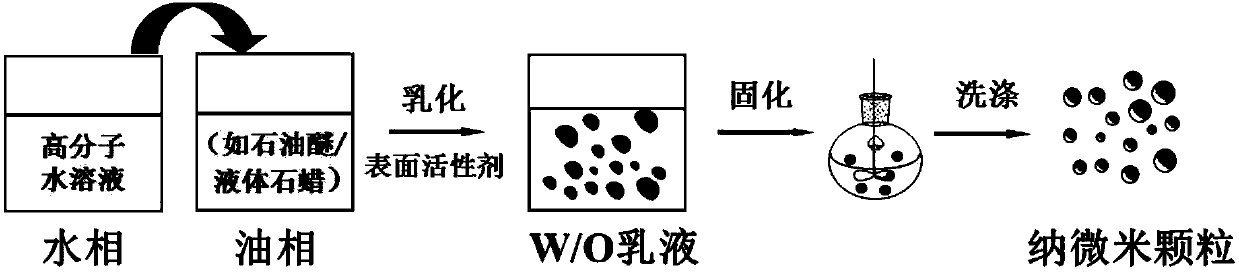
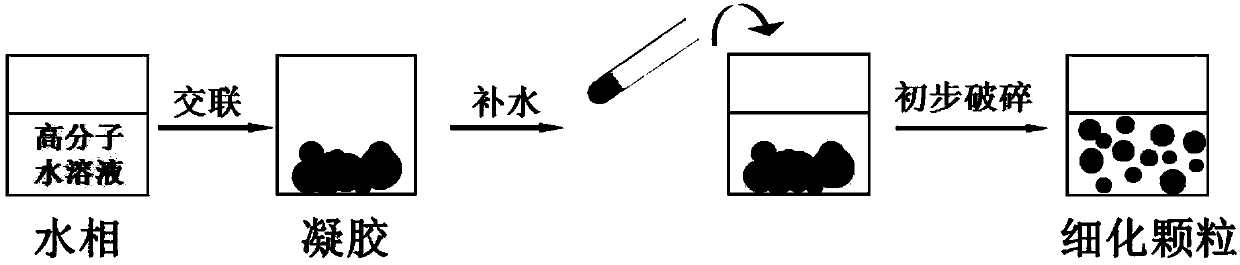
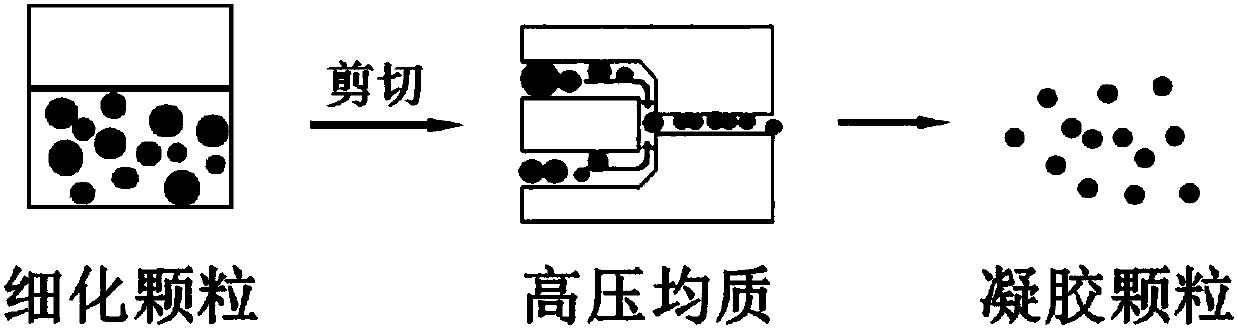
Polymer gel particles, preparation method thereof, composite gel particles containing polymer gel particles and application of composite gel particles
A technology of polymer gel and composite gel, which is applied in the field of biomedical polymer materials, can solve the problems of low drug loading of nanoparticles, decreased effective concentration, and easy burst release.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-3
[0088] Embodiment 1-3 provides chitosan derivative gel particle, adopts high-pressure homogeneous method to prepare, and concrete steps are as follows:
[0089] The chitosan derivative was dissolved in 8 mL of water phase, and stirred magnetically at room temperature and 500 rpm for 3 h until completely dissolved. Under the condition of ice bath, 2 mL of ion crosslinking agent solution was added dropwise to the above chitosan derivative solution, magnetically stirred at 500 rpm for 5 min, and then solidified in an oil bath for a period of time to form a hydrogel. Add water to the above hydrogel to 25mL, and preliminarily crush and refine it. Then add the preliminarily broken hydrogel mixture into the liquid storage cup of the high-pressure homogenizer, adjust the pressure and the number of cycles, and shear the chitosan derivative gel particles by the high-pressure homogenizer.
[0090] The kind and concentration of chitosan derivatives, the kind of aqueous phase, the kind an...
Embodiment 4-11
[0097] Embodiment 4-11 provides composite chitosan derivative gel particles, which are prepared by high-pressure homogeneous method, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0098] The chitosan derivative was dissolved in 8 mL of water phase, and stirred magnetically at room temperature and 500 rpm for 3 h until completely dissolved. Under the condition of ice bath, 2 mL of ion crosslinking agent solution was added dropwise to the above chitosan derivative solution, magnetically stirred at 500 rpm for 5 min, and then solidified in an oil bath for a period of time to form a hydrogel. Add functional substances and water to the above hydrogel to 25mL, and preliminarily crush and refine it. Then add the preliminarily broken hydrogel mixture into the liquid storage cup of the high-pressure homogenizer, adjust the pressure and the number of cycles, and shear the composite chitosan derivative gel particles by the high-pressure homogenizer.
[0099] The kind and concentration of chit...
Embodiment 12-14
[0110] Embodiments 12-14 provide chitosan derivative gel particles, which are prepared by microporous membrane emulsification method, and the specific steps are as follows:
[0111] The chitosan derivative was dissolved in 8 mL of water phase, and stirred magnetically at room temperature and 500 rpm for 3 h until completely dissolved. Under the condition of ice bath, 2 mL of ion crosslinking agent solution was added dropwise to the above chitosan derivative solution, magnetically stirred at 150 rpm for 10 min, and then solidified in an oil bath for a period of time to form a hydrogel. Add the water phase to the above hydrogel to 25mL, and preliminarily crush and refine it. Then add the preliminary broken hydrogel mixture into the liquid storage bottle of the rapid membrane emulsifier, press the microporous polytetrafluoroethylene membrane with nitrogen under a certain pressure, and obtain chitosan derivative gel particles after repeated membrane passage .
[0112] The kind a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| polydispersity index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com