Zirconium-niobium-titanium dental implant material high in strength and low in elastic modulus and preparation method of zirconium-niobium-titanium dental implant material
A dental implant and low elastic modulus technology, which is applied in the field of medical oral materials, can solve the problems of limited application range of implant materials and high density of pure niobium, so as to avoid stress shielding effect, reduce segregation and coarse grains, The effect of the modulus of elasticity on ease
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
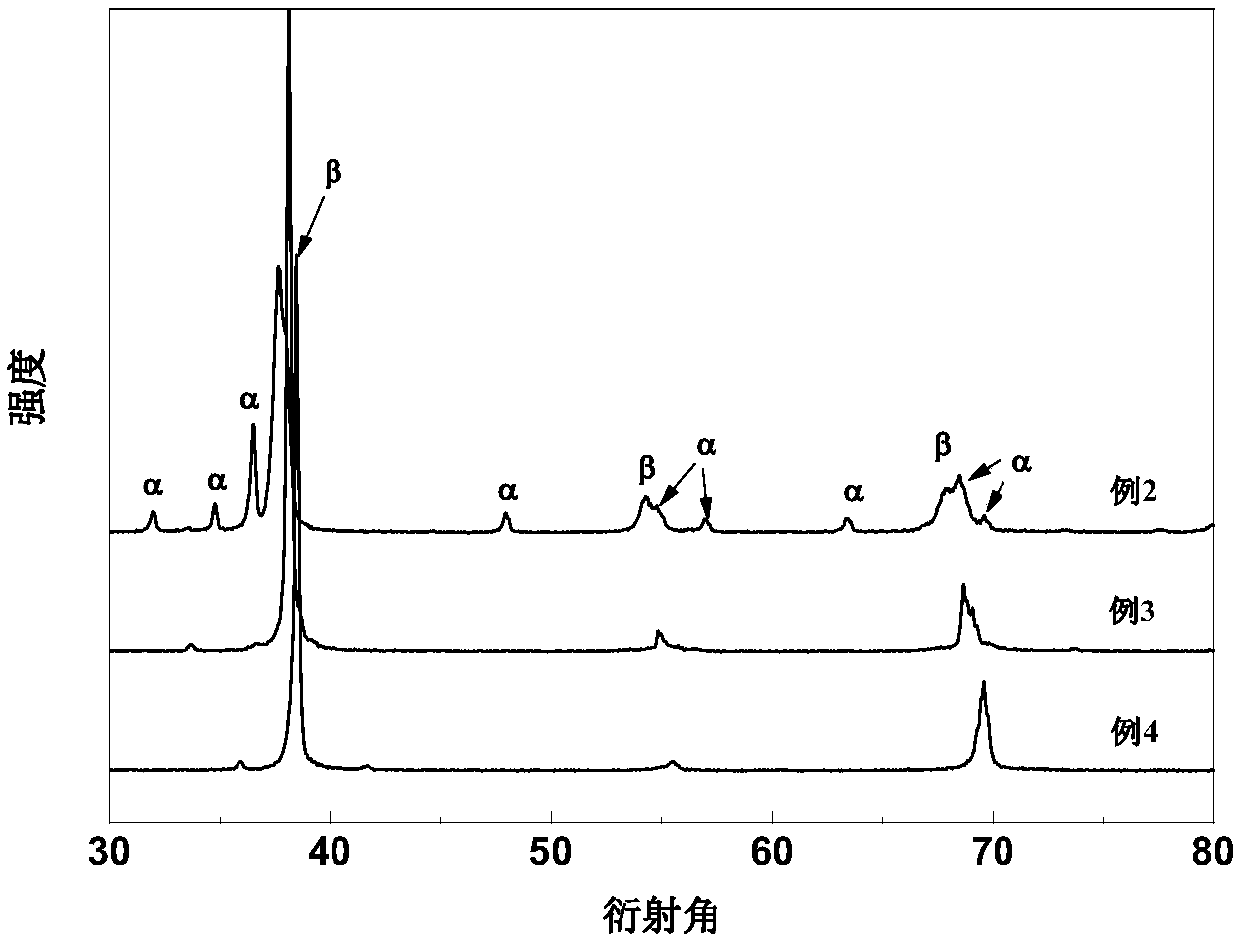
[0033] The atomic ratio of zirconium, niobium and titanium in the high-strength and low-elastic modulus zirconium-niobium-titanium dental implant material is (1:5:8) to (4:5:2).
