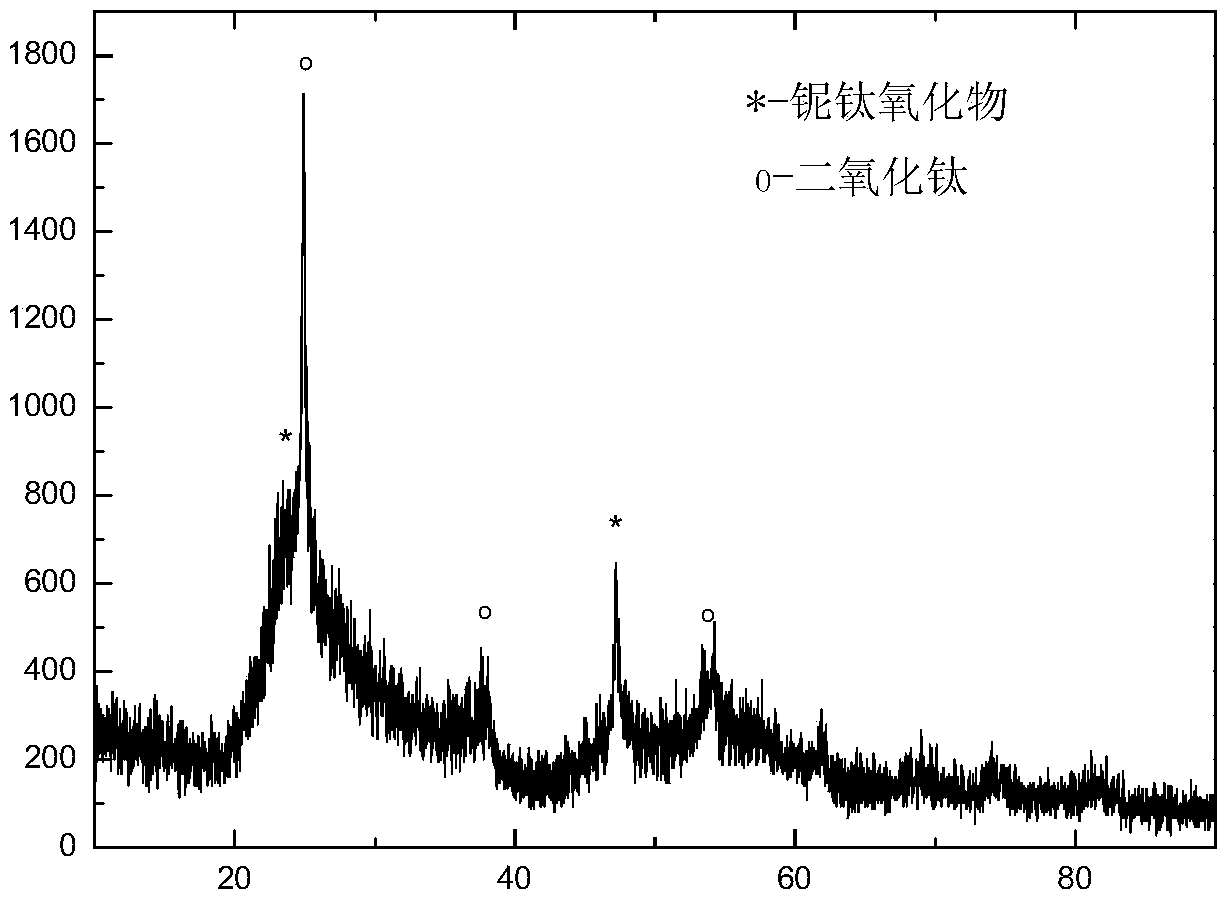
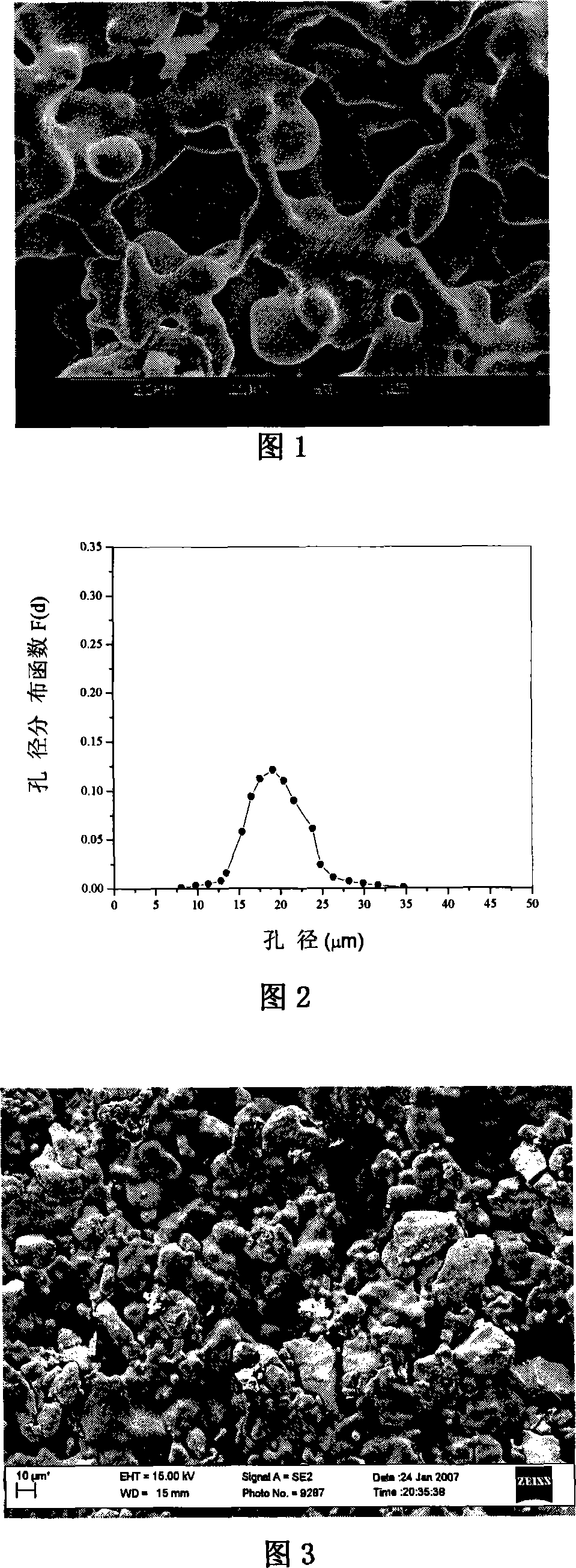
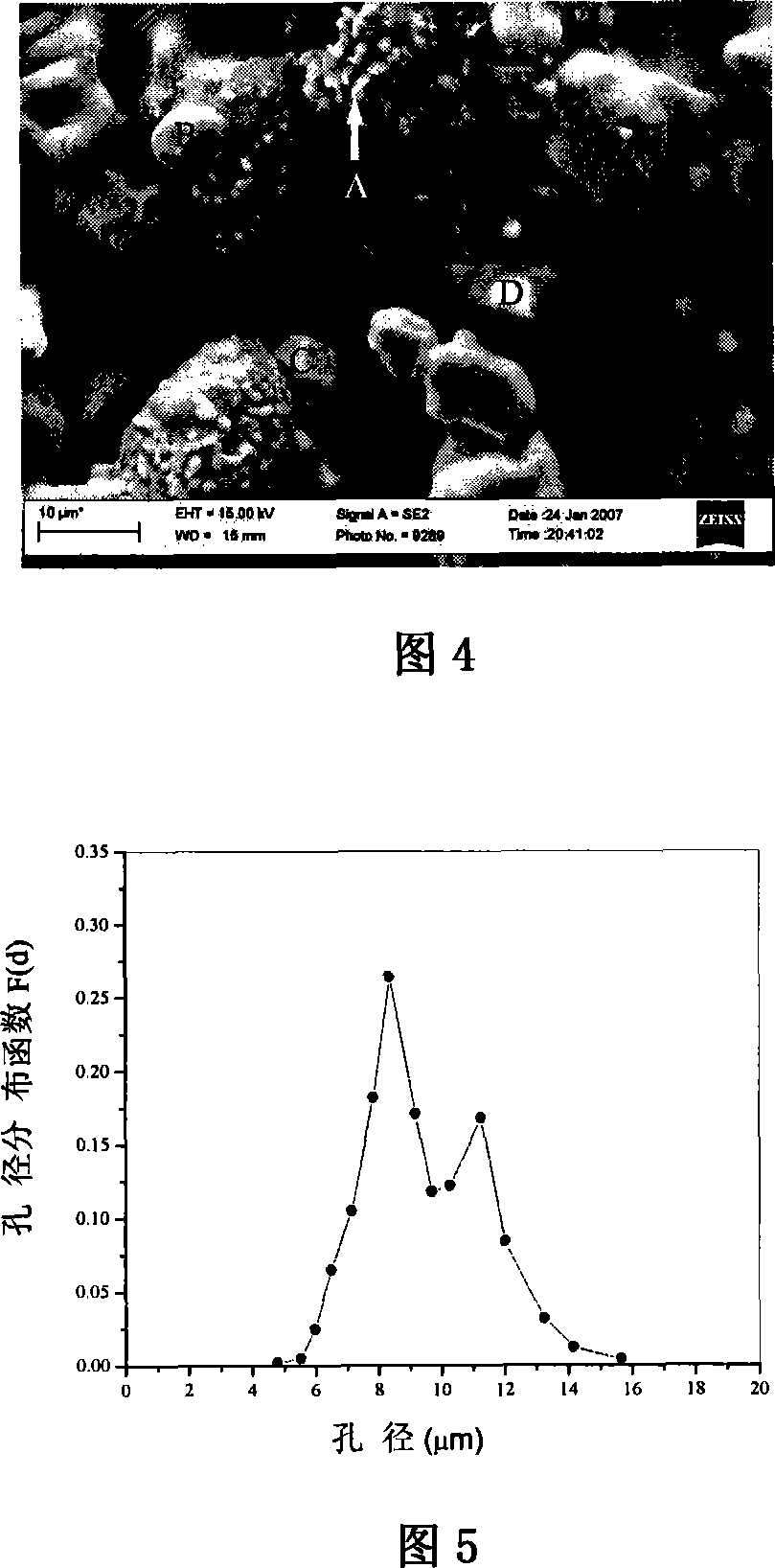
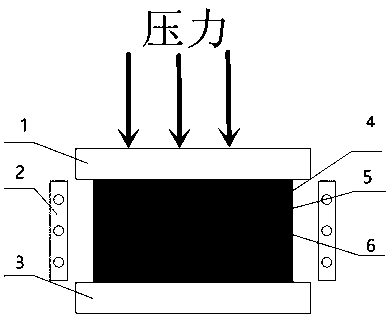
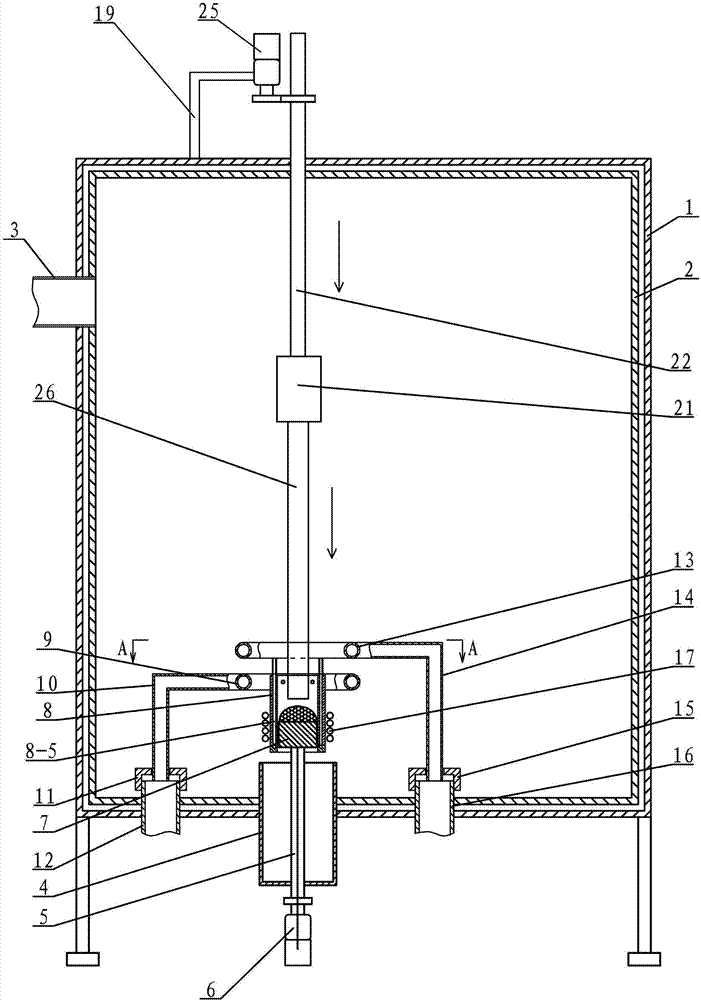
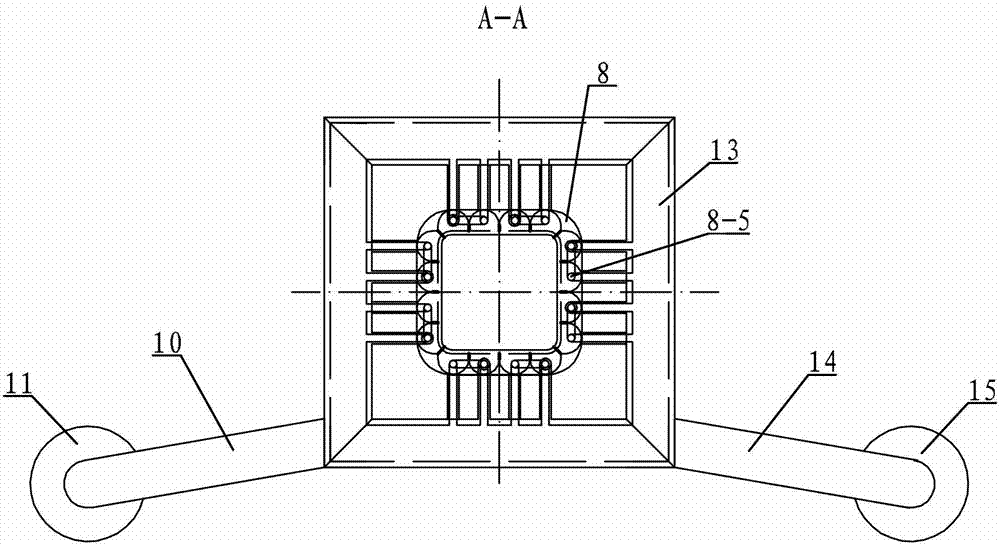
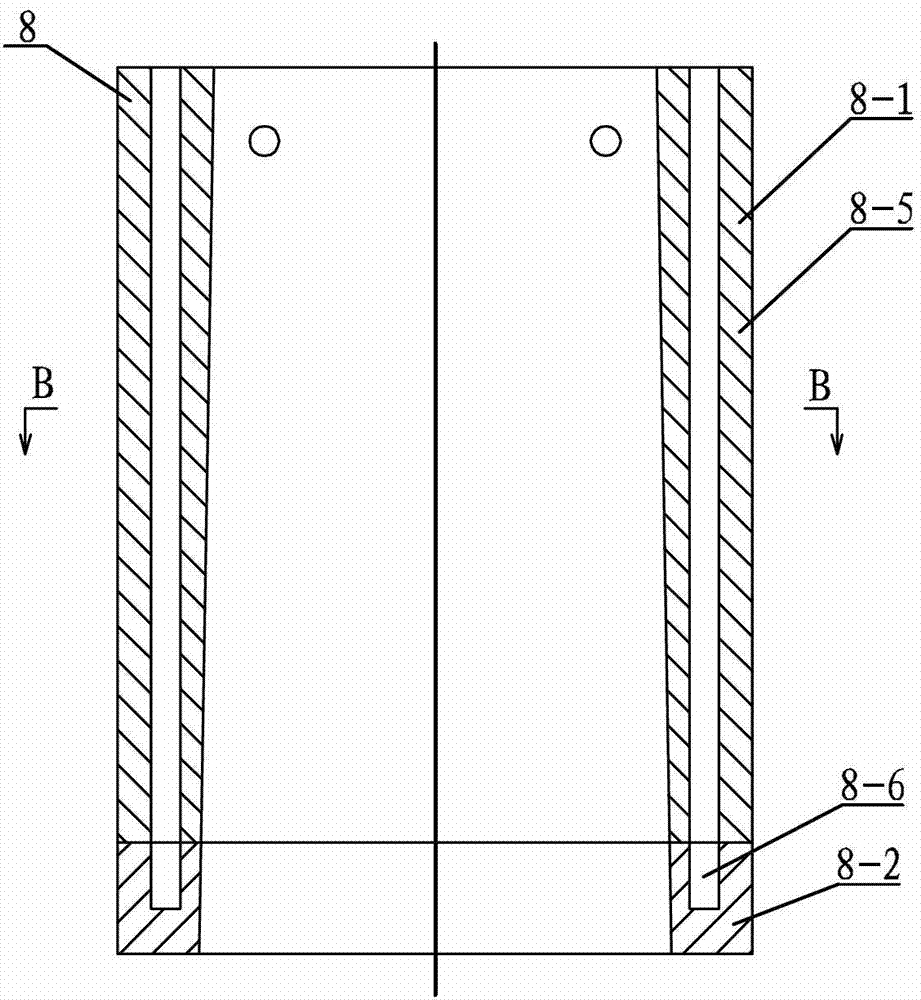
Patents
Literature
241 results about "Titanium-niobium alloy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
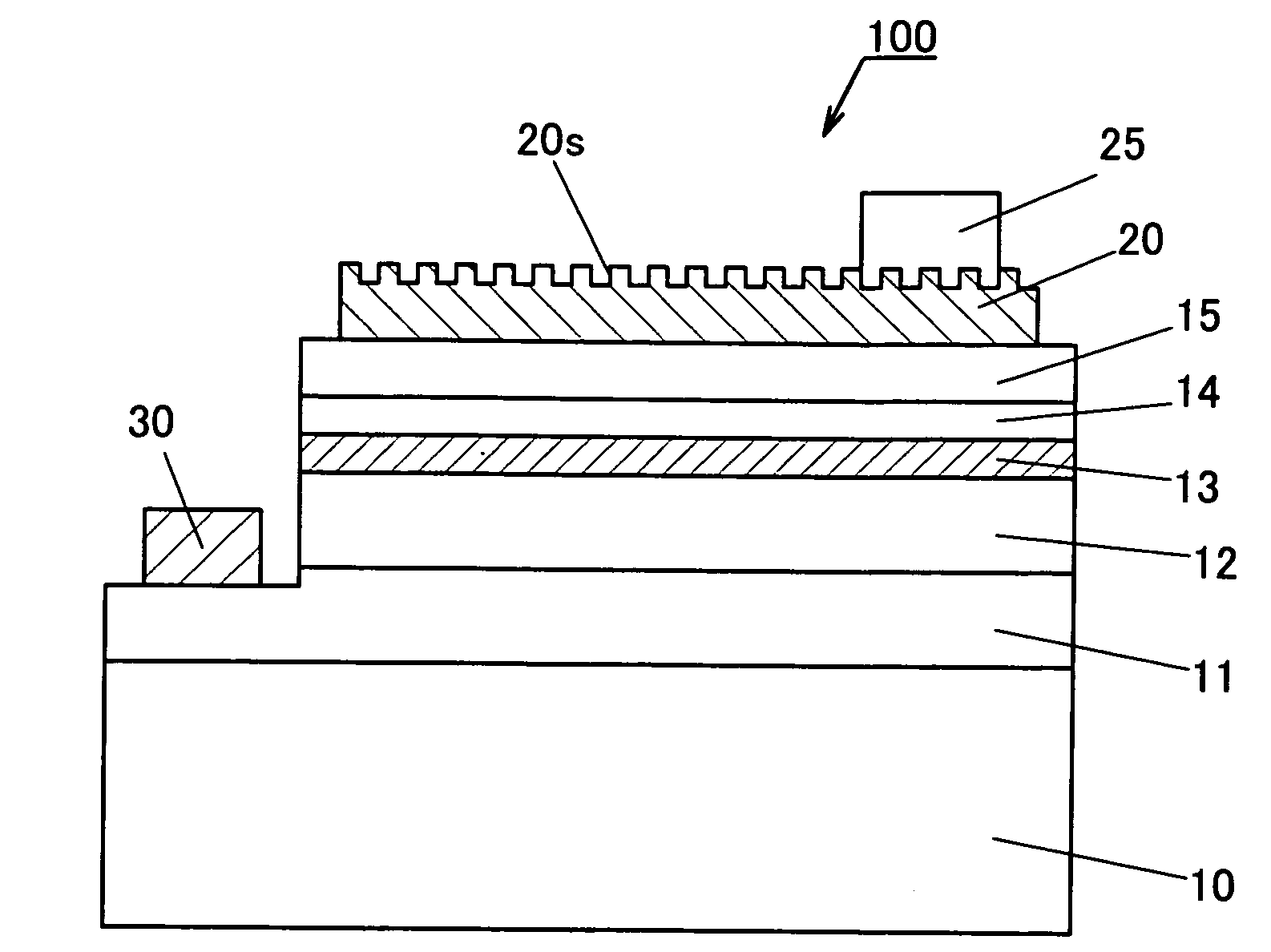
