Double-phase organic fluorescent materials with relatively strong fluorescence in solid state and liquid state and preparation method thereof
A fluorescent material, solid-state technology, applied in the fields of luminescent materials, fluorescence/phosphorescence, semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, etc., can solve the problems of fluorescence quenching, excited state energy dissipation, limitation, etc., achieves simple operation, simple preparation method, The effect of high fluorescence quantum efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0036] The preparation of compound 3: similar to the synthesis of compound 1, under an inert atmosphere, make compound b in Pd(PPh 3 ) 4 In the presence of a catalyst, react with p-esteryl phenylboronic acid to obtain compound 3.
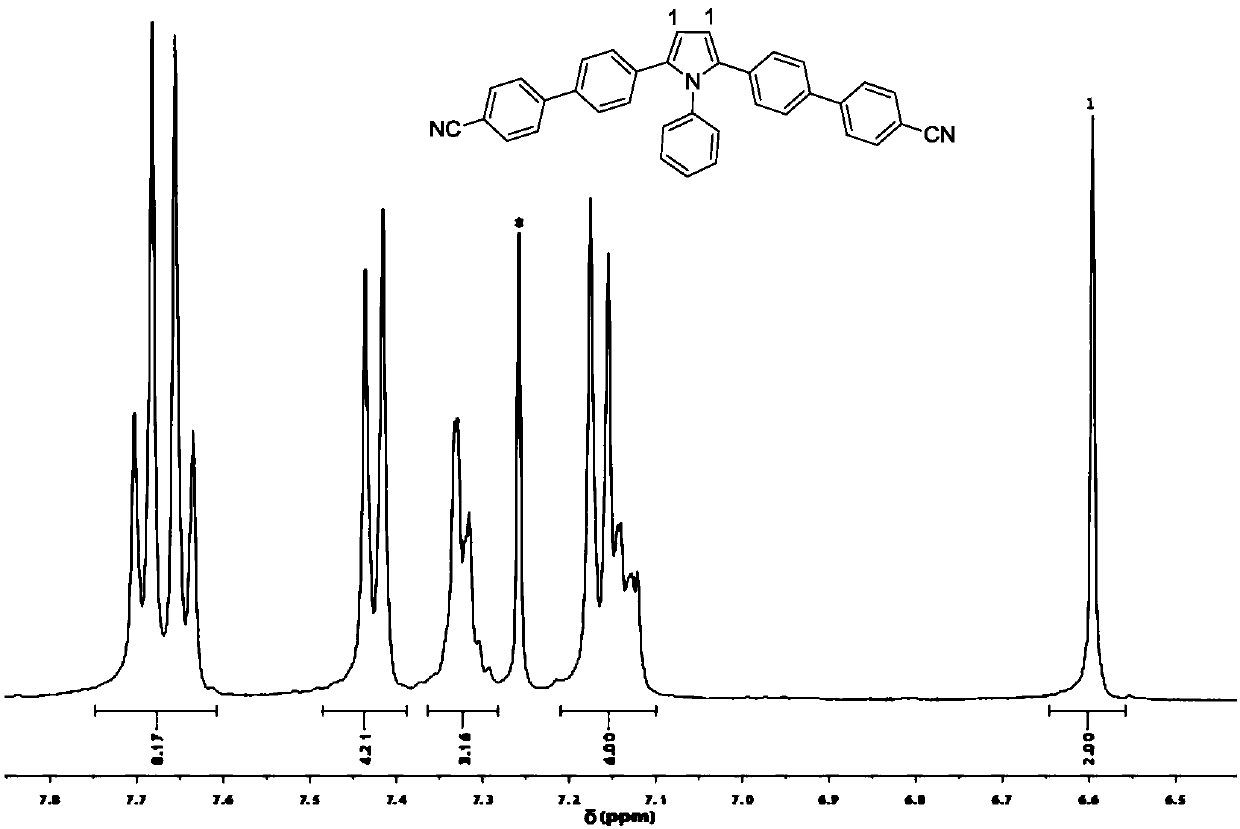
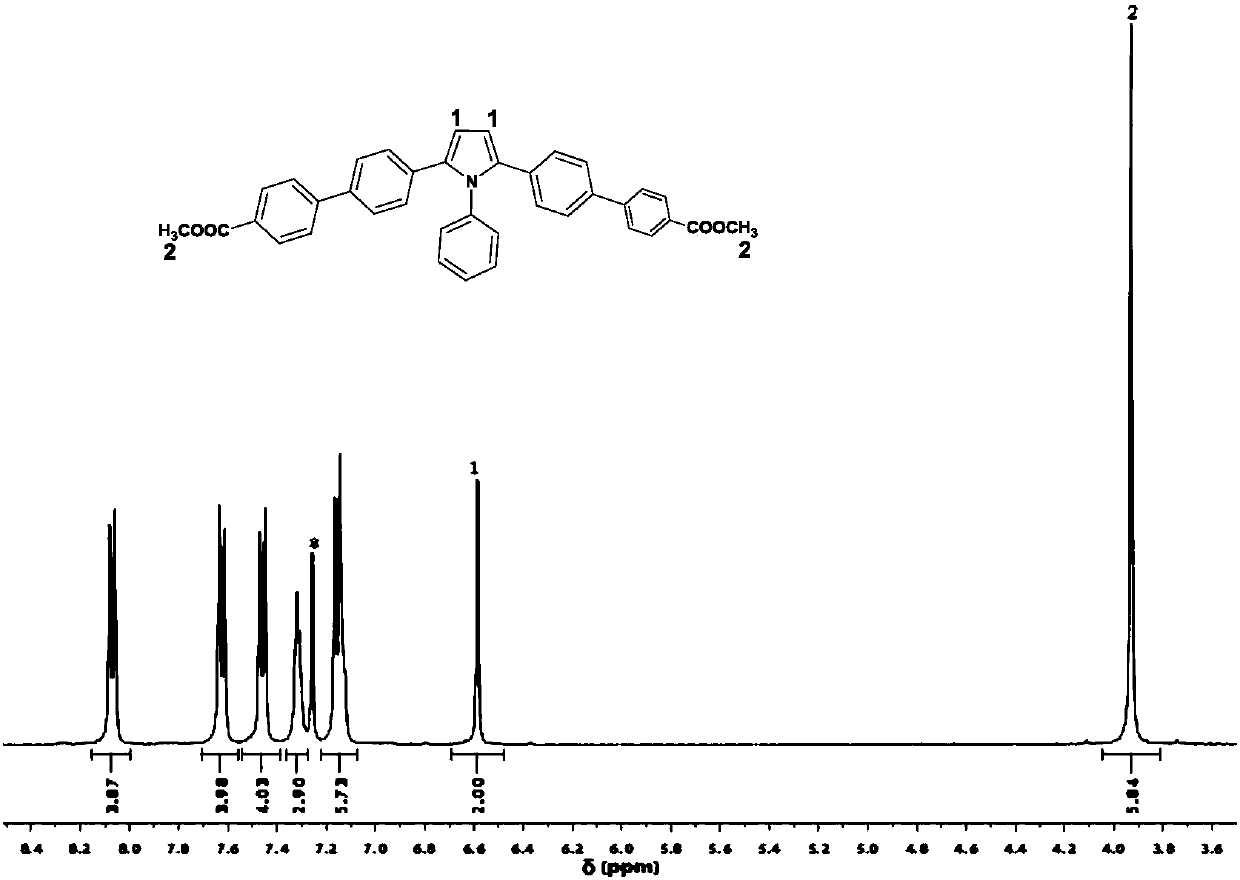
[0037] The fluorescent material synthesized by the invention has strong fluorescent emission in both solid state and solution state, and both the solid state and liquid state fluorescent quantum yields are relatively high. The fluorescent material has different visible fluorescent responses in solvents of different polarities, and has good solvent effect. The preparation method of the fluorescent material is simple, the operation is convenient, and it has potential application prospects in the fields of organic photoelectric materials, biochemical detection, solid-liquid two-phase luminescence and the like.
Embodiment 1
[0039] Embodiment 1: the synthesis of compound b
[0040] The synthesis is divided into two steps:
[0041] (1) The first step is the coupling reaction of p-bromophenylacetylene:
[0042] In a 100mL three-necked flask with an air duct, add 1.50mmol of CuCl, 1.02mmol of N,N,N',N'-tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA) and 110mL of toluene respectively, and air 0.5mL at room temperature h, after stirring evenly, add 27.62 mmol of p-bromophenylacetylene, heat up to 45°C and react for 10 hours, then stop. Then remove toluene, dissolve with appropriate amount of dichloromethane, wash with 5% hydrochloric acid solution and water, remove the solvent after drying the organic phase, and recrystallize the obtained crude product with tetrahydrofuran and n-hexane to obtain 1,4-di-p-bromophenyl 4.2 g of pale yellow needle-like crystals of diacetylene, yield 84%.
