Developing drug-carrying titanium alloy stent
A titanium alloy, drug-carrying technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve problems such as poor systemic drug effect, and achieve the effects of improving clinical practicability, stable properties, and avoiding adverse reactions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
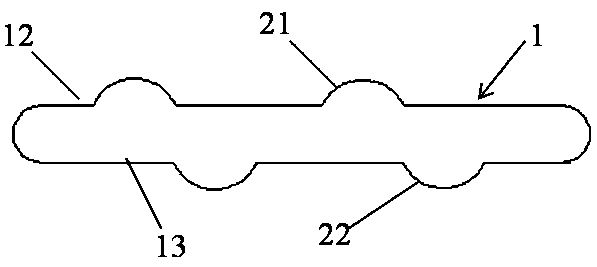
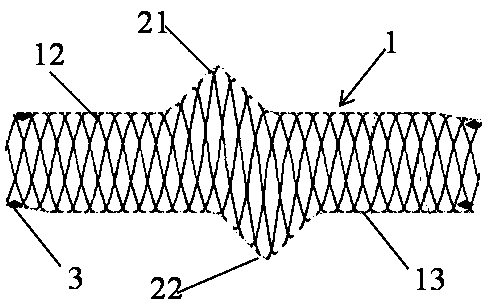
[0041] This embodiment provides a visualized vascular stent, which includes a stent body 1, a visualization structure 3 and an intima, and the stent body 1 is sleeved on the intima. The developing structure 3 is disposed on the support body 1 .
[0042]The stent body 1 is in a hollow tubular structure, and the tube wall is in a hollow mesh structure. The bracket body 1 is divided into a symmetrical upper tube wall 12 and a lower tube wall 13 by the plane where the central axis of the hollow tubular structure is. The stent body 1 in this embodiment can be made of any implantable material in the prior art, such as medical stainless steel or medical polymer material. The diameter of the stent body 1 gradually decreases from the middle to both ends, and the diameter of the two ends is 75%-80% of the diameter of the middle part. In the non-slip vascular stent provided by the present invention, the length of the stent body 1 is 0.5-20 cm, and the diameter of the stent body 1 is 1....
Embodiment 2
[0047] This embodiment provides a glycidyl methacrylate-polylactic acid film, the film is hollow, and the cavity can accommodate guest molecules to increase the contact area with the guest molecules. This glycidyl methacrylate-polylactic acid film is prepared by the following method:
[0048] Weigh polylactic acid and polyethylene glycol respectively according to the mass ratio of 2.3:0.7, disperse them in dimethyl sulfoxide, and heat to 50°C to obtain a polylactic acid mixture; according to the mass of glycidyl methacrylate and polylactic acid Weigh glycidyl methacrylate with a ratio of 0.6:1, and add it to the polylactic acid mixture, stir evenly, and then pass nitrogen gas for 30 minutes to form a nitrogen protection, then add a catalytic amount of azobisisobutyronitrile, and heat up to 60 ℃ and maintained under the protection of nitrogen for free radical polymerization for 20 hours to obtain the casting solution. The casting solution was defoamed and filtered and poured in...
Embodiment 3
[0050] This embodiment provides a kind of method that the hollow glycidyl methacrylate-polylactic acid film diamine grafted in embodiment 2 is mixed with losartan to simultaneously carry out physical and chemical drug loading on losartan, the method includes Follow the steps below:
[0051] Soak the glycidyl methacrylate-polylactic acid film in deionized water, and add tetramethylethylenediamine to the deionized water according to the mass ratio of tetramethylethylenediamine to glycidyl methacrylate-polylactic acid film at 0.1:3. ethylenediamine, and reacted at room temperature for 24 hours to obtain a diamine-grafted glycidyl methacrylate-polylactic acid film. After washing off unreacted tetramethyldiamine with deionized water, soak it in fresh deionized water. The mass ratio of therapeutic formulation to glycidyl methacrylate-polylactic acid film is 0.1:2 Add therapeutic formulation to deionized water and add catalytic amount of 1-ethyl-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbon Diimin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com