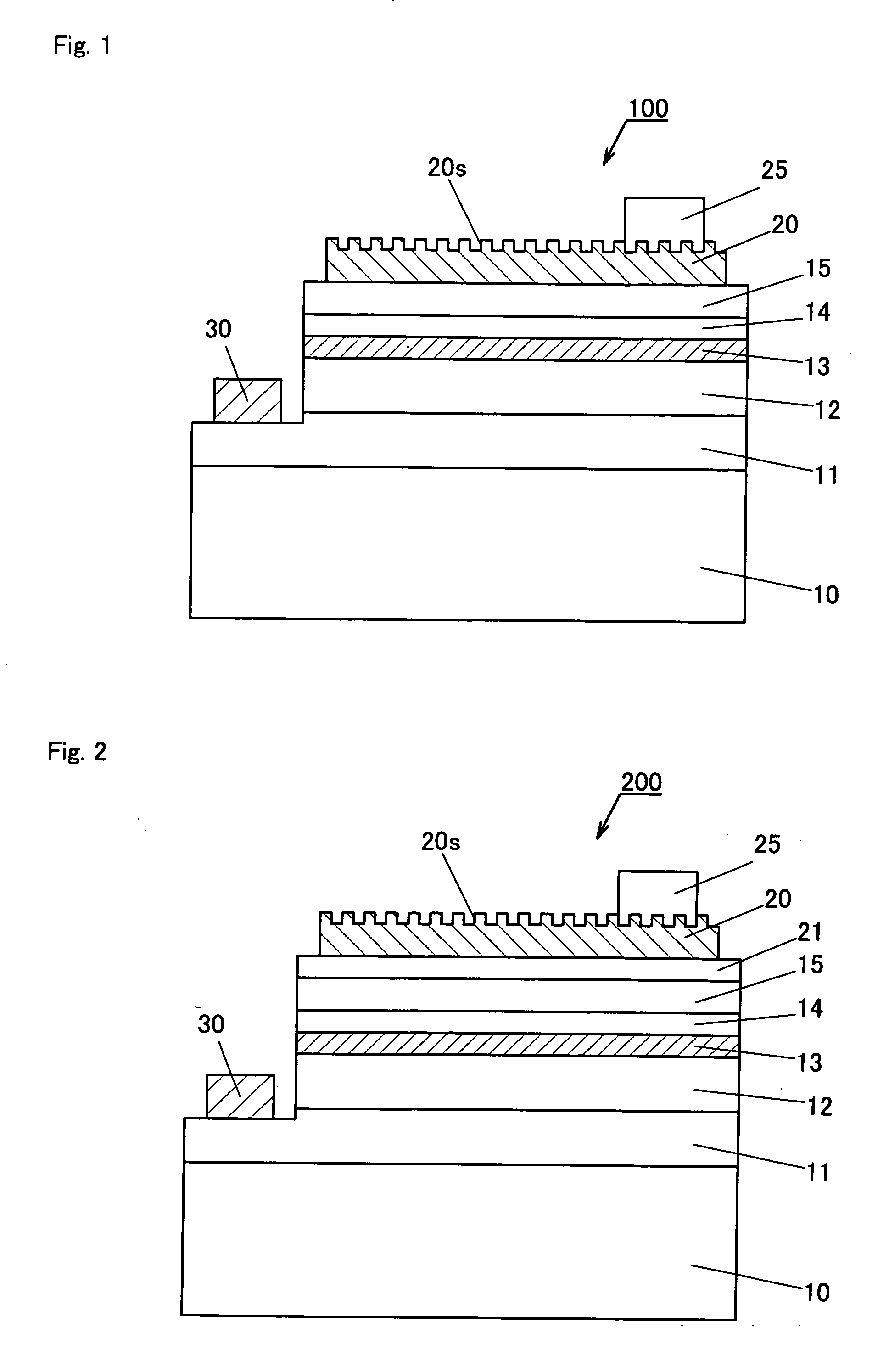
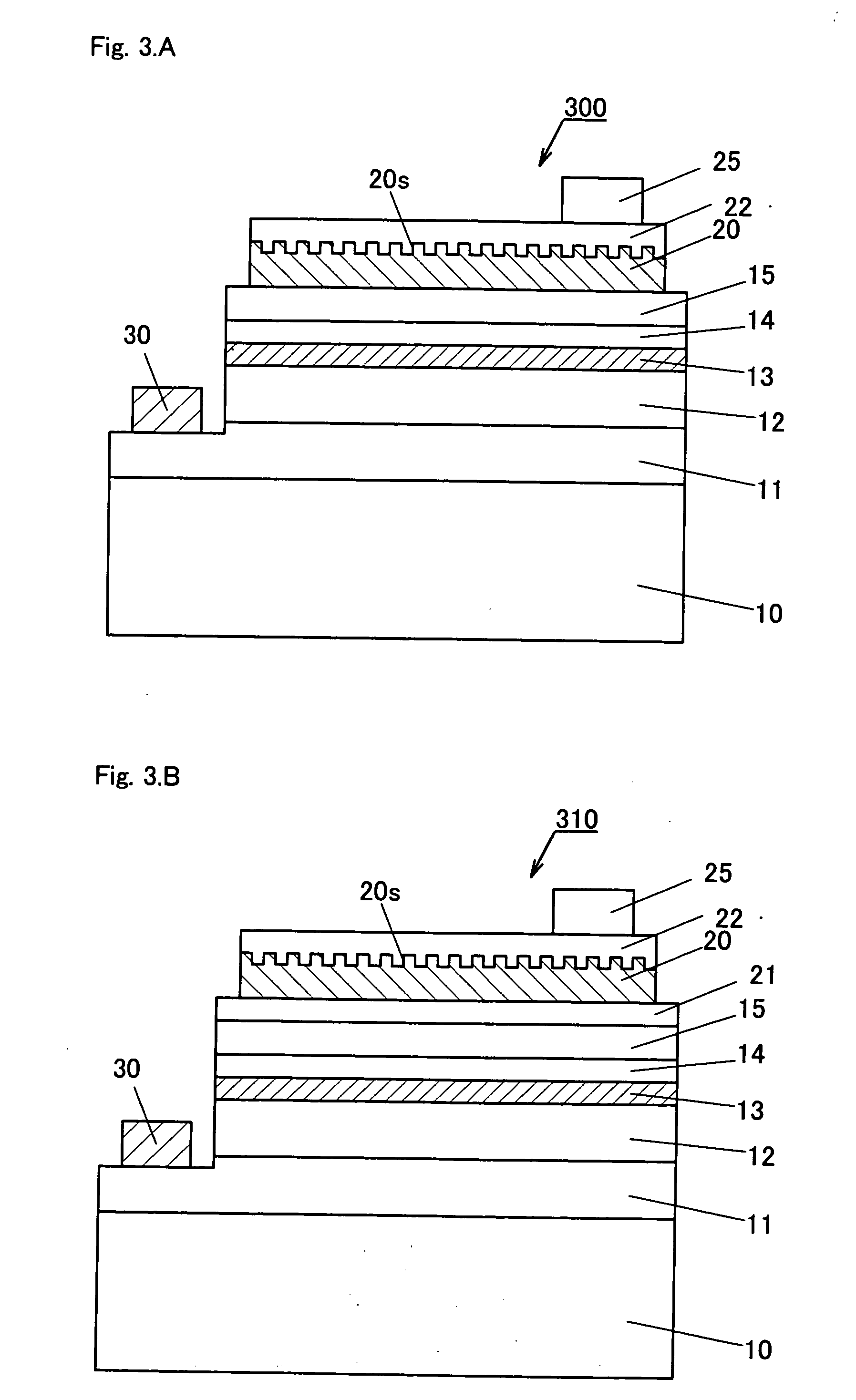
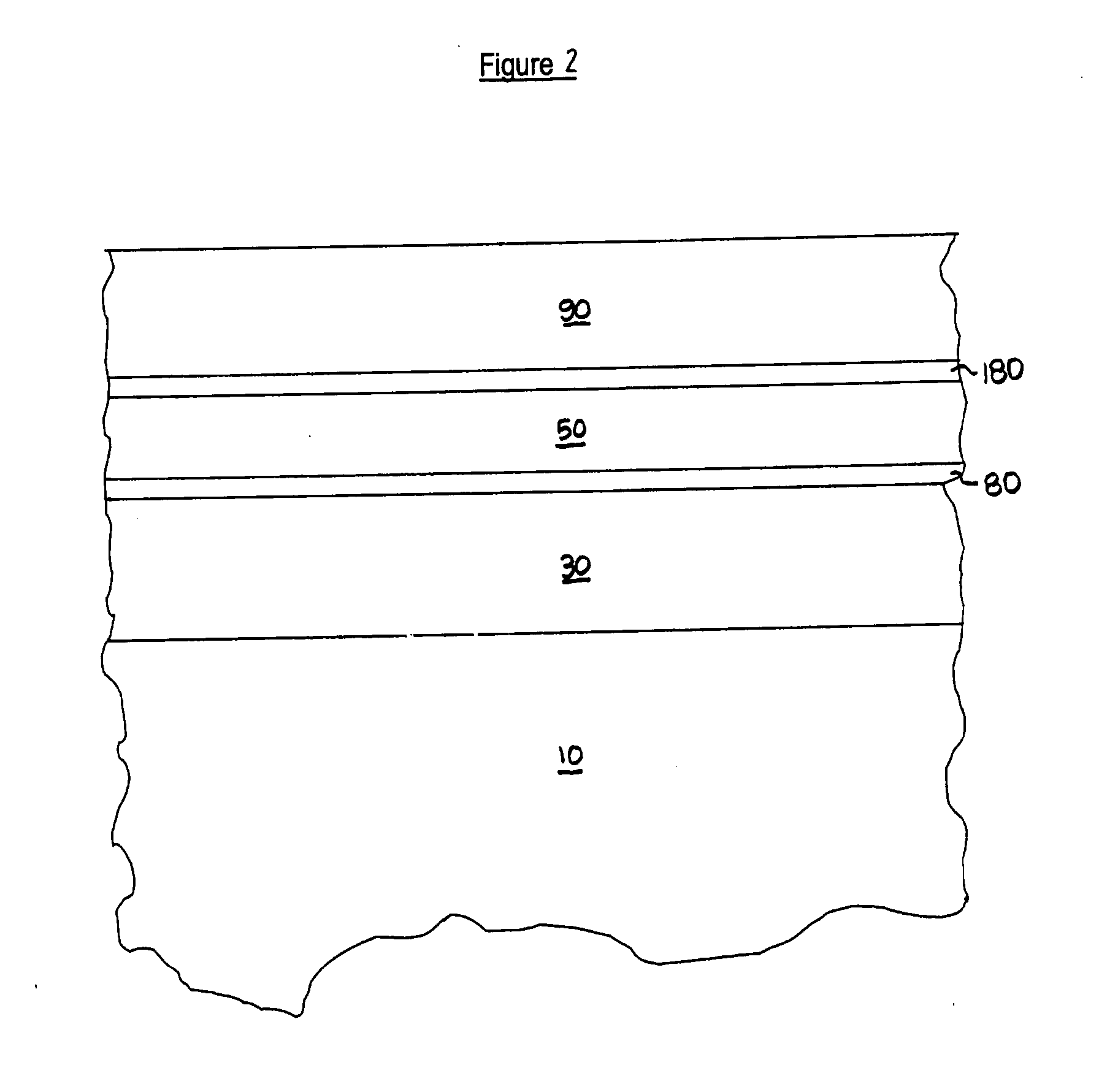
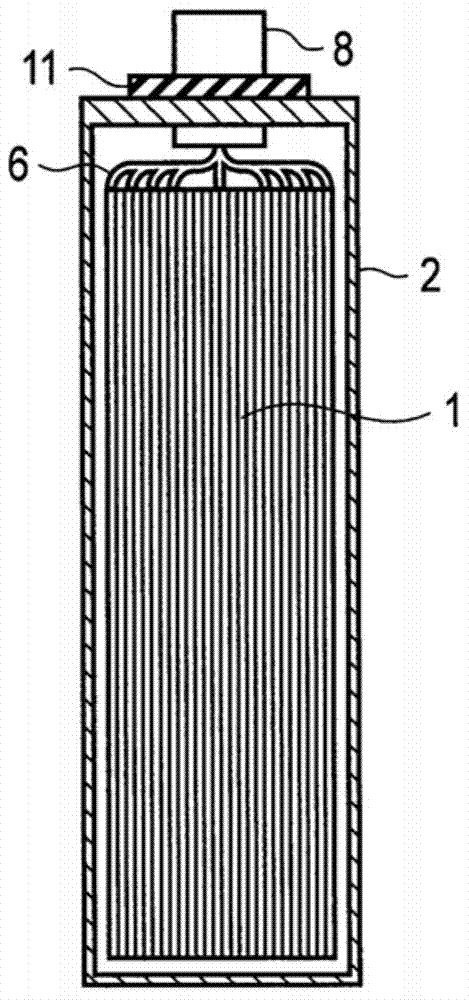
Niobium-titanium (NbTi) is an alloy of niobium and titanium, used industrially as a type II superconductor wire for superconducting magnets, normally as Nb-Ti fibres in an aluminium or copper matrix. Its critical temperature is about 10 kelvin.
