A single matrix negative thermal expansion white light phosphor and its sintering synthesis method
A negative thermal expansion, phosphor technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, luminescent materials, climate sustainability, etc., can solve problems such as decomposition, water absorption, mechanical properties, material phase transition, etc., to achieve sufficient reaction, smooth surface, reaction Simple process effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
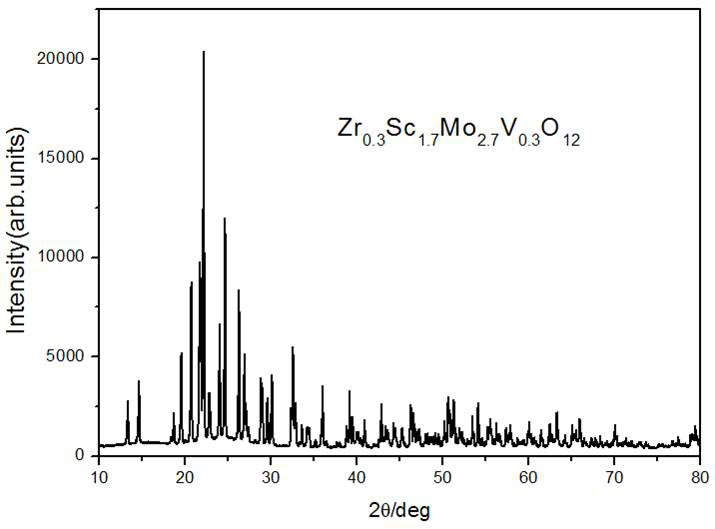
[0036] Analytical reagent ZrO 2 、Sc 2 o 3 、MoO 3 , V 2 o 5 Weigh the materials according to the molar ratio of 0.3:0.85:2.7:0.15, mix them evenly in an agate mortar, add absolute ethanol and grind for 2 h; press under a uniaxial pressure of 300 MPa to make a diameter of 10 mm and a height of about 6 mm Cylindrical sample; set a low-temperature tube furnace at 770°C, put the corundum crucible containing the sample into the tube furnace at the sintering temperature, sinter in normal pressure air for 3 hours, and cool naturally in air to room temperature to obtain the product. For the phase analysis of the XRD pattern corresponding to the product, see figure 1 , figure 1 The XRD results showed that the pure phase of Zr was formed 0.3 sc 1.7 Mo 2.7 V 0.3 o 12 , after structure refinement, it is determined that the prepared material is an orthorhombic phase structure with space group Pbcn(60).
Embodiment 2
[0038] The difference from Example 1 is that the sintering time is 4 h; other steps are the same as in Example 1.
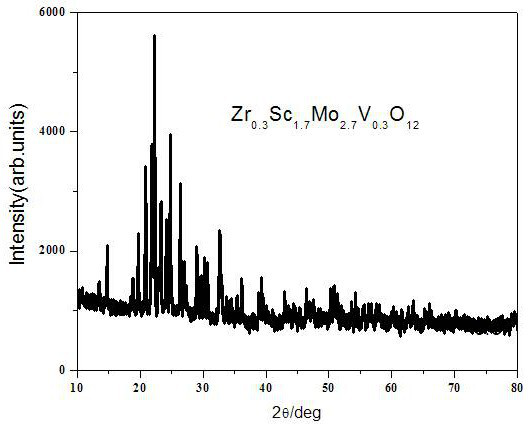
[0039] For the phase analysis of the XRD pattern corresponding to the product, see figure 2 , figure 2 The XRD results showed that the pure phase of Zr was formed 0.3 sc 1.7 Mo 2.7 V 0.3 o 12 , after structure refinement, it is determined that the prepared material is an orthorhombic phase structure with space group Pbcn(60).
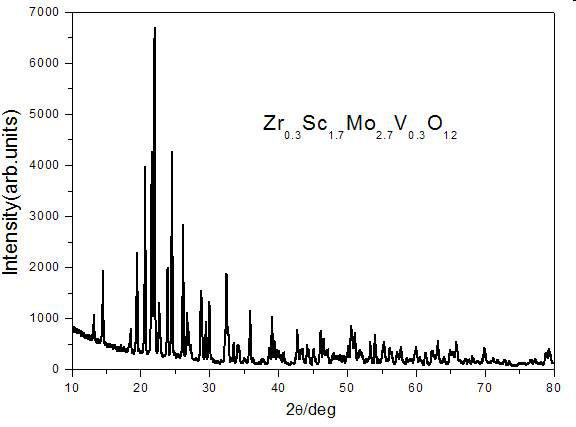
[0040] During the research and development process of the inventor, the inventor found that the molar ratio of the raw materials has a very important influence on the phase composition of the product during sintering by the solid-state method. A comparison example is given here to illustrate, but not exhaustively.
Embodiment 3
[0046] (1), in molar ratio, according to ZrN 2 o 7 :Sc(NO 3 ) 3 :(NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 O: NH 4 VO 3 =0.3:1.7:(2.7 / 7):0.3 Weigh the raw material, and (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 O and NH 4 VO 3 Placed in beaker A, ZrN 2 o 7 and Sc(NO 3 ) 3 Place in beaker B, add deionized water whose mass is 25 times the sum of raw materials in their respective beakers to beakers A and B, and stir for 3 hours with a magnetic stirrer;
[0047] (2) Slowly add the uniformly stirred solution in beaker A to the solution in beaker B while stirring. After stirring at a constant temperature of 80°C for 3 hours, add a molar amount of ZrN 2 o 7 , Sc(NO 3 ) 3 , (NH 4 ) 6 Mo 7 o 24 4H 2 O and NH 4 VO 3 Citric acid C with 0.02 times the sum of moles 6 h 8 o 7 As complexing agent, use concentrated NH 3 ·H 2 O (mass concentration 30%) adjusted the pH of the system to 11, and continued to stir at 80°C for 24 hours to obtain a transparent colloid (i.e. sol);
[0048] (3) Put ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com