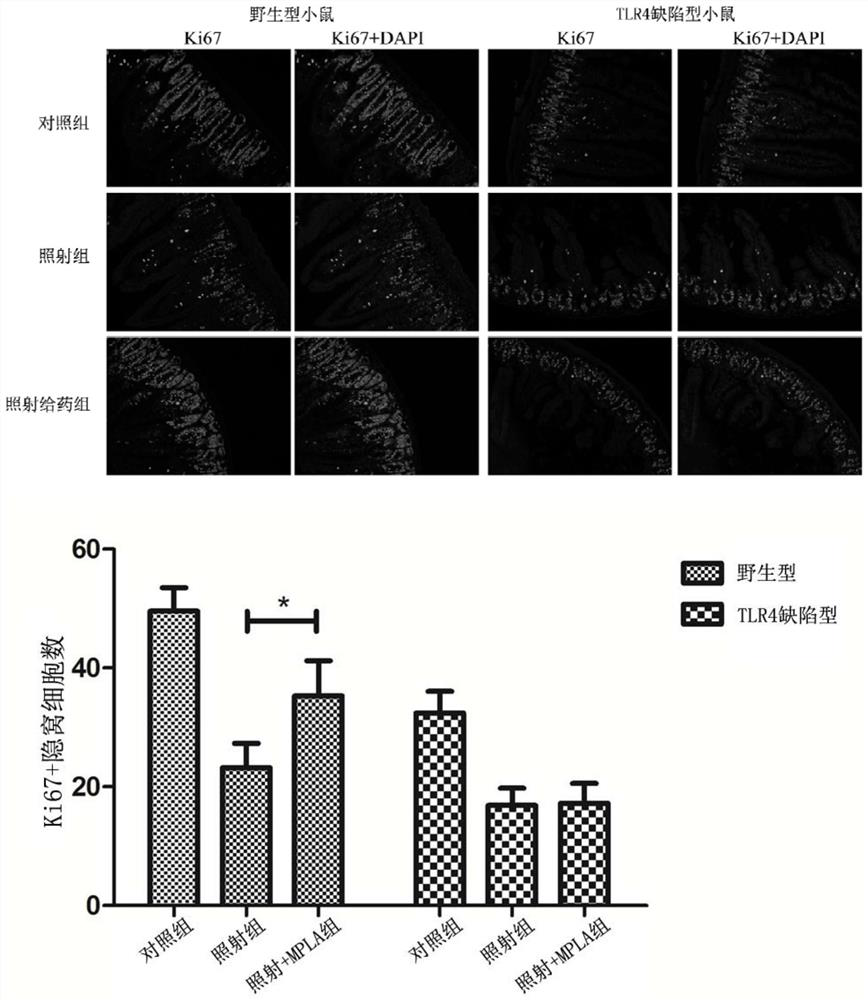
[0037] (2) 6-8 weeks old female C57BL / 6 mice and TLR4-deficient mice were selected and randomly divided into six groups: ①Wild-type mice unirradiated group ②Wild-type mouse abdominal irradiation group (15Gy) ③Wild-type mice Mice were irradiated to MPLA group ④TLR4-deficient mice were not irradiated group ⑤TLR4-deficient mice abdominal irradiation group (15Gy) ⑥Wild-type mice were irradiated to MPLA group. MPLA (1 μg / mouse in 0.1 ml saline) or saline (0.1 ml / mouse) was delivered to the corresponding groups by intragastric administration. The mice were sacrificed 3 days after irradiation, and the small intestine tissues were taken, fixed, embedded in wax blocks, sectioned and immunohistochemically stained with anti-Ki-67 antibody. Ki-67 is one of the marker molecules of cell proliferation. as attached image 3 As shown, the intestinal crypts of wild-type mice in the non-irradiat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com