Preparation method of novel cobalt-free material for high-strength aviation part
A high-strength, high-strength component technology, which is applied in the field of cobalt-free new materials for aviation high-strength components, can solve the problem of limiting the use of cobalt-free maraging steel, the high brittleness of maraging steel, and the huge gap in mechanical properties. problem, achieve the effect of reducing the shortage of cobalt resources, increasing the strength and reducing the production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
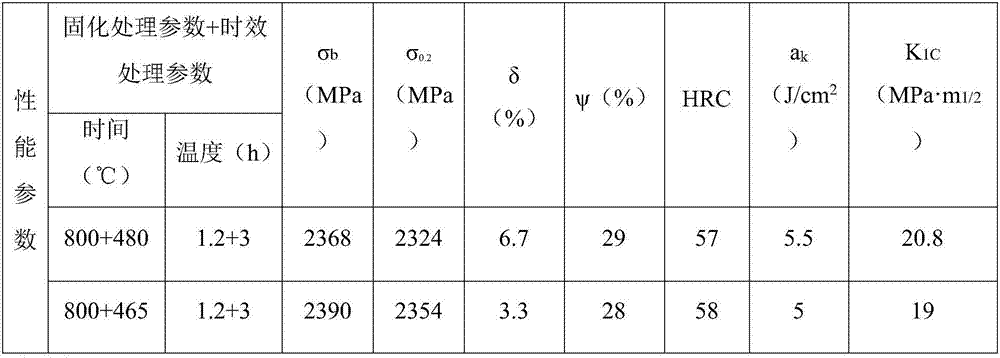
[0025] A method for preparing a cobalt-free new material for aviation high-strength parts in the present invention, the weight percentage (wt.%) of each component of the cobalt-free new material for aviation high-strength parts: nickel (Ni): 19.1, molybdenum ( Mo): 4.4, titanium (Ti): 2.63, carbon (C) 0.0012, aluminum (Al) 0.02, silicon (Si) ≤ 0.01, manganese (Mn) 0.01, sulfur (S) 0.0012, phosphorus (P) 0.0016, oxygen (O) 0.0029, nitrogen (N) 0.001, iron (Fe) and unavoidable impurities in the balance. The steel ingot is subjected to vacuum induction melting and vacuum arc remelting process steps to obtain the second smelting blank, the impurities and harmful elements in the raw material are reduced to the stated weight percentage, and the second smelting blank is homogenized at 1200°C for 12 hours, The obtained initial steel ingot is forged at 1000°C, and the initial billet is hot-rolled at 1200°C, and rolled into a test billet and a mid-stage ingot through multiple passes, an...
Embodiment 2
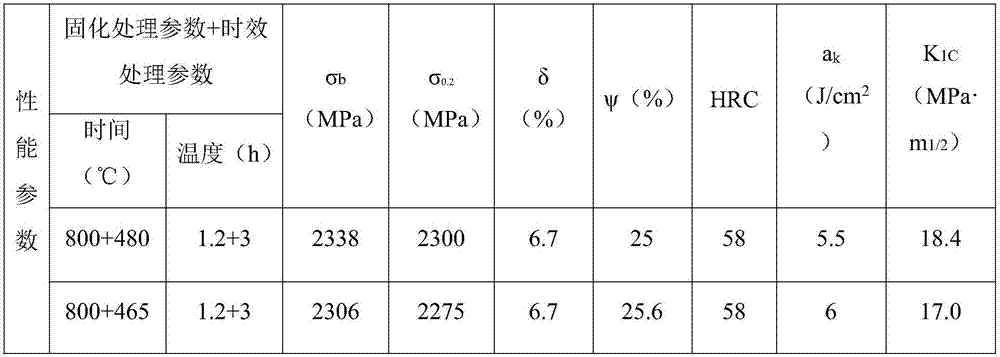
[0029] The weight percentage (wt.%) of each component of the cobalt-free new material for aviation high-strength parts: nickel (Ni): 18.8, molybdenum (Mo): 5.39, titanium (Ti): 2.59, carbon (C) 0.0038, Aluminum (Al) 0.01, silicon (Si) ≤ 0.01, manganese (Mn) 0.01, sulfur (S) 0.0006, phosphorus (P) 0.0023, oxygen (O) 0.0018, nitrogen (N) 0.001, the balance of iron (Fe) and unavoidable impurities. Through the same processing and heat treatment process as in Example 1, the mechanical properties of the cobalt-free new material for aviation high-strength parts obtained are as shown in table 2:
[0030] Table 2
[0031]
Embodiment 3
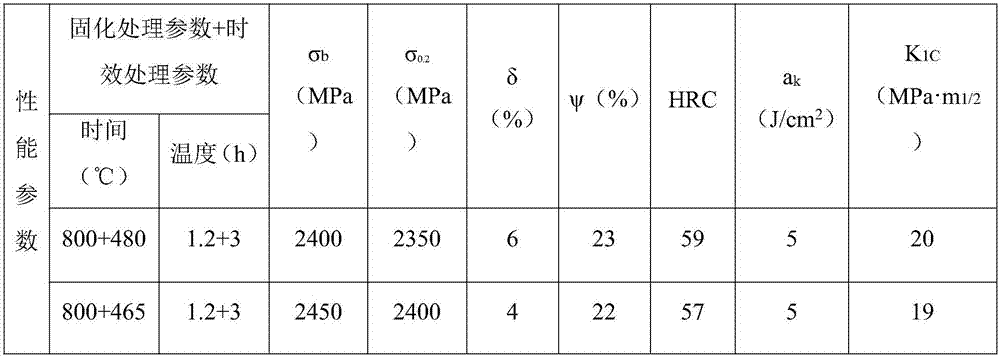
[0033]The weight percentage (wt.%) of each component of the cobalt-free new material for aviation high-strength parts: nickel (Ni): 17.0, molybdenum (Mo): 5.0, titanium (Ti): 3.2, carbon (C) 0.0015, Aluminum (Al) 0.009, silicon (Si) ≤ 0.01, manganese (Mn) ≤ 0.01, sulfur (S) 0.0018, phosphorus (P) 0.0020, oxygen (O) 0.0015, nitrogen (N) 0.001, the balance of iron (Fe ) and unavoidable impurities. Through the same processing and heat treatment process as in Example 1, the mechanical properties of the cobalt-free new material for aviation high-strength parts obtained are as shown in table 3:
[0034] table 3
[0035]
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com