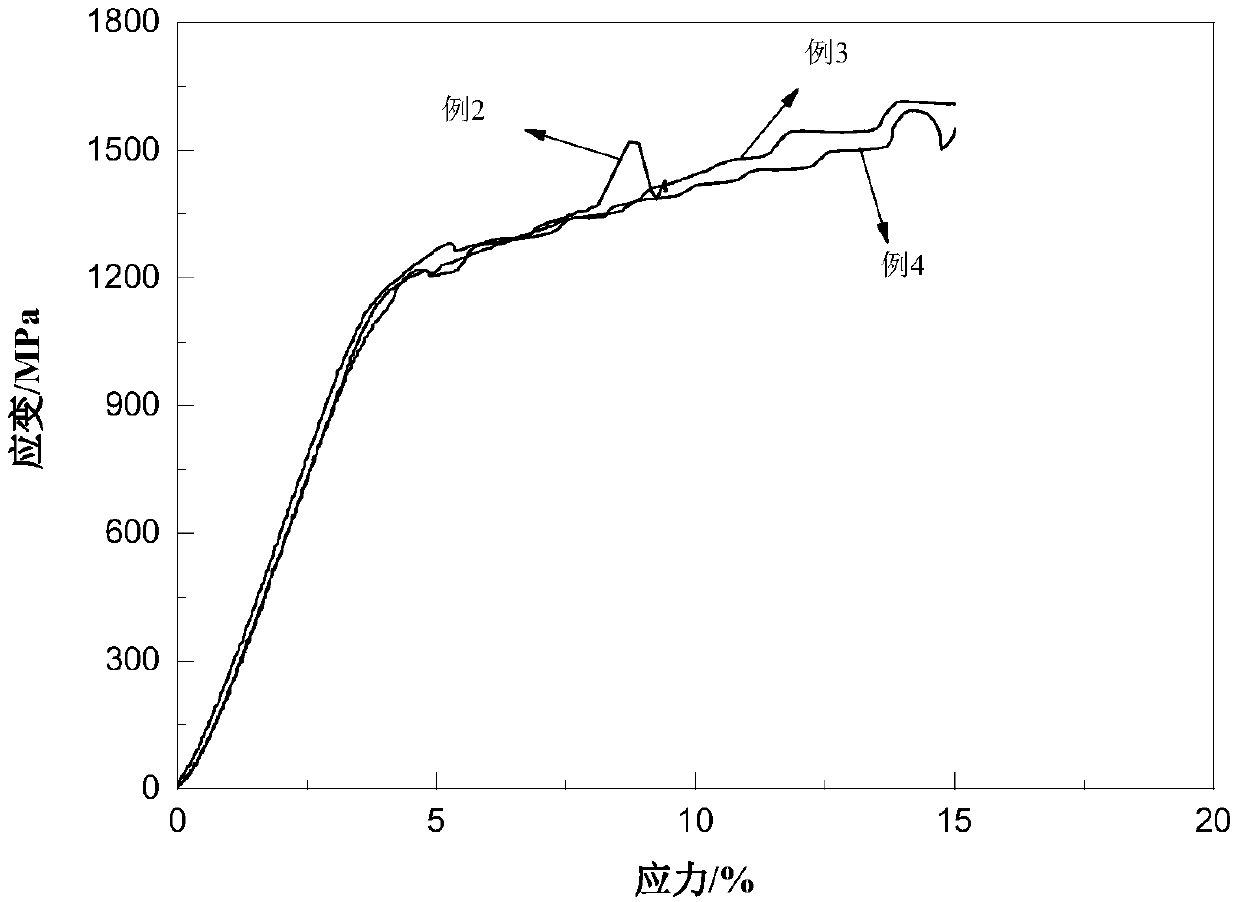
[0034] Wherein, the particle size of the zirconium powder in the high-strength low-elastic modulus zirconium-niobium-titanium dental implant material is 1-14 μm, the particle size of the niobium powder is 1-25 μm, and the particle size of the titanium powder is 1-16 μm. The compressive strength of the high-strength and low-elastic modulus zirconium-niobium-titanium dental implant material is 1111-1280 MPa, the elastic modulus is 32-41 GPa, and the relative density is 90%-95%.
Embodiment 2
[0036] The method for the high-strength low-elastic modulus zirconium-niobium-titanium dental implant material described in embodiment 1 comprises the following steps:
[0037] 1. According to the ratio of zirconium powder, niobium powder and titanium powder atomic ratio of 5:8:6, weigh 46.973g zirconium powder, 78.288g niobium powder and 31.315g titanium powder with a balance. The oxygen content of the powder is required to be less than 0.1%, carbon The content is less than 0.03%. The zirconium-niobium-titanium composite powder is obtained by ball milling zirconium powder, niobium powder and titanium powder.
[0038] 2. The zirconium-niobium-titanium composite powder obtained after ball milling was pressed and formed under a press. Each sample weighed 6g and was formed under a pressure of 300MPa. There was no edge drop and corner drop, and the surface of the green compact was smooth.
[0039] 3. Place the compacted sample in a quartz crucible, put it in a vacuum furnace for s...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The method for the high strength specific elastic modulus zirconium niobium titanium dental implant material described in embodiment 1 comprises the following steps:
[0044] 1. According to the atomic ratio of zirconium powder, niobium powder and titanium powder of 3:8:9, weigh 29.941g of zirconium powder, 74.851g of niobium powder and 44.911g of titanium powder with a balance. The oxygen content of the powder is required to be less than 0.1%, carbon The content is less than 0.03%, and the tantalum-zirconium composite powder is obtained after ball milling the tantalum powder and the zirconium powder.
[0045] 2. The zirconium-niobium-titanium composite powder obtained after ball milling was pressed and formed under a press. Each sample weighed 5g and was formed under a pressure of 250MPa. There was no edge or corner loss, and the surface of the green compact was smooth.
[0046] 3. Place the compacted sample in a tungsten crucible, put it into a vacuum furnace for sint...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com