Preparation method of directional solidification high-niobium TiAl-base alloy
ActiveCN101875106AHigh melting pointImprove room temperature performanceMetallic materialsZone melting
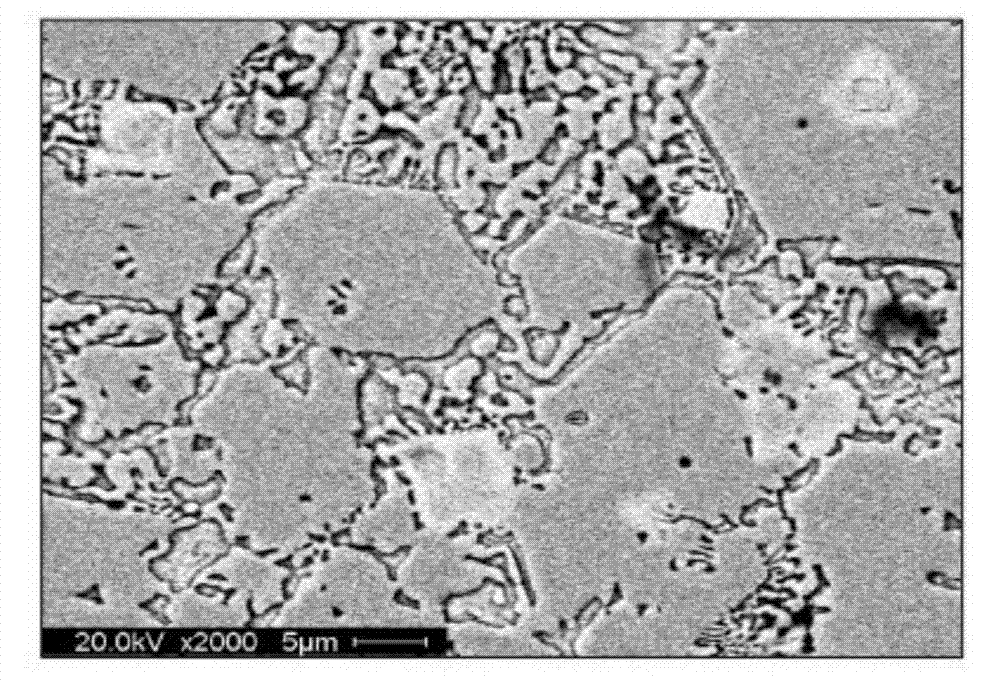
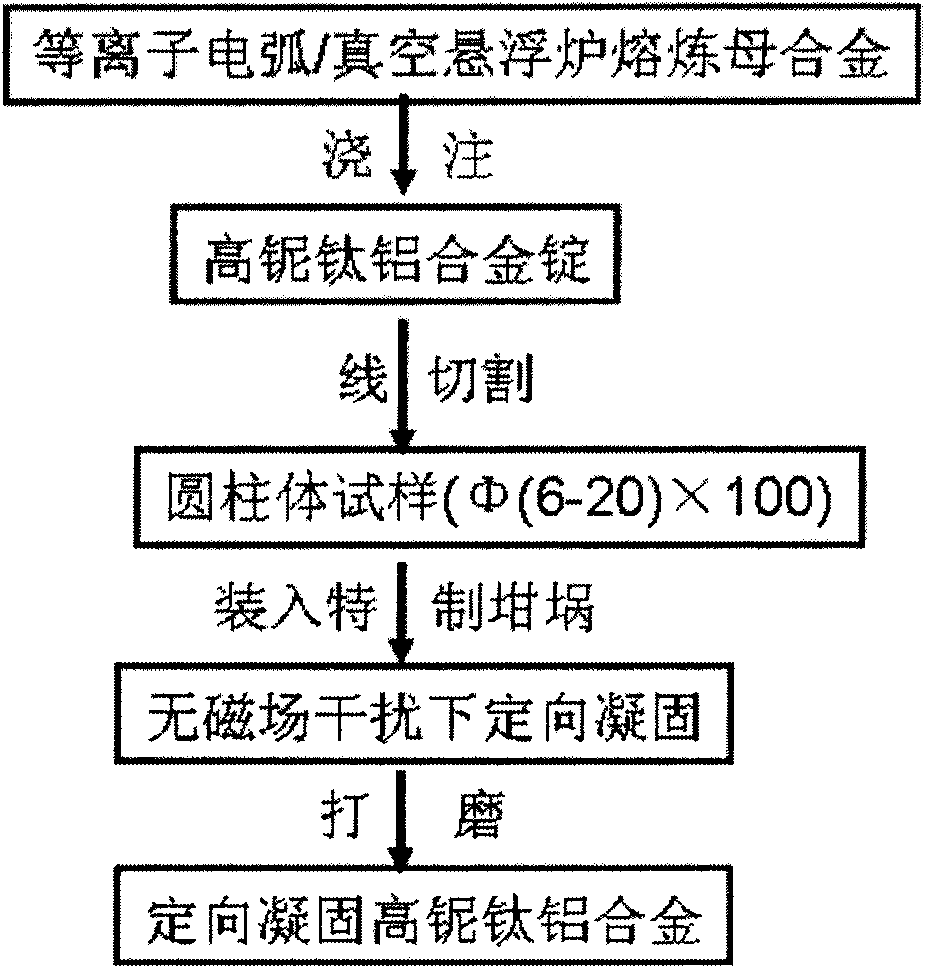
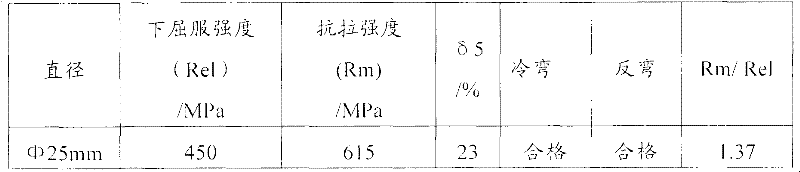
The invention discloses a preparation method of a directional solidification high-niobium TiAl-base alloy, which belongs to the field of metal material preparation. The high-niobium TiAl-base alloy contains Ti, Al, Nb, W, Mn, C, B and Y, and the atomic percentage is: (43-49) Ti-(45-46) Al-(6-9) Nb-(0-0.5) (W and Mn)-(0-0.5) (C and B)-(0-0.5) Y, an as-cast master alloy rod which is smelted by plasma arc or vacuum suspension is taken as a raw material, a high-purity alumina ceramic tube with a coating layer of which the main component is yttrium oxide is used as a crucible, Ga-In-Sn alloy liquid is cooling liquid, and the directional solidification high-niobium TiAl-base alloy is successfully prepared by using an improved zone-melting and directional solidification system. The processing technology is simple and reliable, the directional solidification effect is obvious, and the method has universal applicability. The directional solidification high-niobium TiAl-base alloy which is prepared by the directional solidification method has comprehensive and good high temperature performance and room temperature ductility and has wide application prospect in terms of high temperature structural materials.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Niobium-titanium composite micro-alloyed hotrolled deformed bar and production method thereof
The invention provides a niobium-titanium composite micro-alloyed hotrolled deformed bar which comprises the following chemical components: 0.15-0.25wt% of C, 0.30-0.60wt% of Si, 1.20-1.60wt% of Mn, 0.010-0.040wt% of Ti, 0.010-0.025wt% of Nb, less than or equal to 0.030wt% of P, less than or equal to 0.030wt% of S and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. According to the invention, the hotrolled deformed bar is produced by utilizing a niobium-titanium composite micro-alloying process, thus the addition of microalloy can be reduced, the production cost can be effectively lowered, and the produce market competitiveness can be improved.
Owner:LAIWU IRON & STEEL GRP
Corrosion resistant niobium-titanium alloy, and method for manufacturing plates and pipes with the same
InactiveCN102703757AImprove corrosion resistanceExpand the range of corrosion resistanceSolid solution strengtheningTitanium alloy
The invention relates to a corrosion resistant niobium-titanium alloy, and a method for manufacturing plates and pipes with the corrosion resistant niobium-titanium alloy, wherein the corrosion resistant niobium-titanium alloy contains the following components by weight: 0.1-4.9% o Nb, not more than 0.08% of C, not more than 0.03% of N, not more than 0.012% of H, not more than 0.1% of O, not morethan 0.1% of Fe, and the balance of Ti. In Ti-(0.8-6%) Nb alloy pipes disclosed by the invention, titanium is as a matrix; little niobium is added; mechanical property of the niobium is improved by asolid-solution strengthening way; shearing strength and tensile strength of the alloy are higher than pure titanium; the tensile strength is increased by 10-20%; good plasticity and formability are kept; cold working performance is excellent; the niobium is added to further increase corrosion resistance of titanium and enlarge corrosion resistant range of titanium, so that the corrosion resistantniobium-titanium alloy is a good easily-formed corrosion resistant material.
Owner:NINGXIA ORIENT TANTALUM IND
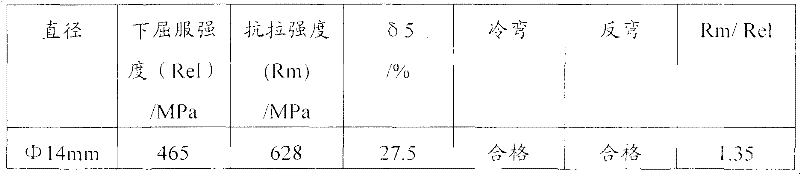
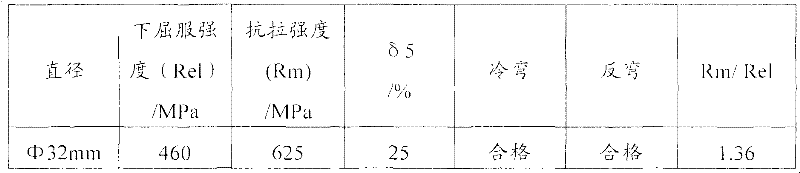
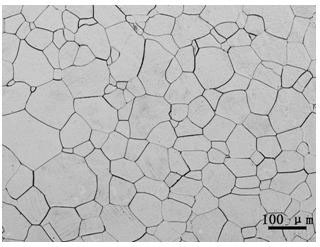
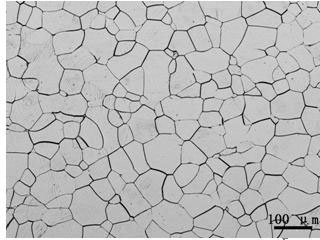
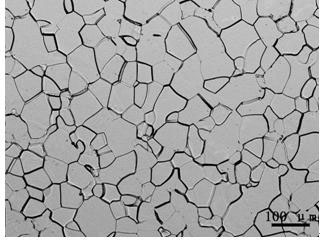
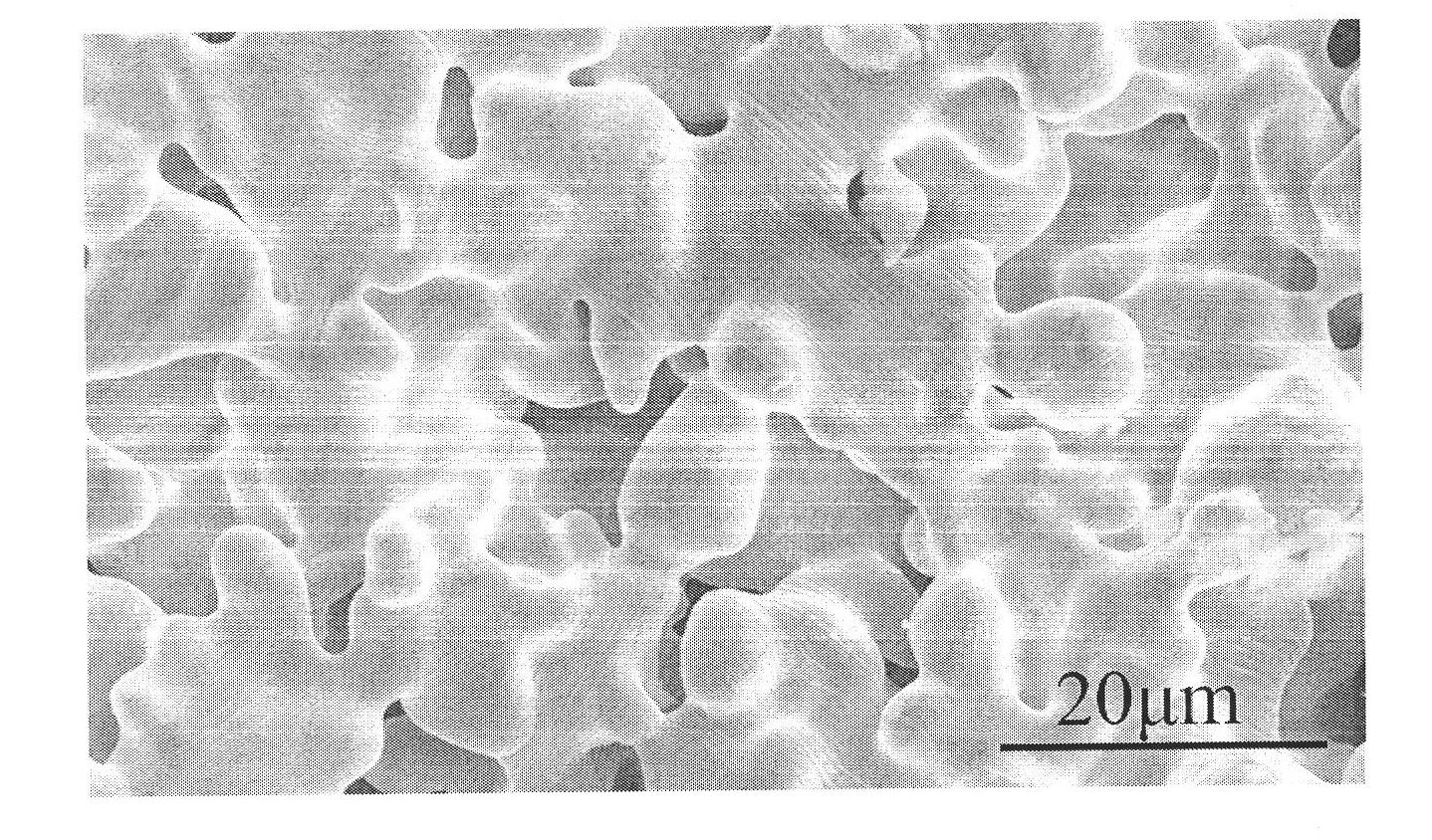
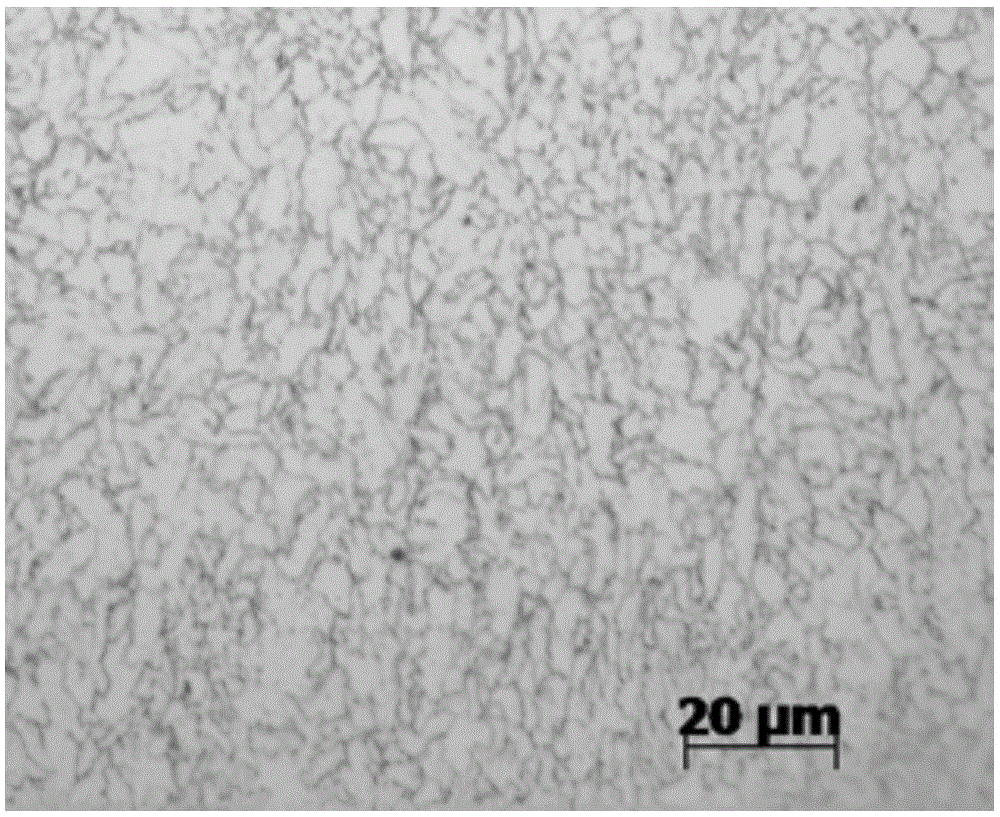
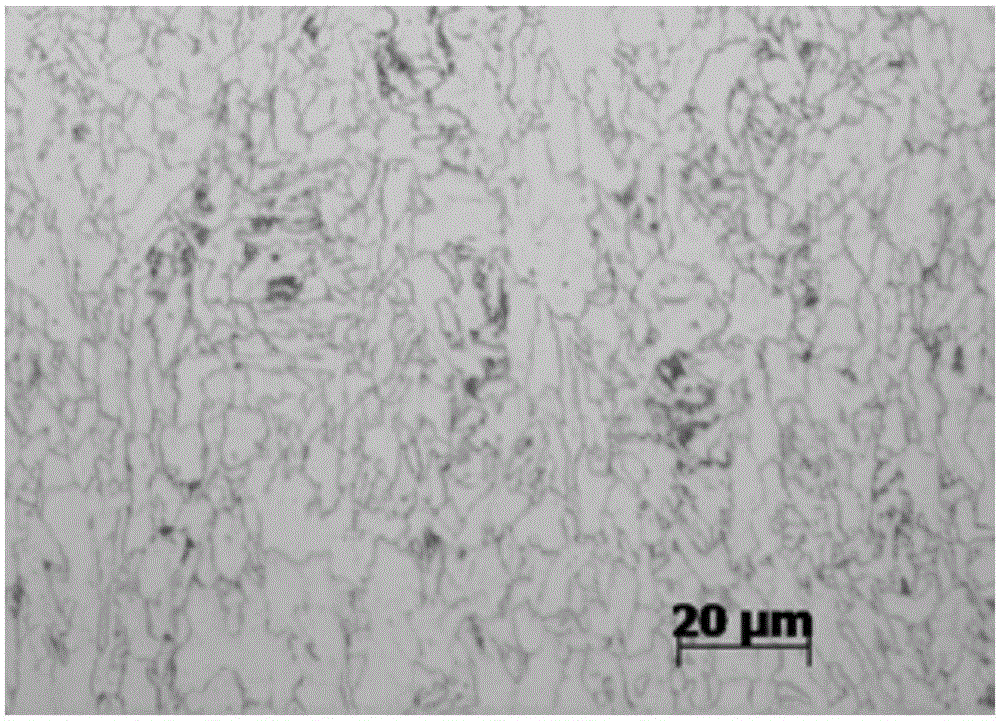
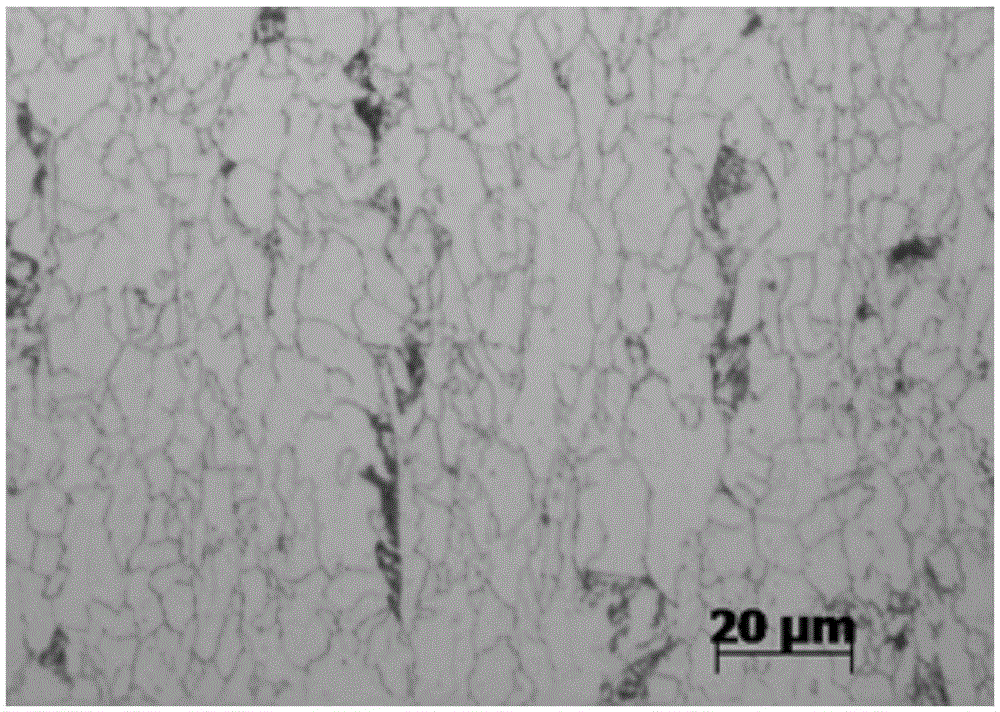
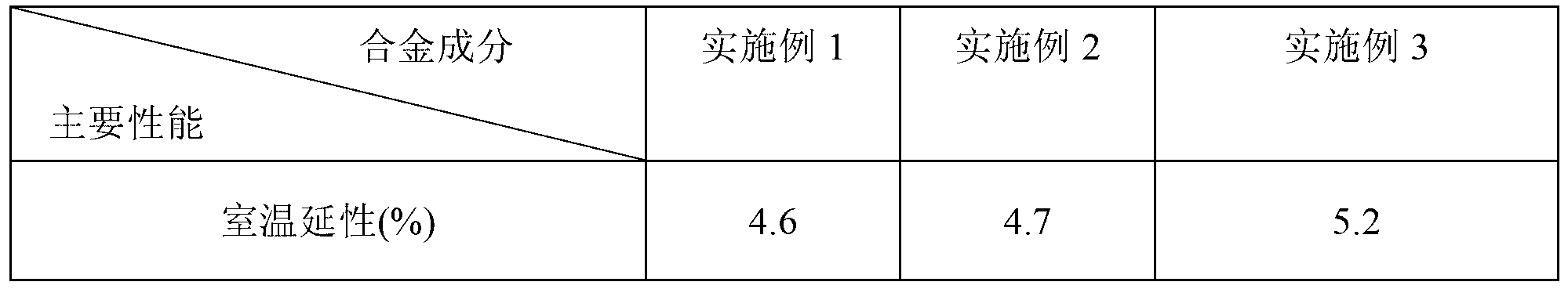
Method for observing metallographic structure of niobium-titanium alloy
InactiveCN102331363AObserve clearlySmall amount of corrosionPreparing sample for investigationHydrofluoric acidTitanium alloy
The invention relates to a method for observing the metallographic structure of niobium-titanium alloy, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: firstly, grinding a sample on a grinding machine, polishing the sample on a polishing machine, and chemically polishing the sample in a mixed solution of sulfuric acid + nitric acid + hydrofluoric acid; then, selecting a reagent of sulfuric acid + nitric acid + hydrochloric acid + hydrofluoric acid to erode the sample, and observing the metallographic structure. By using the method, the metallographic structure of niobium-titanium alloy can be observed clearly. The method provided by the invention is easy to operate without any special equipment, and good effect is achieved in the preparation of a metallographic sample of niobium-titanium alloy.
Owner:WESTERN METAL MATERIAL
Group III nitride-based compound semiconductor light-emitting device
InactiveUS20080308833A1Low densityLow refractive indexSemiconductor devicesRefractive indexContact layer
The refractive index of a titanium oxide layer is modified by adding an impurity (e.g., niobium (Nb)) thereto within a range where good electrical conductivity is obtained. The Group III nitride-based compound semiconductor light-emitting device of the invention includes a sapphire substrate, an aluminum nitride (AlN) buffer layer, an n-contact layer, an n-cladding layer, a multiple quantum well layer (emission wavelength: 470 nm), a p-cladding layer, and a p-contact layer. On the p-contact layer is provided a transparent electrode made of niobium titanium oxide and having an embossment. An electrode is provided on the n-contact layer. An electrode pad is provided on a portion of the transparent electrode. Since the transparent electrode is formed from titanium oxide containing 3% niobium, the refractive index with respect to light (wavelength: 470 nm) becomes almost equal to that of the p-contact layer. Thus, the total reflection at the interface between the p-contact layer and the transparent electrode can be avoided to the smallest possible extent. In addition, by virtue of the embossment, light extraction performance is increased by 30%.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD +1
