Semiconductor thin-film electrolyte fuel cell and manufacturing method thereof
A fuel cell and semiconductor technology, applied in fuel cells, battery electrodes, circuits, etc., can solve the problems that the working mechanism of batteries has not been widely understood, and achieve adjustable and controllable electrolyte film thickness, low price, and thin electrolyte film thickness Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
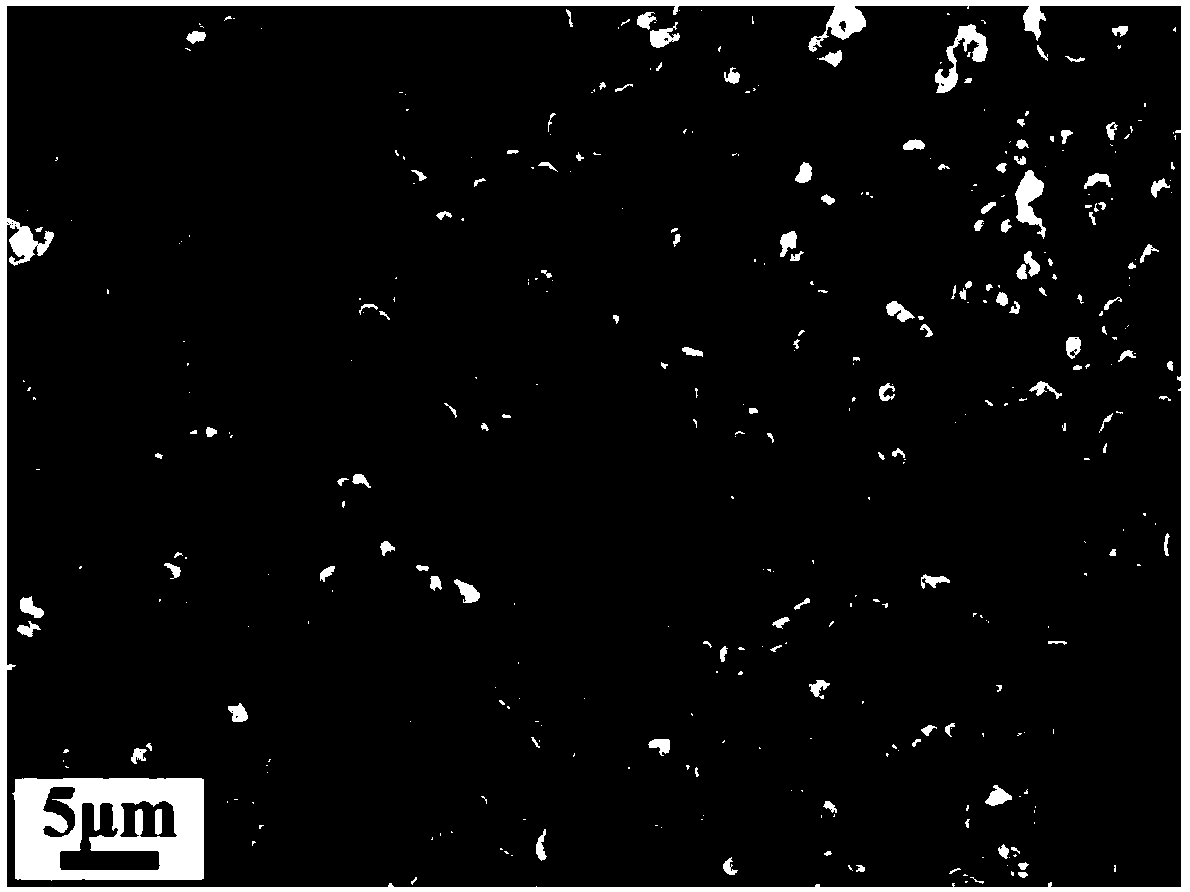
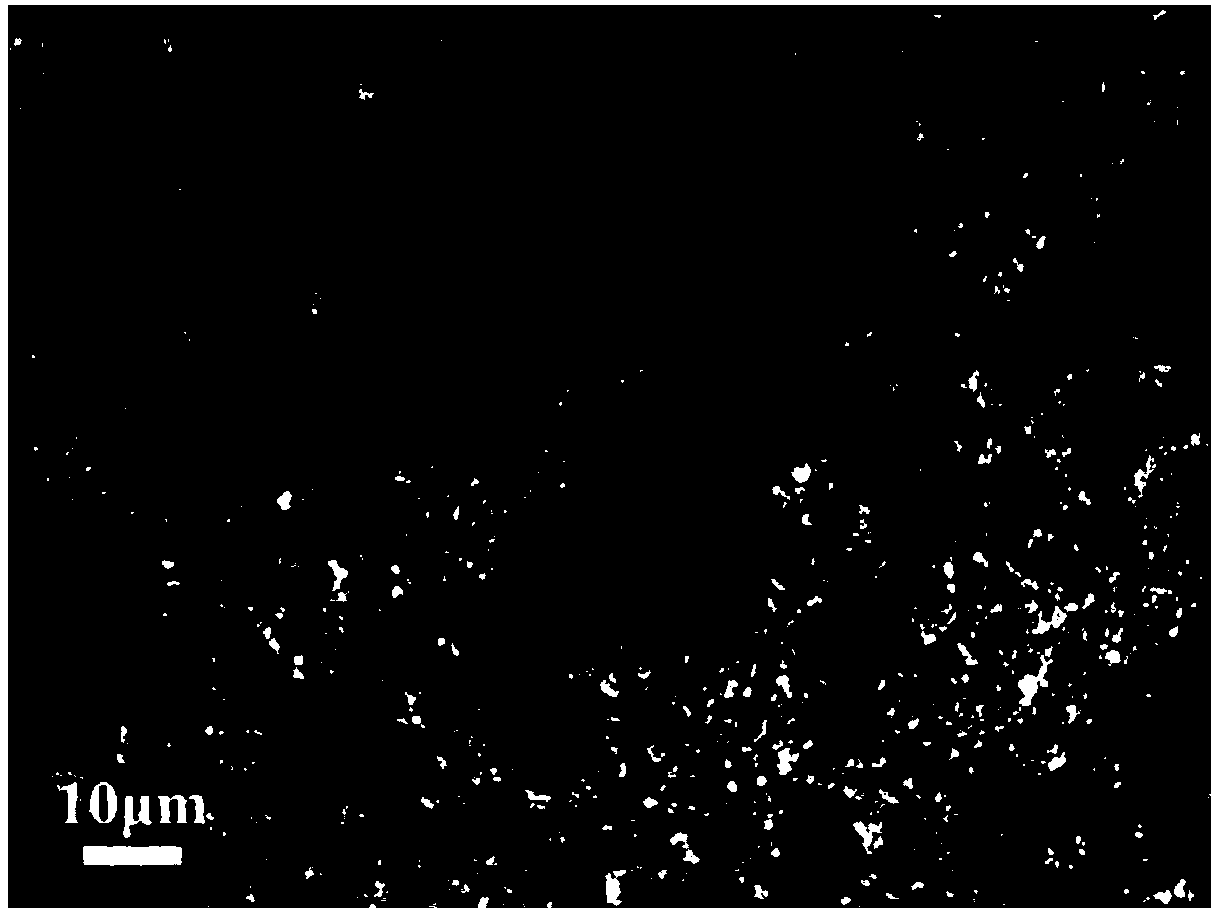
[0028] Powdered anode material LiNi 0.8 co 0.2 o 2 (Here Al y , y=0) is pressed into a 1500 micron thick ceramic sheet; then, on the anode ceramic sheet obtained above, utilize magnetron sputtering to prepare a layer of 500 nanometer thick film-like cerium oxide electrolyte layer; then, the powdered cathode Material La 0.6 Sr 0.4 co 0.2 Fe 0.8 o 3 A ceramic sheet with a thickness of 500 microns is pressed with nickel foam as a support; finally, the surface where the cathode material of the above-mentioned cathode ceramic sheet is located and the electrolyte layer on the anode ceramic sheet are pressed together and sintered at a high temperature at 500 degrees Celsius to obtain a semiconductor thin film electrolyte type The fuel cell.
Embodiment 2