[0043] (2) The second step is the synthesis of compound b:
[0044] Add 5.6mmol of 1,4-di-p-bromophenylbutadiyne, 2.8mmol of anil...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Embodiment 2: the synthesis of compound 1
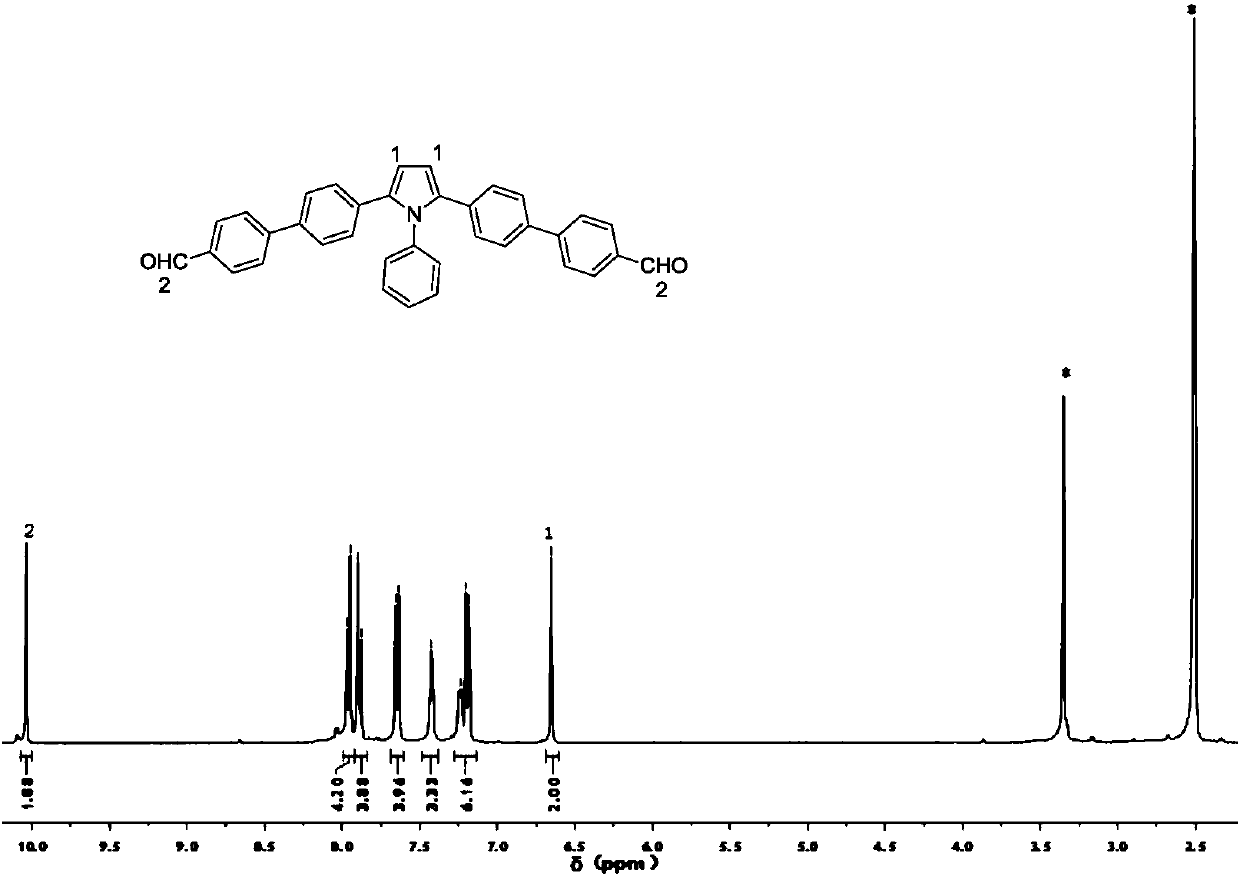
[0046] Add 1.1 mmol of compound b, 2.8 mmol of p-formylphenylboronic acid, 0.06 mmol of tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium and 6.3 mmol of sodium carbonate into a single-port reaction flask, and raise the temperature to 80°C for 12 hours under an inert gas atmosphere. , the resulting crude product was separated by column chromatography using pure dichloromethane as the eluent, and then recrystallized from tetrahydrofuran and n-hexane to obtain 0.31 g of a yellow powder with a yield of 55%; its nuclear magnetic spectrum is shown in the attached figure 1 .
[0047] 1 H NMR (400MHz, DMSO), (δ, TMS, ppm) 10.04(s, 2H), 7.96(d, J=8.3 Hz, 4H), 7.89(d, J=8.2Hz, 4H), 7.64(d, J=8.4Hz, 4H), 7.42(s, 3H), 7.21(t, J=11.0Hz, 6H), 6.65(s, 2H).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com