Low temperature superconducting assembly with low joint resistance for high temperature superconducting current lead cold end
InactiveCN101694908ASatisfy <1 nano-oh requirementSuperconducting magnets/coilsConnection contact member materialElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh-temperature superconductivity
The invention discloses a low temperature superconducting assembly with low joint resistance for a high temperature superconducting current lead cold end. The resistance of a 40-70kA high temperature superconducting super current lead of which the lower end is connected with a low temperature superconducting bus must be as low as 1 nano-ohm. A rectangular section niobium-titanium / copper superconducting wire or a high conductivity copper material and a paired box type joint structure connected with the superconducting bus are adopted in the low temperature superconducting assembly. Tests prove that the joint resistance of the low temperature superconducting assembly and a high temperature superconducting assembly can be as low as 0.5 nano-ohm, and the joint resistance of the superconducting bus is lower than 1 nano-ohm. The low temperature superconducting assembly is a middle result for developing super current leads of an international thermonuclear fusion test reactor and has the characteristics of novel conception and low manufacturing cost.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
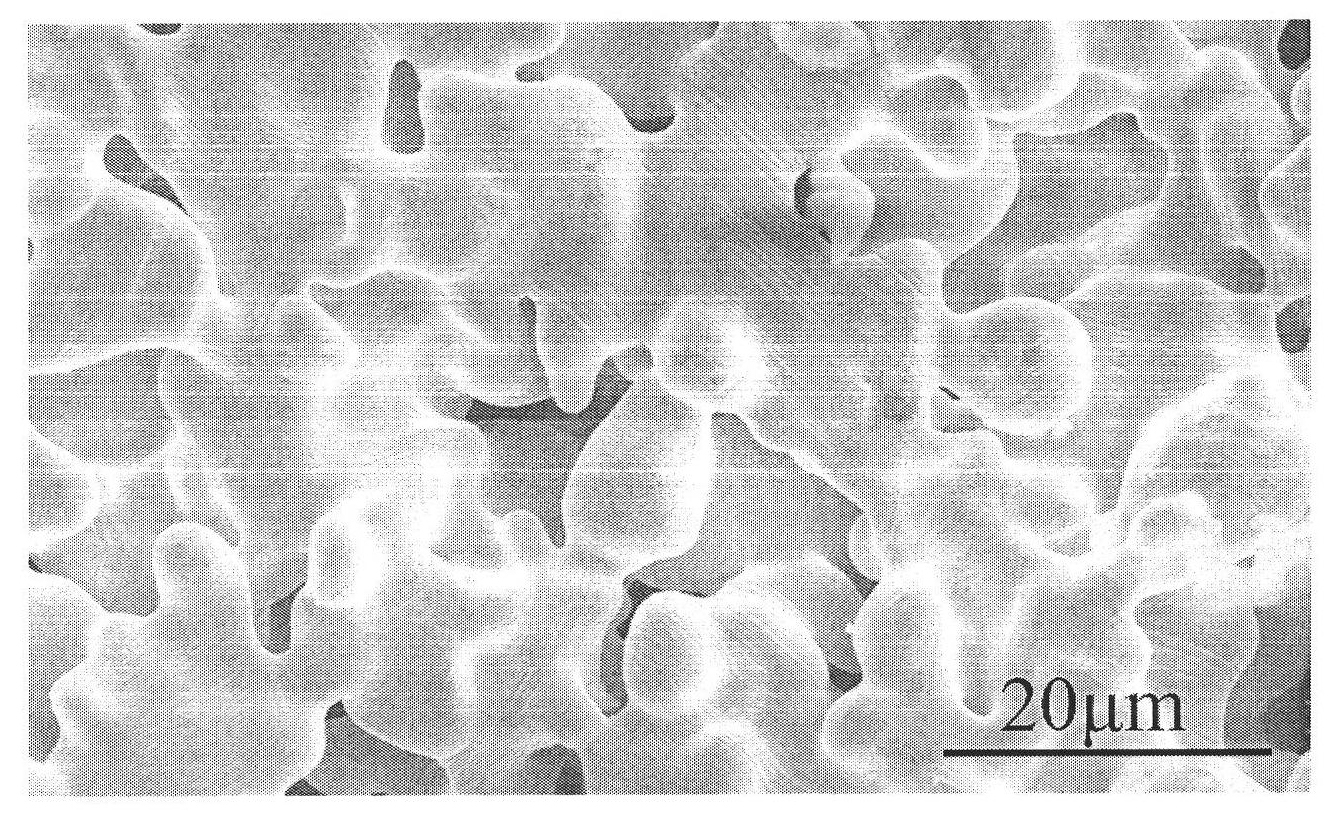
Preparation method of gradient pore porous high-niobium titanium-aluminum alloy
InactiveCN101967578AHigh porosityFree adjustment of porosity gradient changeMaterial DesignVacuum drying
The invention belongs to the field of porous metal materials and particularly relates to a preparation method of a gradient pore porous high-niobium titanium-aluminum alloy. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing pure titanium powder, pure aluminum powder and pure niobium powder and sintering the mixture by a Kerkendill effect reaction pore-forming method and a pore-forming agent physical pore-forming method; adding a plurality of ingredients; compacting the ingredients which contain different pore-forming agents and have different content into single blanks respectively; rolling a plurality of single blanks with different pore-forming agent content into the total blank; and performing a vacuum drying degreasing pore-foaming and high-temperature sintering reaction pore-forming process so as to finally obtain a porous high-niobium titanium-aluminum alloy material with a gradient hole structural characteristic and adjustable porosity. The material has gradient porosity change, optionally-adjustable pore structural characteristic, adjustable stress cross section, light weight, high specific stiffness and high heat insulation performance; simultaneously, the material has high material design flexibility and can be widely applied to the industrial fields of high temperature heat insulation, filtering separation, catalysis and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for preparing high niobium containing titanium aluminium alloy powder
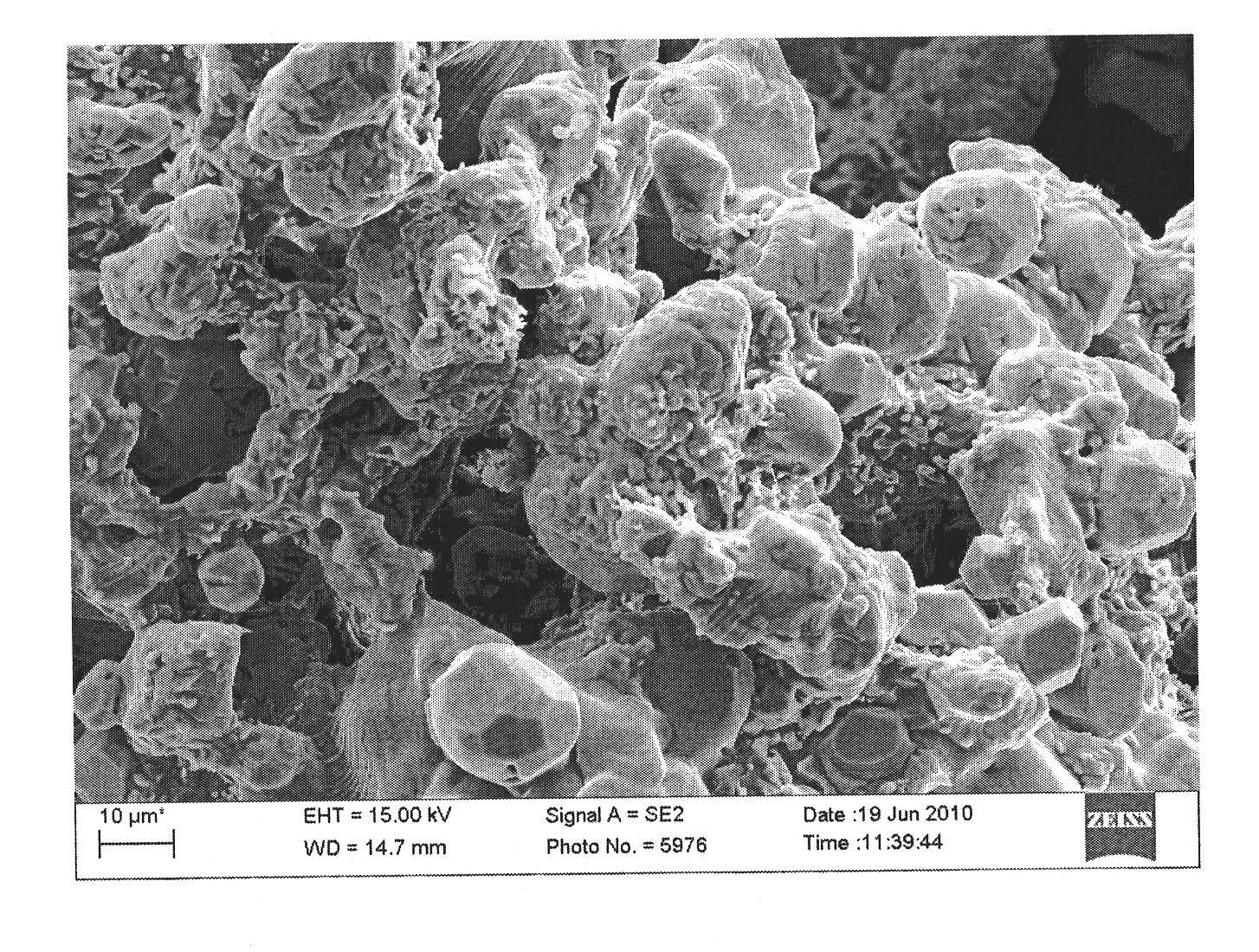
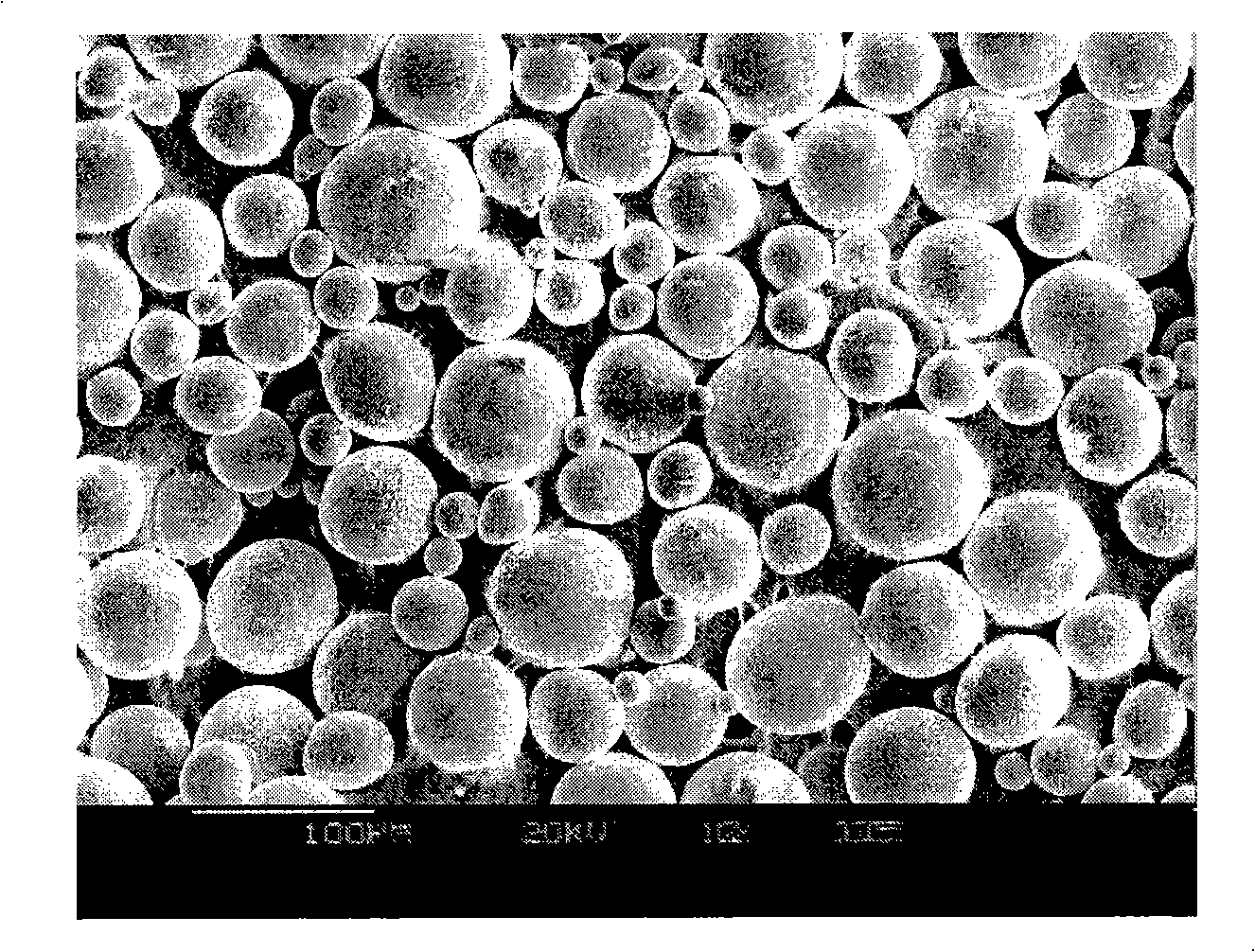
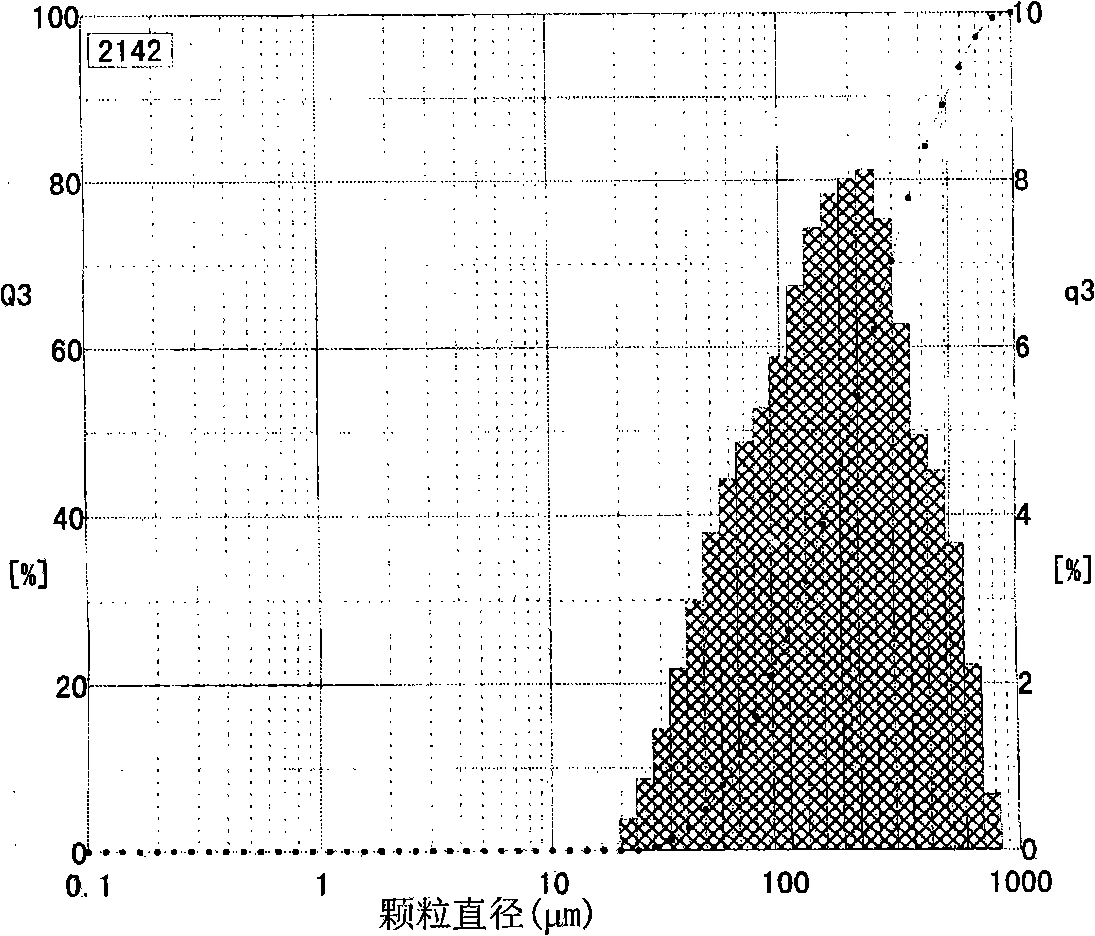
The invention pertains to the field of powder metallurgy technology, in particular to a preparation method of high-niobium titanium aluminum alloy powder. The raw material adopts a casting-state high-niobium titanium aluminum alloy cast ingot, the process comprises: melting - soaking treatment - turning - machining into a rod which can be connected - continuous inert gas atomization method by induction heating without a crucible, the preparation method comprises the specific steps of: (1) melting by adopting the plasma cooling bed process; (2) carrying out the soaking treatment by keeping the temperature at 1100 to 1300 DEG C for 24 to 48 hours; then removing the oxide scale on the surface of the cast ingot; (3) adopting the wire cutting and machining methods to process the cast ingot into the rod which has thread connection, the diameter of 20 to 25mm and the length of 200 to 500mm, and then carrying out turning to remove the oxide scale on the surface of the rod; (4) adopting the continuous inert gas atomization process by induction heating without the crucible to process the rod into the powder, and the process parameters are that the pressure of the inert gas is 2.0 to 5.0MPa and the argon gas flow rate is 160 to 220Ls <-1>. The preparation method has the advantages of excellent degree of sphericity of the prepared powder, high purity, great mobility and high yielding rate of the powder. The degree of sphericity of the prepared powder achieves 80 to 95 percent, and the yielding rate of the powder is 75 to 85 percent.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Active substance, nonaqueous electrolyte battery, and battery pack
InactiveCN104466150AImprove featuresTantalum compoundsMolybdeum compoundsPeak intensityUltimate tensile strength
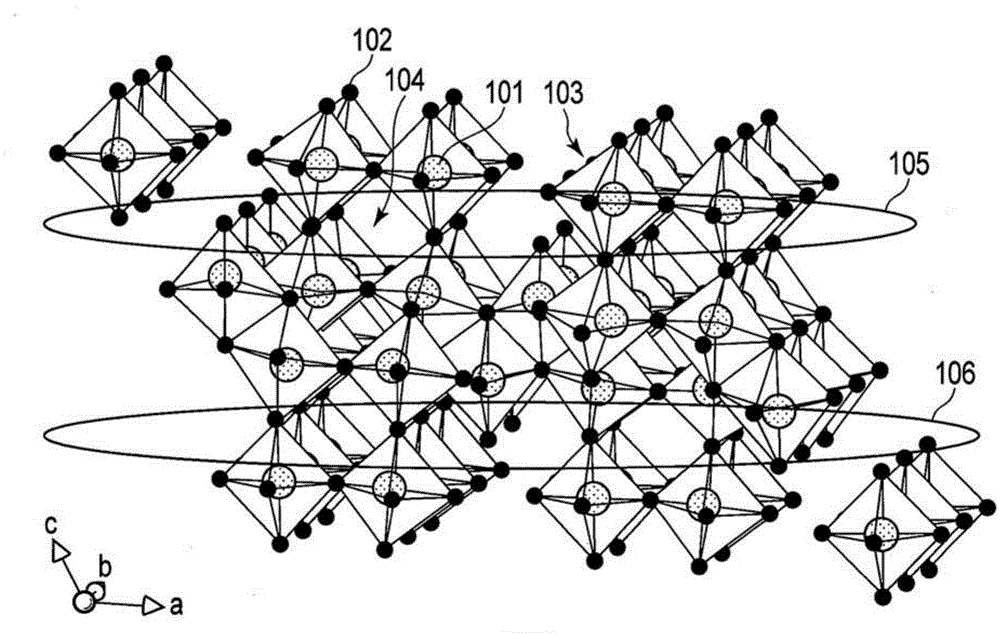
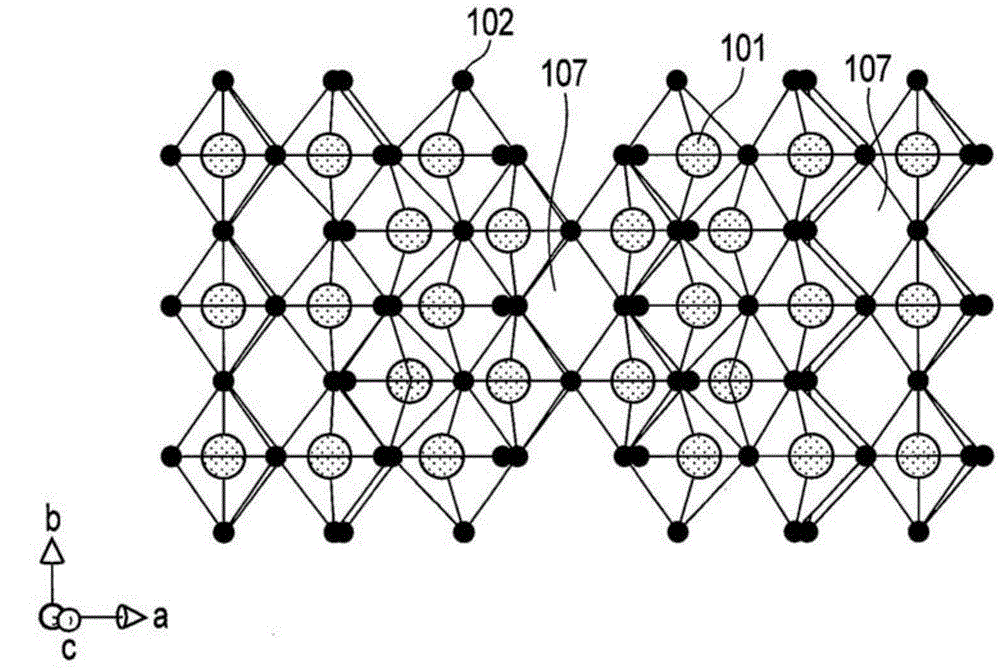
The invention relates to an active substance, a nonaqueous electrolyte battery and a battery pack. According to one embodiment, there is provided an active substance. The active substance includes particles of niobium titanium composite oxide and a phase including a carbon material. The niobium titanium composite oxide is represented by Ti1-xM1xNb2-yM2yO7. The phase is formed on at least a part of the surface of the particles. The carbon material shows, in a Raman chart obtained by Raman spectrometry, a G band observed at from 1530 to 1630 cm-1 and a D band observed at from 1280 to 1380 cm-1. A ratio IG / ID between a peak intensity IG of the G band and a peak intensity ID of the D band is from 0.8 to 1.2.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
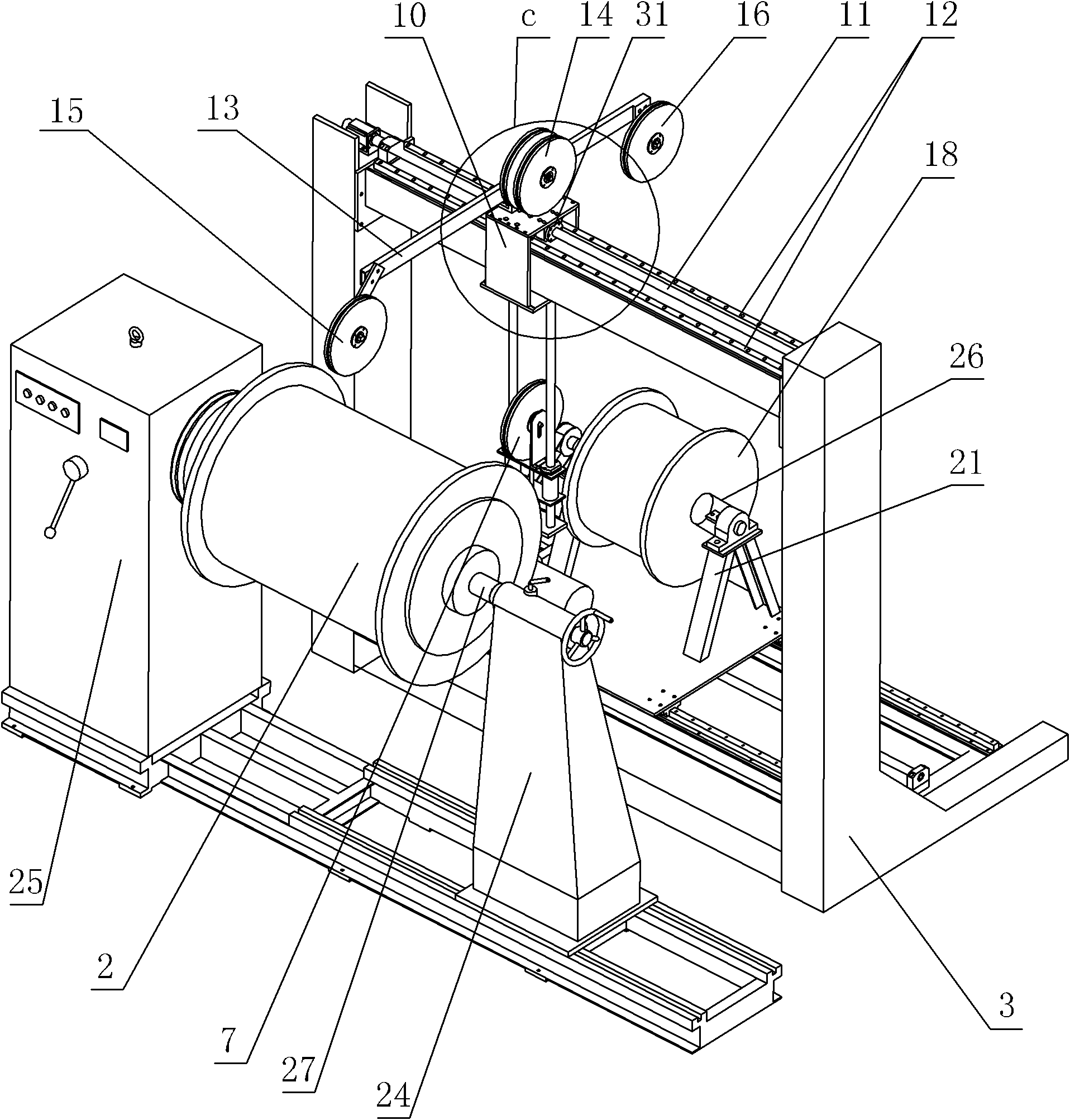
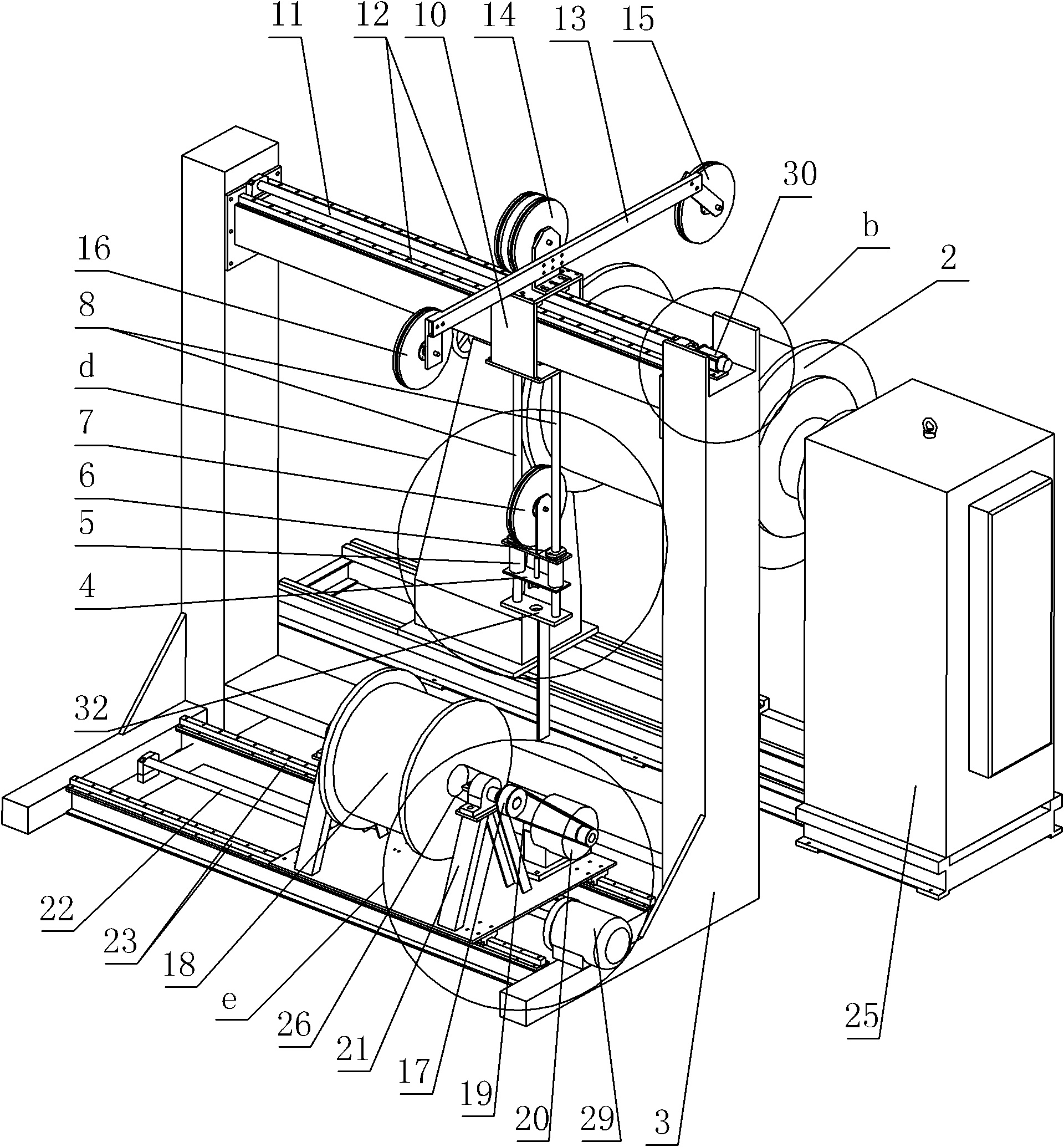
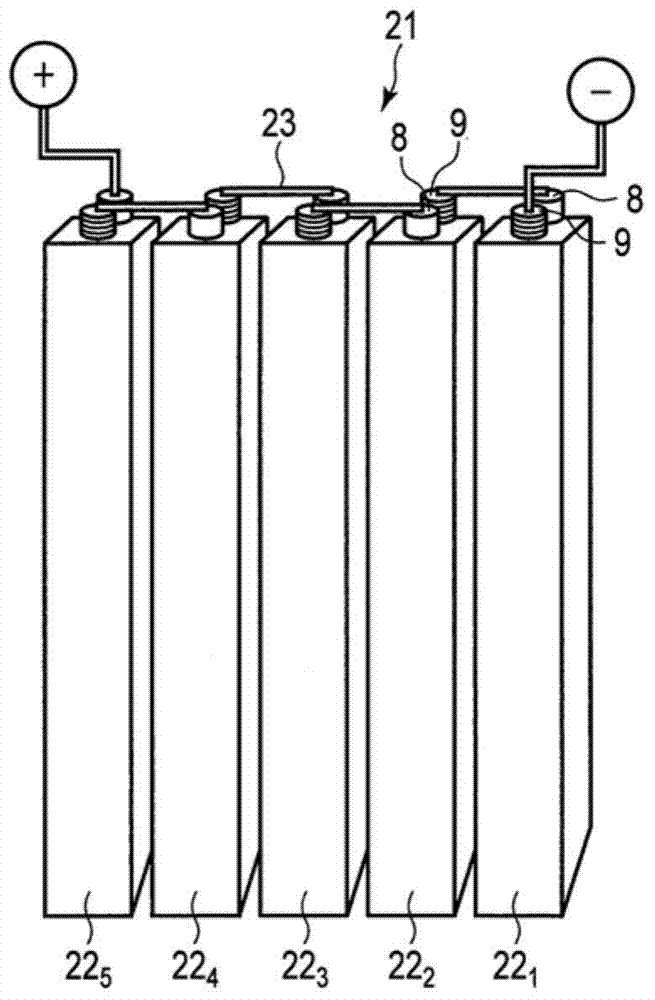
Constant-tension winding machine for niobium titanium-copper superconducting solenoid coils
