Method of recycling phosphorus in concentrated acid residue from wet process phosphoric acid and co-producing dihydrate gypsum and sodium fluosilicate
A technology of sodium fluorosilicate and dihydrate gypsum, which is applied in the fields of fluorosilicic acid, chemical instruments and methods, and silicon halide compounds, and can solve problems such as difficult disposal of waste residue, low efficiency of solid phase settlement, and large loss of phosphoric acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
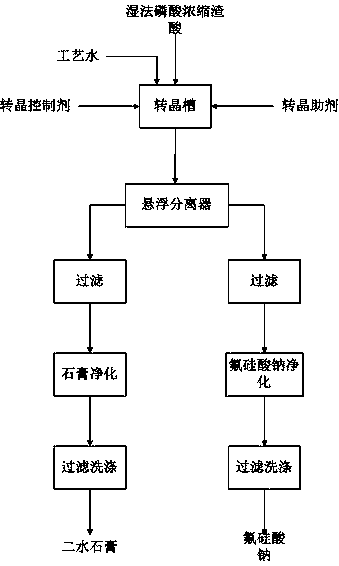
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
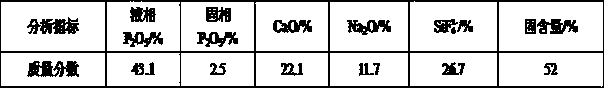
[0037] The composition of the concentrated slag acid of raw material wet-process phosphoric acid used in the present embodiment is as follows:
[0038]
[0039]The wet-process phosphoric acid concentrated slag acid and water with the above indicators are prepared at a mass ratio of 1:0.5, and added to the crystal conversion tank. Then add concentrated sulfuric acid with 1.5% slag acid content, 1% calcium sulfate dihydrate, 8% fluosilicic acid, 0.005% diammonium phosphate, crystal transformation temperature 55°C, stirring line speed 0.7m / s, crystal transformation time 120 minutes. After the crystal conversion is completed, the material enters the suspension separator, the stirring line speed is 0.5m / s, and the material residence time is 120 minutes. The slurry discharged from the bottom of the suspension separator is filtered and separated, and the filter residue is mixed with water at a ratio of 1:1. The pH of the gypsum slurry is adjusted to 3 with sulfuric acid. The puri...
Embodiment 2
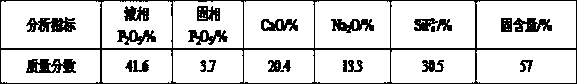
[0041] The composition of the concentrated slag acid of raw material wet-process phosphoric acid used in the present embodiment is as follows:
[0042]
[0043] The wet-process phosphoric acid concentrated slag acid and water with the above indicators are prepared at a mass ratio of 1:1, and added to the crystal conversion tank. Then add 3% concentrated sulfuric acid, 2% calcium sulfate dihydrate, 12% fluosilicic acid, 0.005% ethoxylated alkyl sulfate sodium salt, 0.01% fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate For salt, the crystallization temperature is 60°C, the linear stirring speed is 0.8m / s, and the crystallization time is 110 minutes. After the crystal conversion is completed, the material enters the suspension separator, the stirring line speed is 0.6m / s, and the material residence time is 140 minutes. The slurry discharged from the bottom of the suspension separator is filtered and separated, and the filter residue is mixed with water at a ratio of 1:1.2....
Embodiment 3
[0045] The composition of the concentrated slag acid of raw material wet-process phosphoric acid used in the present embodiment is as follows:
[0046]
[0047] The wet-process phosphoric acid concentrated slag acid and water with the above indicators are prepared at a mass ratio of 1:1.2, and added to the crystal conversion tank. Then add concentrated sulfuric acid with 4% slag acid content, 1.5% calcium sulfate dihydrate, 0.01% diammonium phosphate, 0.01% triethanolamine dodecylbenzenesulfonate, crystal transition temperature 55°C, stirring line speed 0.8m / s, the crystallization time is 100 minutes. After the crystal conversion is completed, the material enters the suspension separator, the stirring line speed is 0.6m / s, and the material residence time is 130 minutes. The slurry discharged from the bottom of the suspension separator is filtered and separated, and the filter residue is mixed with water at a ratio of 1:1.6. The pH of the gypsum slurry is adjusted to 5 wit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com