Serratia marcescens as well as separation method and application thereof
A Serratia marcescens, separation method technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of unsafe aquatic animals, high control costs, etc., achieve the effect of reducing pesticide residues and good insecticidal effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Isolation and reinfection experiment of Serratia marcescens
[0047] Collected from the park and immersed in 75% ethanol for 10 seconds to sterilize the surface of the worm body. Under sterile conditions, the tissue in the cavity was taken as a material, and it was ground into a homogenate, and sterile ddH was added. 2 0.5ml, get 100 μ l and be coated on the LB solid medium plate, cultivate 12-16h at 37 ℃, pick single bacterium colony and purify and obtain Serratia marcescens bacterial strain LS-1;
[0048]Described LB solid culture medium consists of: sodium chloride 10.0g, peptone 10.0g, yeast extract 5.0g, agar powder 15g, distilled water 1000ml;
[0049] Inoculate the strain LS-1 into the LB medium, culture it on a shaker at 37°C and 180 rpm for 2 days, obtain the bacterial suspension of the bacterial strain LS-1, and adjust the concentration of the bacterial suspension to 10 8 cfu / ml, the reinfection experiments were carried out on healthy Chilo suppressalis larva...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Identification of strains
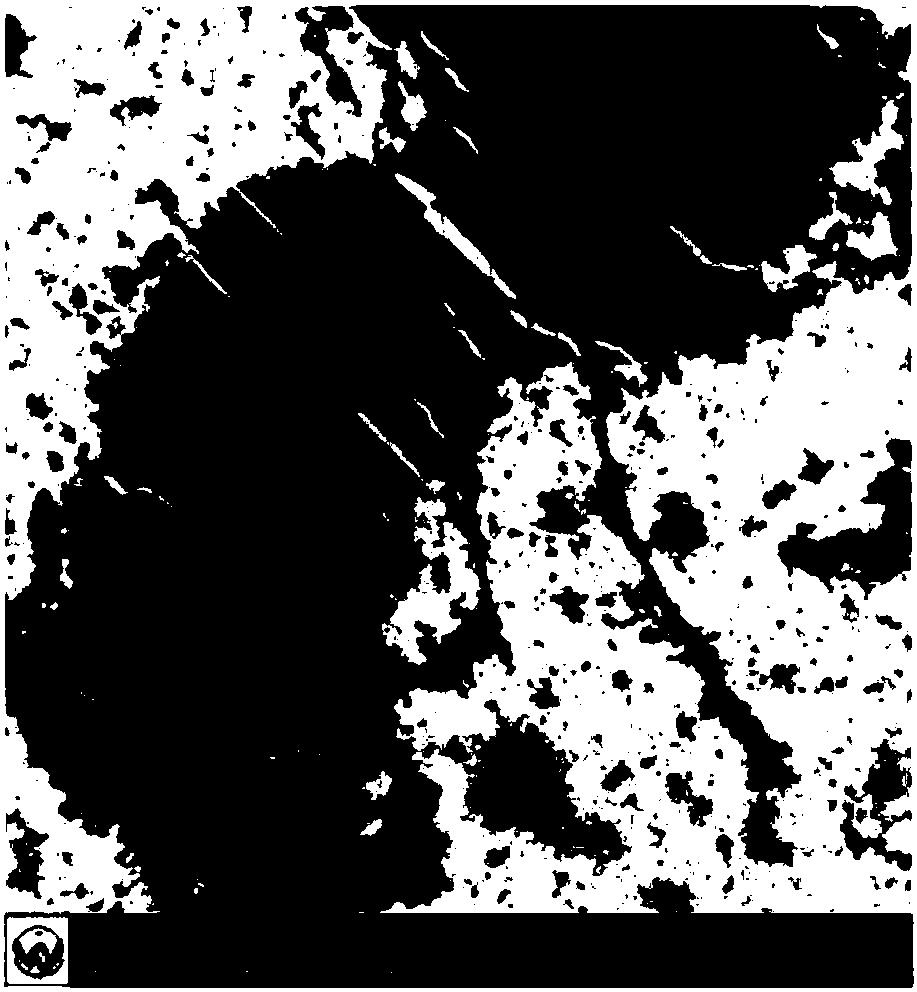
[0053] Morphological analysis of strains: strain LS-1 was inoculated on LB solid medium and cultured at a constant temperature of 37°C for 14 hours. Observe the shape, size and color of single colonies: strain LS-1 was short rod-shaped, without spores, with fluorescence, Gram Negative staining, perigene flagella, motile (see Figure 1). After 14h on the LB solid medium, the bacterial colonies are round, smooth and moist, with neat edges and raised surfaces (see figure 2 ), there is no difference in color between 28°C and 37°C constant temperature culture;