InactiveCN102030223ACompact space arrangementSmall footprintFilament handlingCoils manufactureWinding machineSuperconducting solenoid
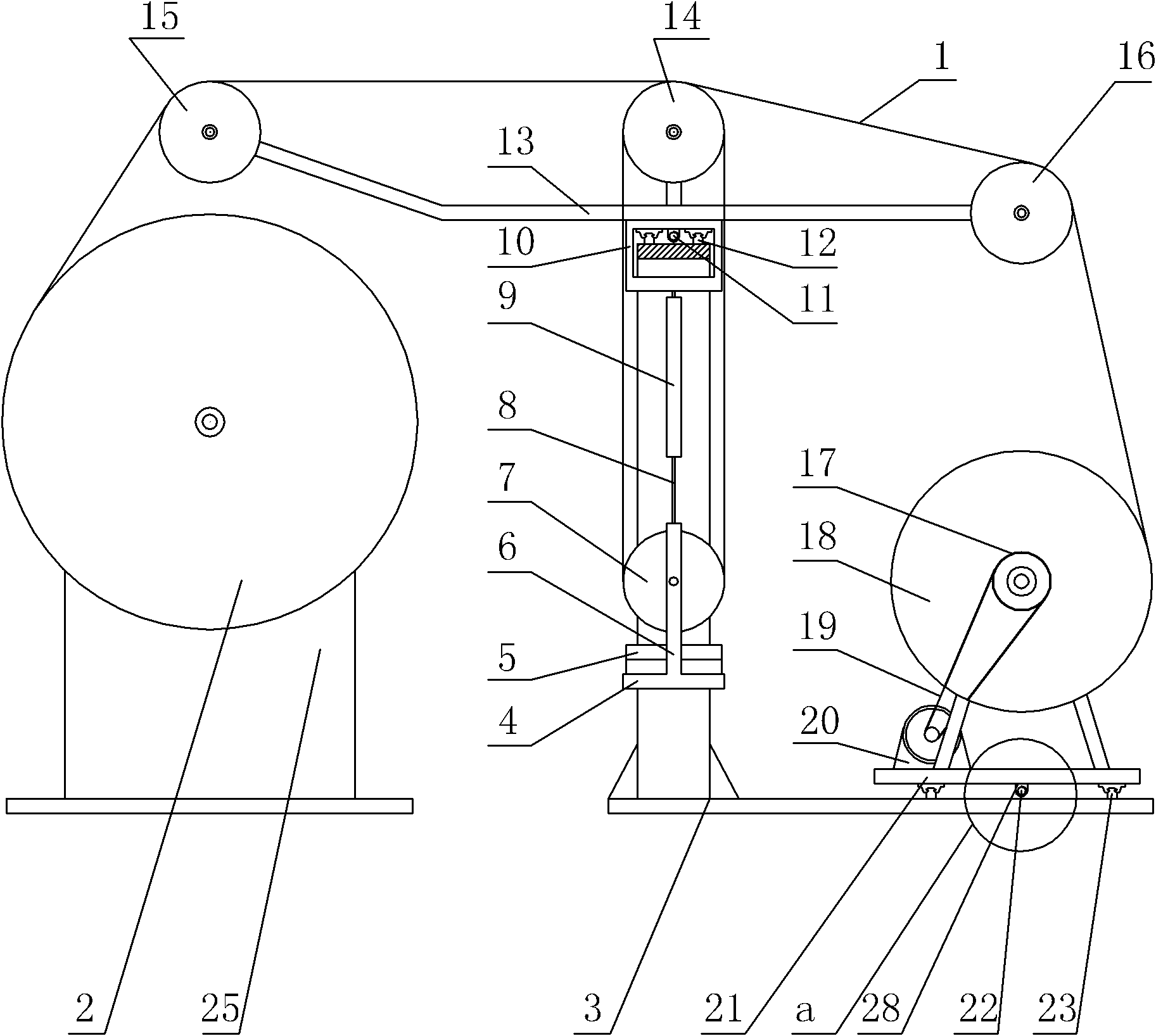
The invention provides a constant-tension winding machine for niobium titanium-copper superconducting solenoid coils, relating to a winding machine for superconducting solenoid coils. The invention solves the problems of complex winding process, high labor intensity of operators and low use ratio of equipment space of the current winding machine for superconducting solenoid coils. In the invention, an L-shaped portal frame is provided with two first slider linear guide rails and a first ball screw, and a double-track pulley is installed on a wiring arm. A wiring support arm of the wiring arm is provided with a wiring pulley, and a wire loading support arm of the wiring arm is provided with a wire loading pulley. A movable pulley is installed on a movable pulley axis support, and a wire loading tray is rotatably installed on a wire loading support. A superconducting solenoid coil to be wound is rotatably installed on a winding support, and a lead wire is led out through the wire loading tray and wound on the superconducting solenoid coil to be wound after moving round the wire loading pulley, one slideway of the double-track pulley, the movable pulley, the other slideway of the double-track pulley and the wiring pulley. The constant-tension winding machine is suitable for winding niobium titanium-copper superconducting solenoid coils.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Niobium titanium -combined microalloying steel for cooling-control reinforced bar and method for producing same
ActiveCN1952199AImprove performanceGuaranteed strength performanceTemperature control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsElemental compositionReinforced concrete
Steel with micro amount of Niobium-titanium combination used for controlled cooling steel and its production methods, belongs to the hot rolling steel used in ferroconcrete, especially steel rod with micro-niobium-titanium combination and its production method. The steel rod contains the following elements: (by wt. ratio): 0.15-0.25%C, 0.30-0.80%Si, 1.00-1.60%Mn, <=0.045%P, S, 0.005-0.02%Nb,<=0.0080%N, Fe as the rest and impurities elements. The production method of the steel rod contains the following steps: smelting, according to the specified elements and content, with conventional smelting method in a revolver or an electric furnace, rolling with a merchant bar mill, at temperature 1050-1220DEG C, rolling at a temperature over 950DEG C, rapidly cooling at a temperature of 800-1050DEG C, shearing, bundling, and warehousing after natural cooling. Through combination of micro niobium-titanium and proper cooling controlled, the steel rod has good properties. The method of the invention solves the problems low steel intensity at 400Mpa during macroallaying of niobium and safe production.
Owner:MAANSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Titanium dioxide/niobium-titanium oxide composite material as well as preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN103594693AHigh bulk densityImprove electrochemical activityMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesDispersityMicron scale
The invention relates to a titanium dioxide / niobium-titanium oxide composite material as well as the preparation and application thereof, and belongs to the field of lithium ion batteries. According to the titanium dioxide / niobium-titanium oxide composite material, anatase type titanium dioxide particles are distributed on the surface of a spherical amorphous niobium-titanium oxide, and the amorphous niobium-titanium oxide is a compound with the general formula of TixNbyO2x+2.5y, wherein x ranges from 0.1 to 1, and y ranges from 1 to 2. The composite material adopts the subcritical solvothermal method, and the synthesis and recombination of components of the composite material are completed synchronously, so as to ensure good dispersity and interfacial compatibility of the system. The composite material has both the advantage of high bulk density of the micron-scale spherical electrode material and the advantage of short lithium ion diffusion distance of a nanometer material, so that the composite material achieves excellent electrochemical activity.
Owner:海悦高科电池技术(大连)有限公司
Smelting method for high-Nb-TiAl based alloy
The invention provides a smelting method for a high-Nb-TiAl based alloy. According to the smelting method, titanium sponge, a niobium-titanium alloy and aluminum shots are used as raw materials and are pressed and welded to form a consumable electrode; the consumable electrode is smelted in a vacuum consumable electric arc furnace to obtain the high-Nb-TiAl based alloy. According to the smelting method, an electrode block is prepared by a manner of combining material mixing and material distribution; the vacuum consumable electric arc furnace is used for carrying out three times of smelting; after the materials are discharged from the furnace, the materials are slowly cooled by adopting a manner of sand burying treatment or annealing treatment so that the high-Nb-TiAl based alloy with uniformly-distributed components and no cracks can be obtained. The smelting method for the high-Nb-TiAl based alloy is simple in method and strong in maneuverability; with the adoption of the method, the high-Nb-TiAl based alloy with the uniformly-distributed components and no segregation or impurities can be produced.
Owner:西安超晶科技股份有限公司
Method for preparing high Nb-Ti-Lu porous material
This invention relates to the production of intermetallic compounds. The raw materials of titanium powder, aluminium powder and niobium powder mixture is pressed to form billets by using die forming method. The lower temperature pre-reaction at temperature of 500-800 deg.C for 50-150 min is proceeded upon the billets; and then higher temperature sintering synthesis of up-said billets is proceeded at temperature of 1300-1400 deg.C for 60-180 min. vacuum low pressure sintering method is used for said reaction with its vacuum degree of 0.1-0.001 Pa, and its pressure of 0.5-10 KPa to produce high niobium titanium aluminium porous intermetallic compound.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Slag-free self-protection flux-cored wire for niobium-titanium compound reinforcement hardfacing
