Light-driven SiC/GaN-based semiconductor device and manufacturing process thereof
A light-driven, semiconductor technology, applied in semiconductor devices, electrical components, circuits, etc., can solve the problem of reducing the effective area of light energy absorption and photo-generated current density, the groove of the device cannot reach the expected depth, and affecting the performance of light-driven power devices. and other problems, to achieve the effect of reducing the surface breakdown electric field, reducing the cost of device application, and solving the weak anti-interference ability of EMI.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] Example 1 An optically driven SiC-based semiconductor device
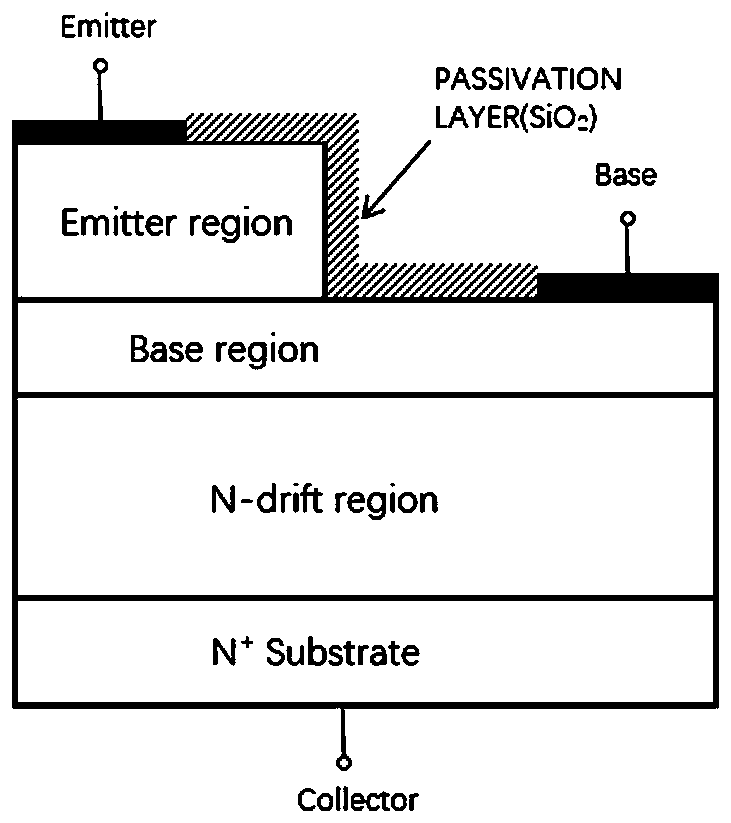
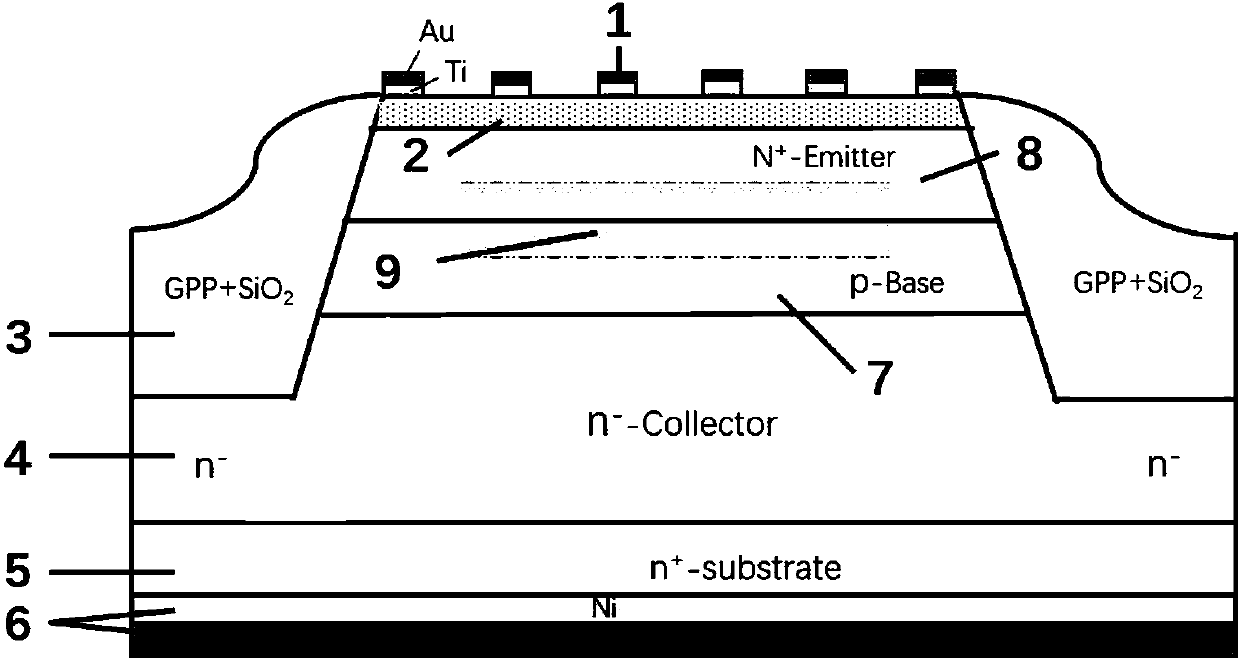
[0057] This embodiment provides a light-driven SiC-based semiconductor device, such as Figure 3-Figure 5 As shown, it includes an emitter structure, a P-type base region 7, a collector structure with an n-type collector region 4, an n+ type substrate structure, and a PN junction passivation protective layer arranged sequentially from top to bottom Structure 3; where
[0058] ①Emitter structure
[0059] The emitter structure includes a comb-shaped metal multilayer electrode 1, a transparent electrode 2 and an n+-type emitter region 8 arranged sequentially from top to bottom. The comb-shaped metal multilayer electrode 1 is located on the surface of the transparent electrode 2 and is in direct contact with the surface , The transparent electrode 2 forms an ohmic contact with the n+ type emitter region 8;
[0060] The comb-shaped metal multilayer electrode 1 is composed of a comb-shaped structure formed by multiple su...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Example 2 An optically driven GaN-based semiconductor device