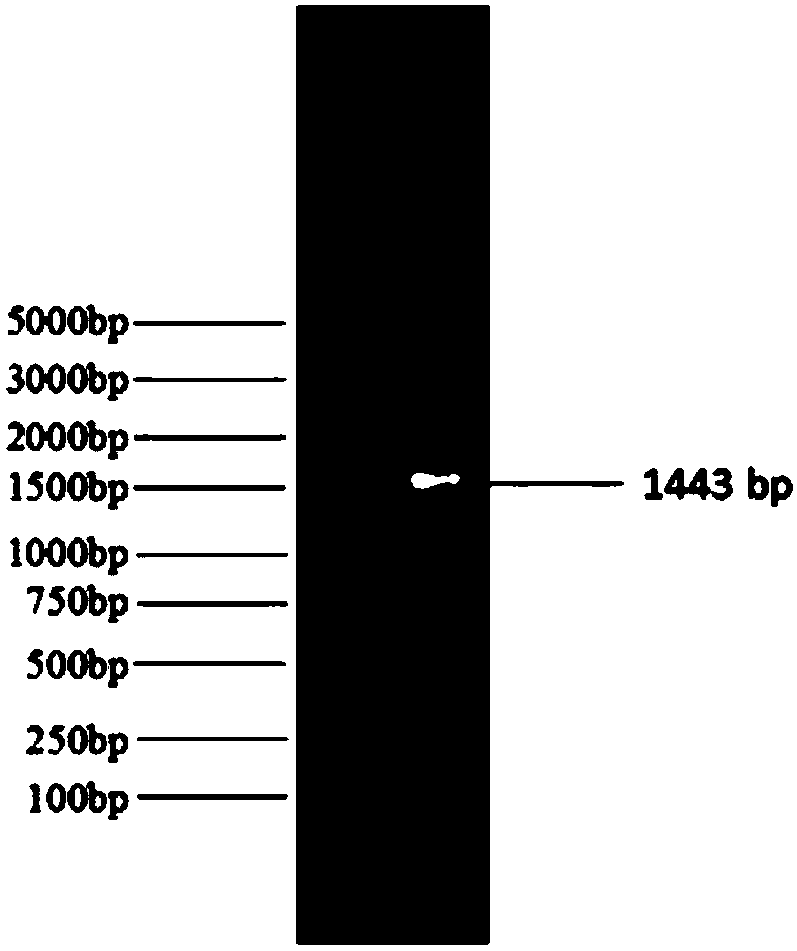
[0054] 16S rDNA sequence determination: Inoculate the strain LS-1 into LB liquid medium, culture it on a shaker at 37°C and 180 rpm for 2 days, obtain the bacterial suspension of the strain LS-1, centrifuge at 1000 rpm for 10 min, take the supernatant, and carry out DNA extraction. Universal primers F27 and R1492 were used for PCR amplification of 16S rDNA from the genomic DNA of strain ...
Embodiment 3
[0064] Determination of Toxicity to Cinnamomum moth
[0065] Inoculate the identified representative strains in 5mL of ordinary LB broth medium, culture in a shaker (180rpm) at 37°C for 12h to activate the strains, take 1ml from the activated bacterial suspension and inoculate into 250ml LB liquid medium After cultivating on a shaker (180rpm) at 28°C for 16h, the concentration of the bacterial solution was determined to be 3.38×10 by the colony counting method. 8 cfu / ml concentration for later use.
[0066] Infection test of C. camphora: Negative control worms were fed with ordinary LB broth medium, and artificial infection experiments were carried out on healthy C. camphorae respectively, and the test was repeated 3 times. Get the same batch of Cinnamomum camphorii and culture them in groups in the laboratory. After three days, they are still healthy as test worms. After processing the camphor leaves, test insects; make the test insects feed naturally (equivalent to inocula...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com