InactiveCN103785967AHigh hardnessImprove thermal stabilityArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsSlagFerrotitanium
The invention discloses a slag-free self-protection flux-cored wire for niobium-titanium compound reinforcement hardfacing. The slag-free self-protection flux-cored wire for niobium-titanium compound reinforcement hardfacing comprises a mild-carbon steel strip and a flux core, and the steel strip is filled with the flux core. The flux core contains, by mass, 55-65 percent of high carbon ferro-chrome, four to eight percent of ferroniobium, four to eight percent of ferrotitanium, three to five percent of graphite, two to three percent of ferroboron, eight to fourteen percent of deoxidizing agent and the balance of iron powder, wherein the deoxidizing agent is a mixture of aluminum-magnesium alloy, manganese powder and silicon iron, the mass ratio of the aluminum-magnesium alloy, the manganese powder and the silicon iron is (2-3):(5-8):(1-4), the weight percent of the manganese powder is larger than or equal to the sum of the weight percent of the silicon iron and the weight percent of the aluminum-magnesium alloy, and the ratio of the weight of the flux core to the total weight of the flux-cored wire is between 49 percent and 56 percent. The flux-cored wire is low in cost; (Nb,Ti)C double carbide is dispersed and separated out in the welding process, and the flux-cored wire is low in cost, high and uniform in rigidity, good in abrasion resistance, free of slag clearing in multi-layer welding, low in pore sensitivity and good in welding processing property.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Injection forming method for preparing high Niobium containing Ti-Al alloy components
A method for preparing complex shaped high-niobium titanium aluminum alloy parts with high dimension precision pertains to the field of material forming technology of high-niobium titanium aluminum intermetallic compounds. The process is that argon atomized high-niobium titanium aluminum powder and a polymer which is composed of paraffin PW with the different weight mixing ratio, low-density polyethylene LDPE, polypropylene PP and stearic acid SA are mixed and granulated by a binding agent with the load of 63 to 69 percent, the injection molding is carried out, after that, the solvent degreasing and the thermal degreasing in vacuum atmosphere are adopted for removing the binding agent, the pre-sintering is carried out at the temperature of 600 to 1000 DEG C, and the sintering is finally carried out at the temperature of 1460 to 1480 DEG C in the vacuum atmosphere for preparing the high-Nb-TiAl alloy parts. The method has the advantages that: the method can directly prepare the complex shaped high-Nb-TiAl alloy parts with high dimension precision and good performance, thus realizing the batch production of the high-Nb-TiAl alloy parts with low cost.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for preparing alloy material of high niobium-titanium-aluminum by discharging plasma agglomeration
This invention discloses a method for preparing high-Nb Ti-Al alloy by discharge plasma sintering. The method comprises: loading element mixed powder alloy powder into a graphite mold, placing in a discharge plasma-sintering furnace, applying an axial pressure of 10-80 MPa, heating at a rate of 50-800 deg.C / min in 10-2-6 Pa vacuum or inert atmosphere, sintering at 900-1400 deg.C, keeping the temperature, and cooling to room temperature to obtain high-Nb Ti-Al alloy blocks. The method can prepare highly compact high-Nb Ti-Al alloy blocks with uniform composition and high performance in a short time and at a low sintering temperature. Besides, the method also has such advantages as low energy consumption, little pollution, easy operation and good repeatability.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
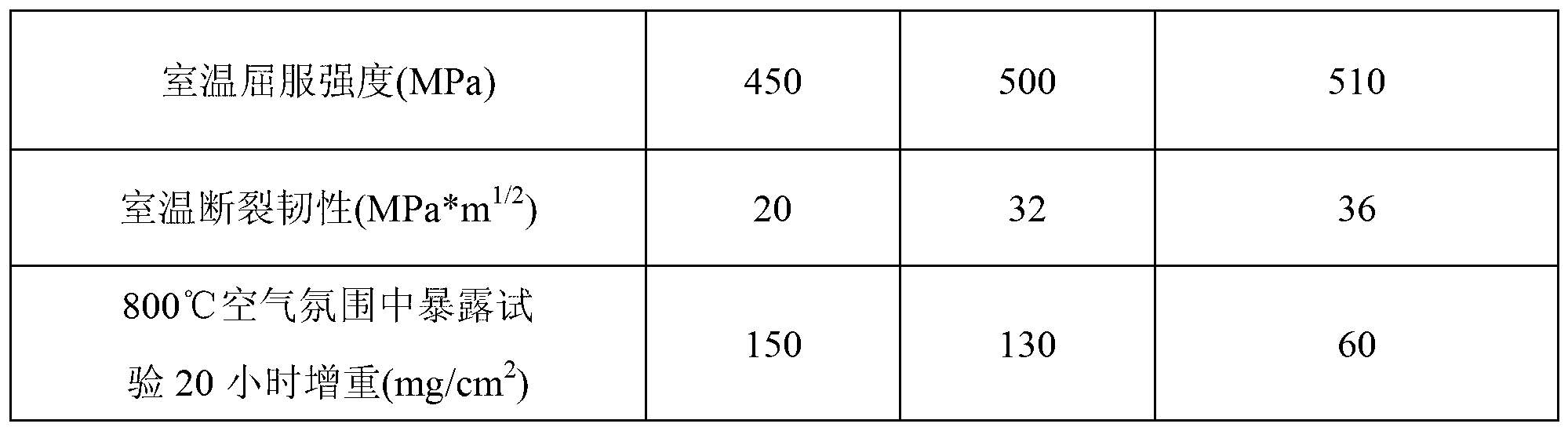
High temperature high performance high-niobium titanium-aluminium alloy
A high-niobium Ti-Al alloy consists of Al 45-46 atoms%, Nb 8-10 atom%, C 0-0.2 atom%, W 0-0.2 atom%, Y 0-0.1 atom% and the remainder being Ti. The alloy texture consists of two ordered phases, i.e. gamma phase and alpha phase and has complete homogeneous and fine laminated texture with crystal grain size of 100-150 microns and interlamilar interval of 0.3-0.4 micron. The high-niobium Ti-Al alloy has the advantages of usage temperature as high as 840-900 deg.C.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Vertical graphene/niobium-titanium-oxygen/sulfur-carbon composite material with three-dimensional porous array structure and preparation method and application of vertical graphene/niobium-titanium-oxygen/sulfur-carbon composite material
ActiveCN108649190AIncrease contact areaShorten the transmission pathMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesCarbon layerCarbon composites
The invention discloses a vertical graphene / niobium-titanium-oxygen / sulfur-carbon composite material with a three-dimensional porous array structure and a preparation method and application of vertical graphene / niobium-titanium-oxygen / sulfur-carbon composite material. The method comprises the steps of vertically growing a graphene nanosheet on a substrate in an intertwining manner; forming a VG / TiNb2O7 nanosheet by TiNb2O7 coating the graphene nanosheet; and forming a VG / TiNb2O7@S-C three-dimensional porous array by a sulfur-doped carbon layer coating the VG / TiNb2O7 nanosheet. According to thepreparation method, a VG / TiNb2O7 nanoarray is reversely synthesized; and the composite material is prepared by using the VG / TiNb2O7 nanoarray as a carrier through constant-current anodic deposition.The composite material disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high cycling stability, high rate capability, coulombic efficiency and the like and is capable of significantly improving the energy density / power density and the cycling stability of a total battery when matched with lithium iron phosphate or a ternary material. The novel composite material disclosed by the invention issuitable for being used as a negative electrode material for a lithium-ion battery and can be applied to various electronic devices, electric vehicles and hybrid vehicles.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Smelting method for titanium-niobium alloy ingot