[0030] Powdered anode material LiNi 0.8 co 0.15 Al 0.05 o 2 Pressed into a 100-micron-thick ceramic sheet; then, on the anode ceramic sheet obtained above, a 50-nanometer thick film-like titanium dioxide electrolyte layer was prepared by using a sol-gel method; then, the powdered cathode material LiNi 0.8 co 0.15 Al 0.05 o 2 A ceramic sheet with a thickness of 1000 microns is pressed with nickel foam as a support; finally, the surface where the cathode material of the above-mentioned cathode ceramic sheet is located and the electrolyte layer on the anode ceramic sheet are pressed together and sintered at a high temperature at 650 degrees Celsius to obtain a semiconductor thin film electrolyte type The fuel cell.
Embodiment 3
[0032] Powdered anode material LiNi 0.8 co 0.15 Al 0.05 o 2 mixed with samarium-doped cerium oxide with a weight ratio of 50wt.%, and pressed into a ceramic sheet with a thickness of 800 microns; then, a 2000-nm-thick thin-film zinc oxide electrolyte layer was prepared on the anode ceramic sheet obtained above by casting method ; Next, the powdery cathode material LiNi 0.8 co 0.15 Al 0.05 o 2 Mix it with samarium-doped cerium oxide with a weight ratio of 50wt.%, and press it into a ceramic sheet with a thickness of 50 microns with nickel foam as a support; finally, press the surface where the cathode material of the above-mentioned cathode ceramic sheet is located and the electrolyte layer on the anode ceramic sheet Carry out high-temperature sintering together at 600 degrees Celsius to obtain a semiconductor thin-film electrolyte fuel cell.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com