[0077] The difference between this embodiment and embodiment 1 is:
[0078] In this embodiment, an n-type GaN wafer with a thickness of 300 μm is used as the substrate, the doping element selected for the p-type base region 7 is magnesium, and the n+ type emitter region 8, the n- type collector region 4 and the n+ type substrate 5 are selected The doping element is silicon.
[0079] The structure of the other parts of this embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment.
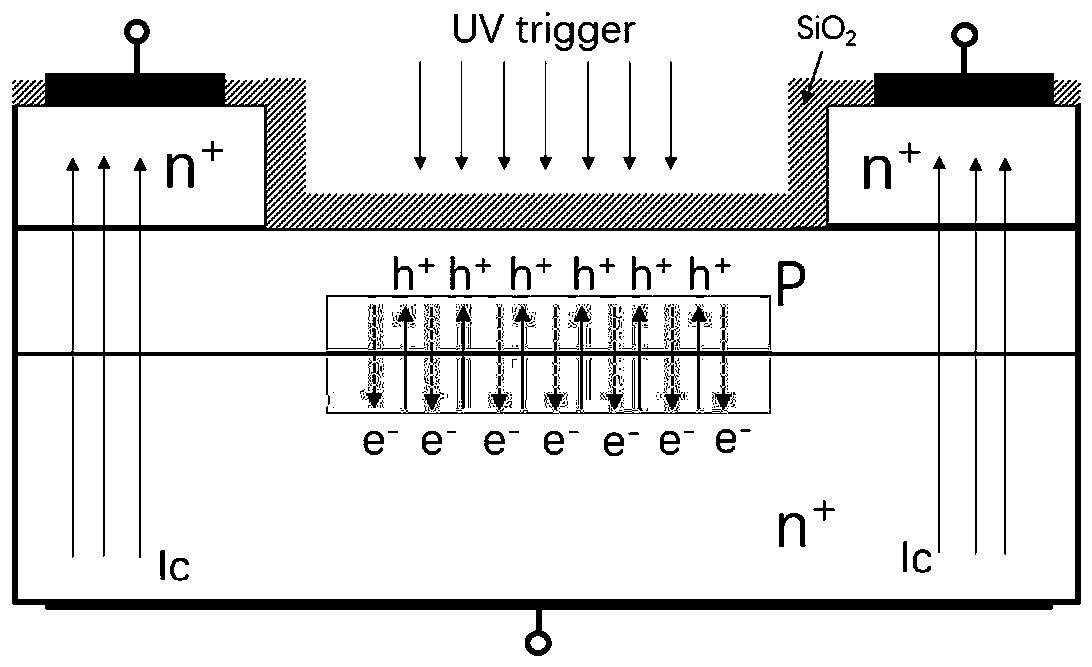
[0080] The working principle of this embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment.
Embodiment 3
[0081] Embodiment 3 A manufacturing process of an optically driven SiC / GaN-based semiconductor device
[0082] This example is used to make examples 1 and 2, such as Figure 7 As shown, the process is simplified and improved on the basis of the traditional BJT process. The manufacturing process mainly includes the following steps in sequence:
[0083] (1) Choose a commercial 8°off-axis n-type 4H-SiC single crystal wafer with a thickness of 400μm or an n-type GaN wafer with a thickness of 300μm as the substrate, and complete the n-type collector 4 and p-type on the substrate in turn For the epitaxial growth of the base region 7, an ion implantation process is used to form an n+ type emitter region 8 to form an epitaxial wafer;
[0084] (2) An ultra-high vacuum DC magnetron sputtering system is used to deposit a layer of indium tin oxide (ITO) transparent conductive film with a thickness of 20 to 200 nm on the epitaxial wafer as the transparent electrode 2, and then undergo annealing t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com