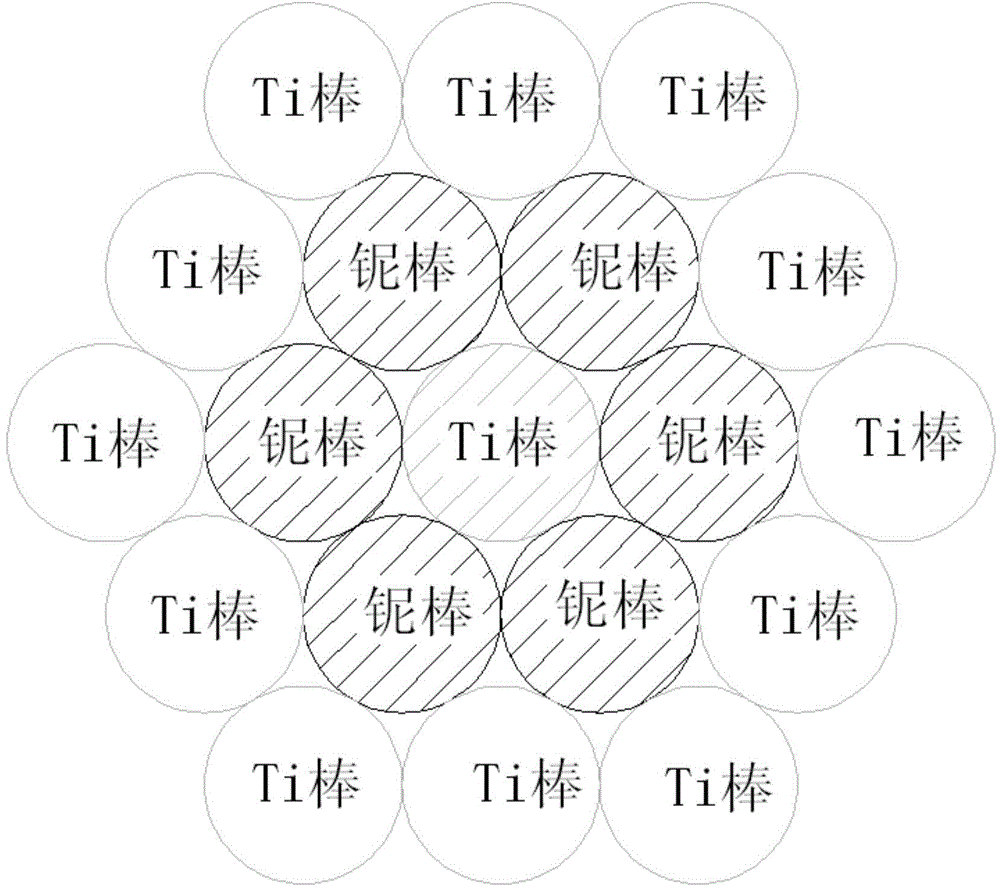
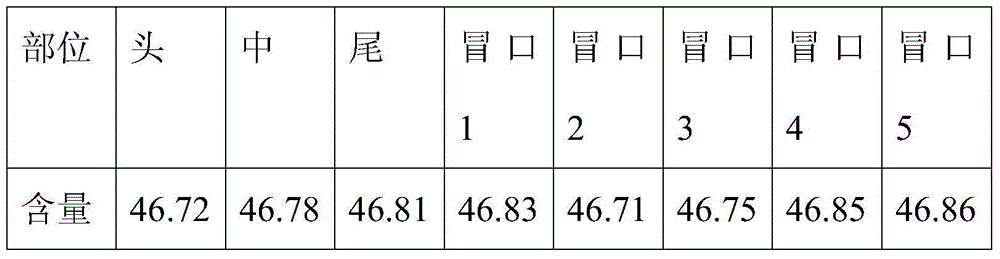
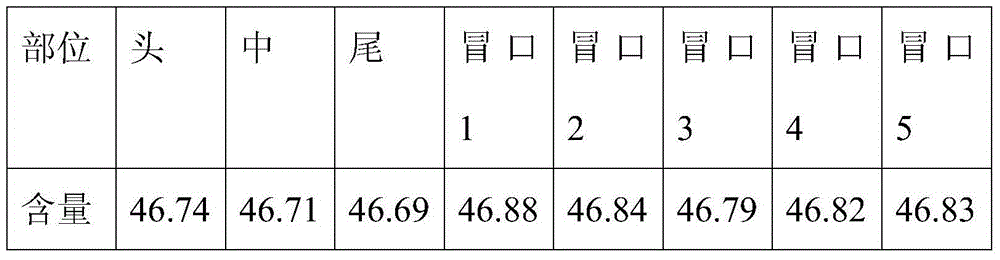
The invention relates to a smelting method for a titanium-niobium alloy ingot. The alloy ingot comprises 46.8-55% by weight of niobium and the balance of titanium. The smelting method comprises the following steps: tailor-welding a plurality of titanium rods and niobium rods into a consumable electrode, wherein a ring of niobium rods is uniformly distributed around one titanium rod and a ring of titanium rods is further uniformly distributed around one niobium rod, and the niobium rods and the titanium rods are arranged in parallel; smelting the consumable electrode in a vacuum consumable electro-arc furnace to obtain a primary ingot, wherein the smelting current is 6-10KA and the smelting voltage is 27-30V; and then, smelting again to obtain the titanium-niobium alloy ingot. The titanium-niobium alloy ingot prepared by the method provided by the invention is uniform and stable in chemical components and the deviation of the chemical components is less than 0.2%. The ingot is segregation-free and high in density with metallurgical defects. The ingot provided by the invention is suitable for producing the titanium-niobium alloy ingot with high metallurgical quality.
Owner:西安超晶科技股份有限公司
Active material, nonaqueous electrolyte battery, and battery pack
InactiveCN104282899AIncrease capacityGood high current discharge performanceNegative electrodesLi-accumulatorsComposite oxideBattery pack
According to one embodiment, there is provided an active material including monoclinic niobium titanium composite oxide particles and a carbon material layer. The monoclinic niobium titanium composite oxide particles can absorb and release Li ions or Na ions and satisfy Formula (1) below. The carbon material layer covers at least a part of surfaces of the niobium titanium composite oxide particles and satisfies Formula (2) below: 0.5≰(α / β)≰2 (1) 0≰(γ / σ)≰0.1 (2)
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Niobium-titanium microalloying HRB400-scale screw-thread steel and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a kind of niobium-titanium microalloying HRB400-scale screw-thread steel and a manufacturing method thereof. The screw-thread steel comprises C, Si, Mn, P, S, Nb, Ti, N and the balance Fe and impurities. The manufacturing method of the niobium-titanium microalloying HRB400-scale screw-thread steel comprises the following steps of smelting in a revolving furnace, treatment outside the furnace, continuous casting, casting blank heating and rolling. During smelting in the revolving furnace, alloy such as silicomanganese and ferroniobium is added for niobium microalloying treatment. During treatment outside the furnace, argon is blown in an argon station, and refining is conducted in an LF furnace. In the process of refining in the LF furnace, a ferrotitanium core-spun yarn is fed for titanium microalloying treatment. According to the technical scheme, before tapping, alloy such as silicomanganese and ferroniobium is added for niobium microalloying treatment, the ferrotitanium core-spun yarn is fed in the process of refining in the LF furnace for titanium microalloying treatment, after titanium is fused into molten steel, proper niobium-titanium microalloying treatment is conducted, the yield of the niobium-titanium alloy is increased, and stable, sustainable and low-cost production of the screw-thread steel is achieved.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL GRP ECHENG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
320MPa low-temperature resistant hot-rolled H-shaped steel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103834861AEnsure low carbon requirementsReduce carbon increase in converterMechanical propertyImpurity
The invention discloses a 320MPa low-temperature resistant hot-rolled H-shaped steel and a preparation method thereof, the 320MPa low-temperature resistant hot-rolled H-shaped steel comprises the following chemical components by weight percent: 0.05-0.11% of C, 0.20-0.35% of Si, 1.05-1.30% of Mn, not more than 0.020% of P, not more than 0.015% of S, 0.020-0.035% of Nb, 0.005-0.025% of Ti, and the balanced of Fe and trace impurity. The production of the 320MPa low-temperature resistant hot-rolled H-shaped steel is realized by using niobium-titanium composite microalloying process through low-carbon content under the high hot-rolling temperature condition, the prepared low-temperature resistant steel is good in mechanical property, and the longitudinal impact is greater than 165J at -30 DEG C.
Owner:LAIWU IRON & STEEL GRP
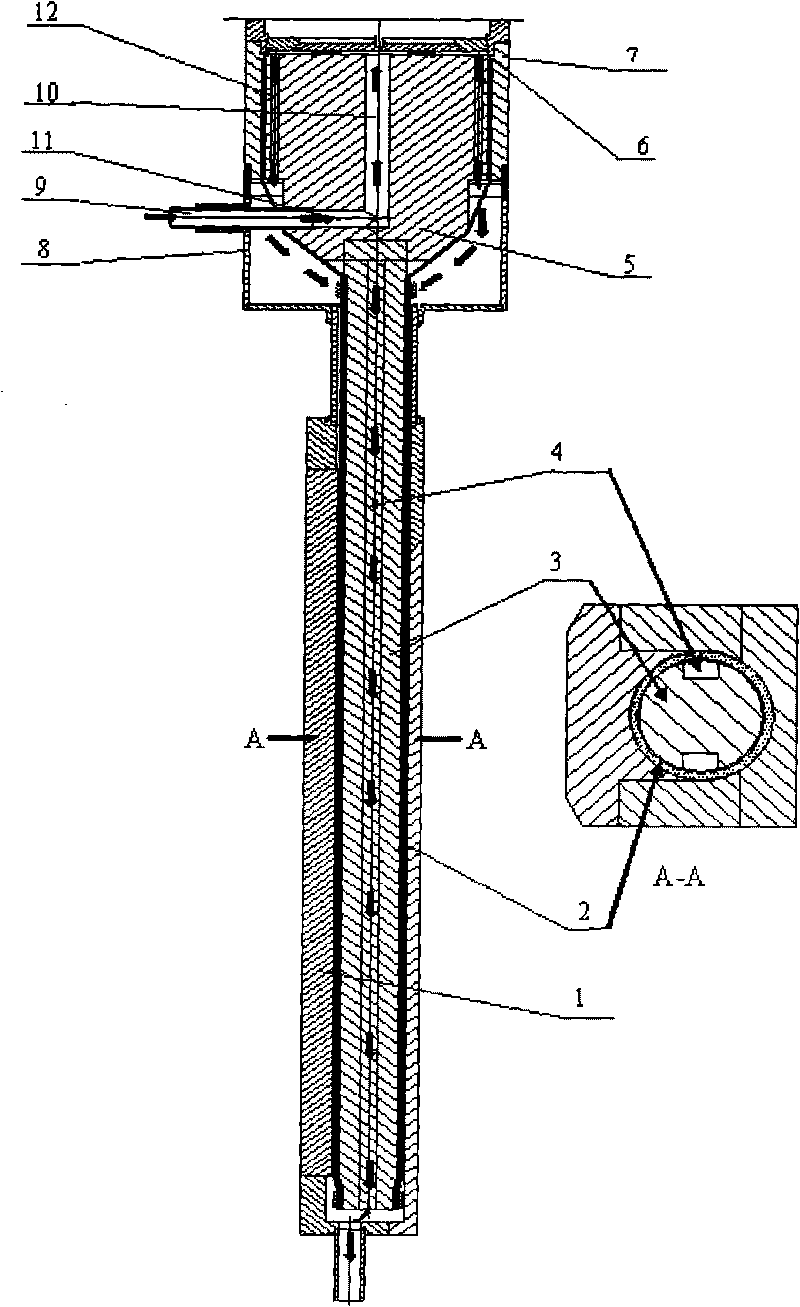
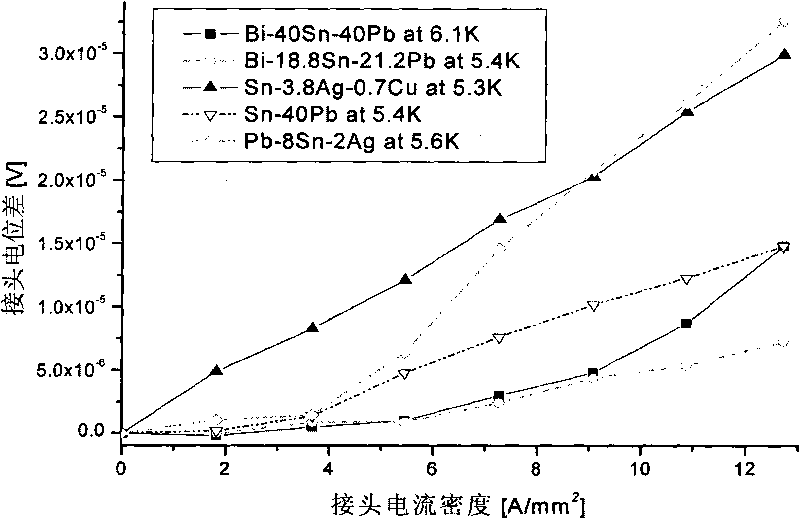
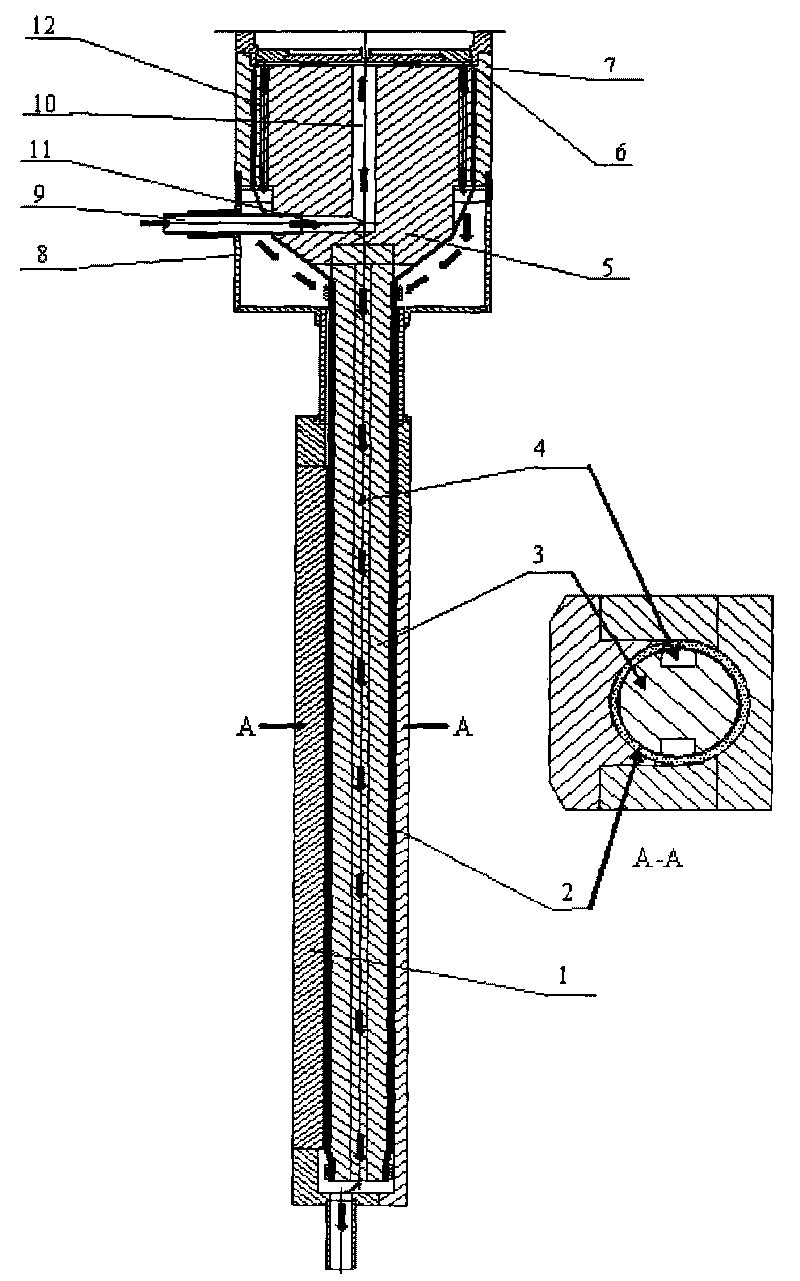
Preparation method of NbTi superconducting wire joint
InactiveCN102738603AEasy to manufactureSimple structureLine/current collector detailsConnection contact member materialRoom temperatureEngineering
The invention discloses a preparation method of a NbTi superconducting joint and relates to a superconducting joint technology. The method comprises the steps of: a) preparing superconducting filaments by NbTi superconducting wires; b) twisting and weaving a plurality of the superconducting filaments together; c) inserting twisted ends of the superconducting filaments into a cold pressing tube in such a manner that the superconducting filaments extend out of the cold pressing tube from the other end; d) applying pressure to a straight section of the cold pressing tube to combine the superconducting filaments and the cold pressure tube together; e) placing the combined cold pressing tube into a copper sleeve and padding welding flux; and f) heating, cooling and solidly jointing at room temperature to obtain a finished product. The preparation method of the NbTi superconducting joint provided by the invention has the advantages of simple structure, simple and convenient preparation, and stable and reliable performance.
