Method for recycling boron carbide from sapphire ground waste materials
A technology for grinding waste and sapphire, applied in chemical instruments and methods, carbon compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of volatile organic matter, lengthy process, and inability to achieve, and achieve the effect of reducing pollutant emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] The grinding waste of a sapphire glass cover in Nanjing was used as the grinding waste of sapphire.
[0050] Because the sapphire grinding waste is in the form of mixed slurry, it can be filtered and dried at 100°C for 6 hours, and then sampled to detect its chemical composition. The results are shown in Table 1.
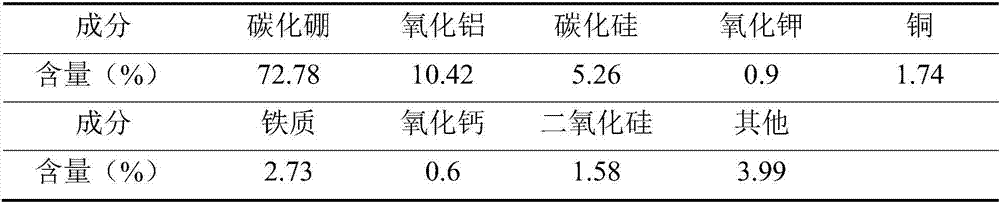
[0051] Table 1 Main composition of sapphire grinding waste
[0052]
[0053] The method for recycling boron carbide from sapphire grinding waste in this embodiment will be described in detail below.
[0054] First, pass the sapphire grinding waste through a 200-mesh standard sieve to remove large particles of sand and stones, and then filter and dry; then, use a magnetic separation belt to remove iron impurities; the third step, use concentrated hydrochloric acid with a volume ratio of 1:1 Mix it with concentrated nitric acid to prepare an acidizing medium, add the dried sapphire grinding waste after removing iron impurities into the acidizing tank, seal ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] The mixed grinding waste from a new material processing factory in Changzhou was used as the sapphire grinding waste.
[0063] Because the sapphire grinding waste is in the form of mixed slurry, it can be filtered and dried at 100°C for 6 hours, and then sampled to detect its chemical composition. The results are shown in Table 3.
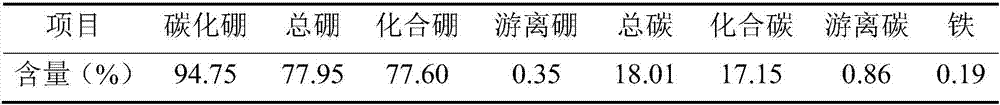
[0064] Table 3 Main composition of sapphire grinding waste
[0065]
[0066] The method for recycling boron carbide from sapphire grinding waste in this embodiment will be described in detail below.
[0067] First, pass the sapphire grinding waste through a 200-mesh standard sieve to remove large particles of sand and stones, and then filter and dry; then, use a magnetic separation belt to remove iron impurities; the third step, use concentrated hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid as the acidification medium , together with the dried sapphire grinding waste after removing iron impurities, was added to the acidification tank, a...
Embodiment 3
[0075] A waste abrasive from a sapphire processing enterprise in Chongqing was used as sapphire grinding waste.
[0076] Because the sapphire grinding waste is in the form of mixed slurry and mixed with other irrelevant impurities, it can be sieved with a 200-mesh standard sieve to remove large particles of impurities and fibers, and then dry the undersize at 100°C for 10 hours , sampling and testing chemical composition, the results are shown in Table 5.
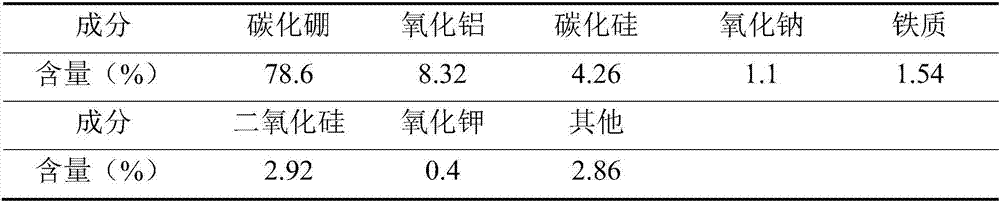
[0077] Table 5 Main composition of sapphire grinding waste
[0078]
[0079] The method for recycling boron carbide from sapphire grinding waste in this embodiment will be described in detail below.
[0080] First, the sapphire grinding waste is passed through a 200-mesh standard sieve to remove large particles of sand, fibers, plastics and other sundries, then filter and dry; then, use a magnetic separation belt to remove iron impurities; the third step is to use a volume ratio of 1: Mix 1 concentrated sulfuric acid a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com