Owner:INST OF HIGH ENERGY PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Layered high niobium-titanium-aluminum alloy composite plate and preparation method thereof
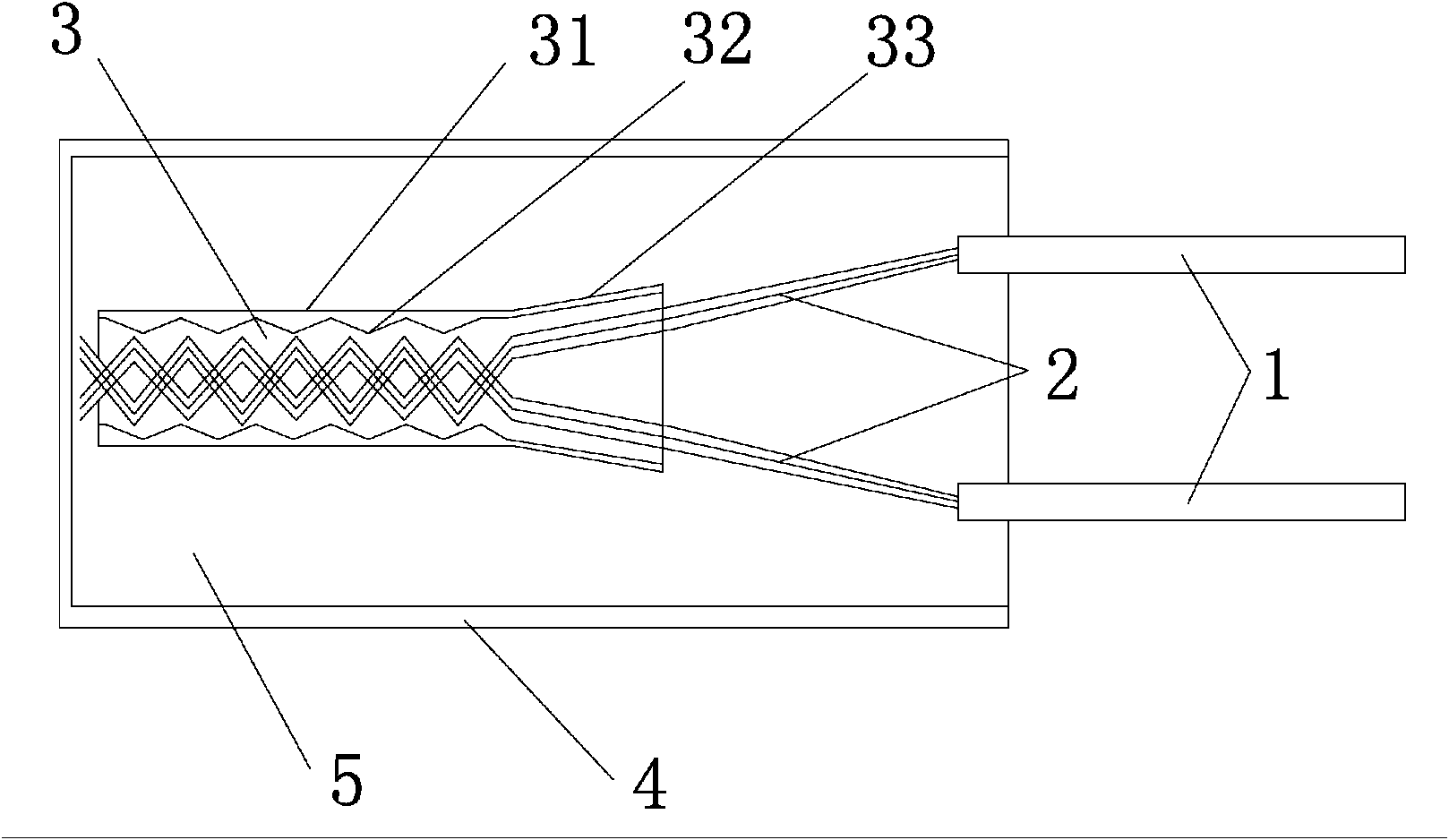
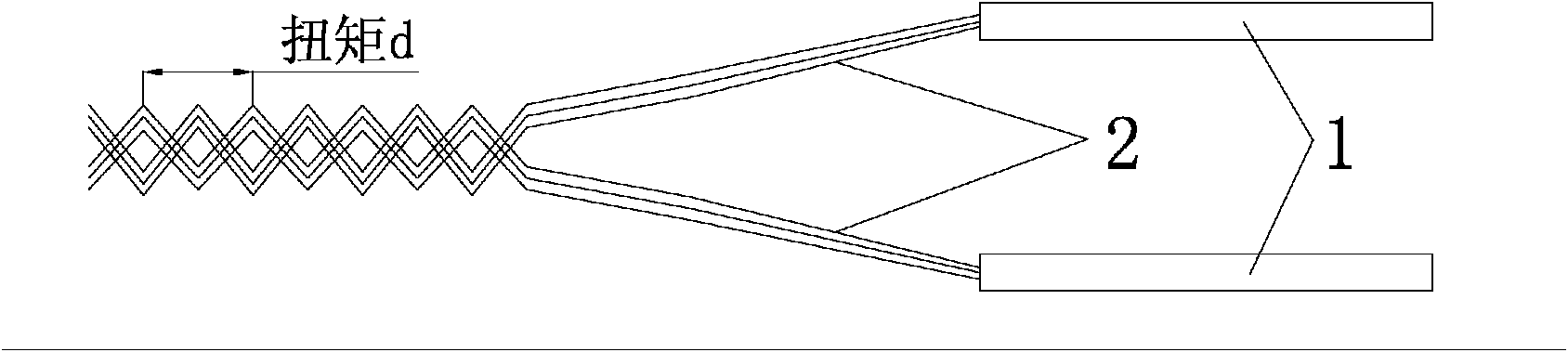
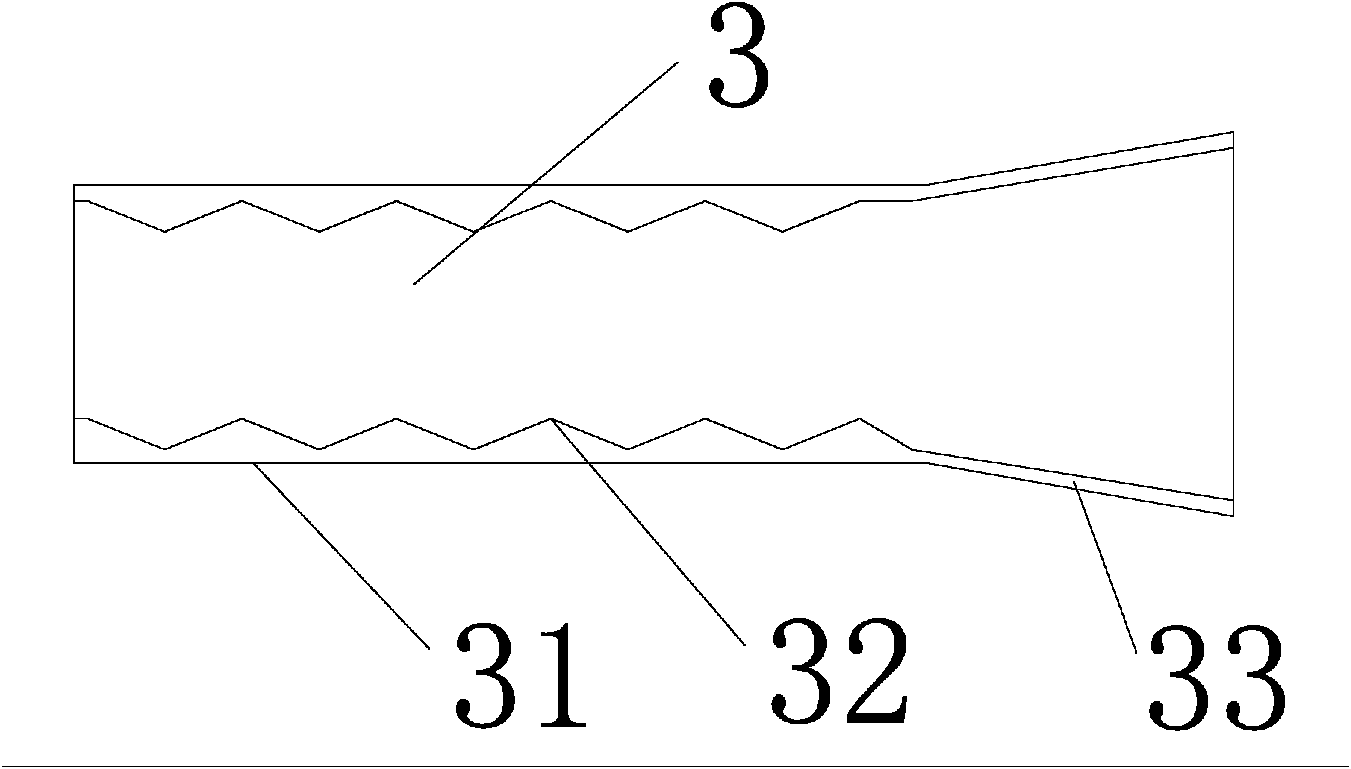
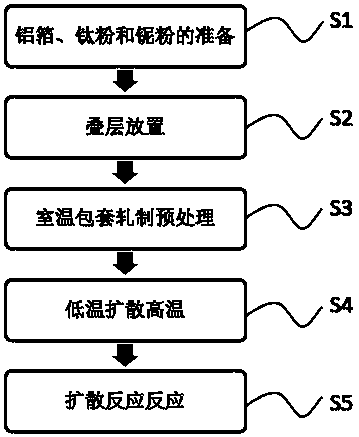
The invention provides a layered high niobium-titanium-aluminum alloy composite plate and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of materials and preparation thereof. A new thought is provided for preparation of a metal-base composite by adopting the laminating hot-pressing composite process of mixed powder of a pure aluminum foil material and titanium powder as well as niobium powder. Titanium-aluminum-based layered materials prepared by adding the niobium element have more excellent mechanical properties such as the high strength and the high toughness. The preparation method comprises the steps that S1, the aluminum foil, the titanium powder and the niobium powder are prepared; S2, laminated storing is conducted; S3, room-temperature pack rolling pretreatment is conducted; S4, a low-temperature diffusion reaction is conducted; and S5, a high-temperature diffusion reaction is conducted. The preparation method of the layered high niobium-titanium-aluminum alloy composite plate can be applied to preparation of the layered high niobium-titanium-aluminum alloy composite plate.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
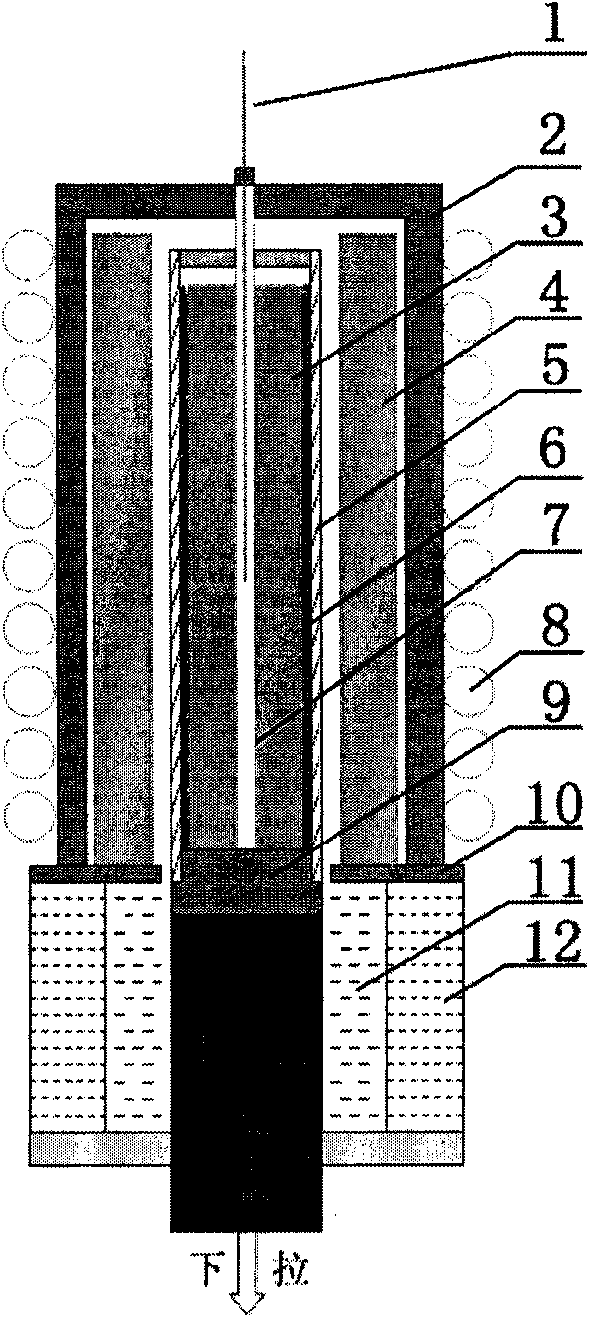
Non-pollution directional solidification method of high-niobium titanium aluminum intermetallic compound
The invention discloses a non-pollution directional solidification method of a high-niobium titanium aluminum intermetallic compound and belongs to the technical field of high-niobium titanium aluminum intermetallic compound materials. The invention solves the problem in the prior art that the high-niobium titanium aluminum alloy is polluted and the dimension is small to reduce the performance of the high-niobium titanium aluminum alloy, and a problem of insufficient superheat degree of smelting the high-niobium titanium aluminum alloy affecting the performance of the high-niobium titanium aluminum alloy further exists in the prior art. The method comprises the following steps of: smelting the upper segment of a pedestal in an electromagnetic red copper crucible and the lower end of a feeding bar through an induction coil; after fused high-niobium titanium aluminum alloy liquid in the electromagnetic red copper crucible forms a hum, driving a pull rod to move downwards, a feeding motor is started, the feeding bar adds materials in the electromagnetic red copper crucible, a cooler provides strong cold to the smelted high-niobium titanium aluminum alloy to form the smelted high-niobium titanium aluminum alloy liquid to columnar crystals with directional solidification tissues; and processing and removing the polycrystalline layer of the columnar crystal high-niobium titanium aluminum alloy ingot to form a high-niobium titanium aluminum alloy ingot with directional solidification. The non-pollution directional solidification method provided by the invention is used for preparing columnar crystal high-niobium titanium aluminum alloy ingots.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Low-temperature ferrite LT-FH40 steel plate applied to hot-rolled ships and production method thereof
The invention relates to a low-temperature ferrite LT-FH40 steel plate applied to hot-rolled ships. The steel plate comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.04-0.09% of C, 0.10-0.30% of Si, 1.35-1.55% of Mn, smaller than or equal to 0.008% of P, smaller than or equal to 0.004% of S, 0.20-0.45% of Ni, 0.010-0.035% of Nb, 0.007-0.020% of Ti, 0.020-0.050% of Alt and the balance being Fe and inevitable impurities. Through cooperation of low-carbon and niobium-titanium alloying composition design, a low-phosphorus and low-sulfur smelting process and a reasonable controlled rolling and cooling process, the low-temperature ferrite LT-FH40 steel plate applied to hot-rolled ships is produced; the hot-rolled state mechanical performance meets the standard requirements. The requirement of low-temperature vessel steel applied to ships is successfully solvedmet by the method; the low-temperature ferrite LT-FH40 steel plate applied to hot-rolled ships can be produced by processes such as converter steelmaking and continuous casting and can be produced by a large number of steel enterprises; the low-temperature ferrite LT-FH40 steel plate applied to hot-rolled ships is produced by a TMCP process, so that the production cost is reduced.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Carbon-silicon-tungsten-yttrium lamellar structure high-niobium titanium-aluminum alloy and preparation method thereof
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com