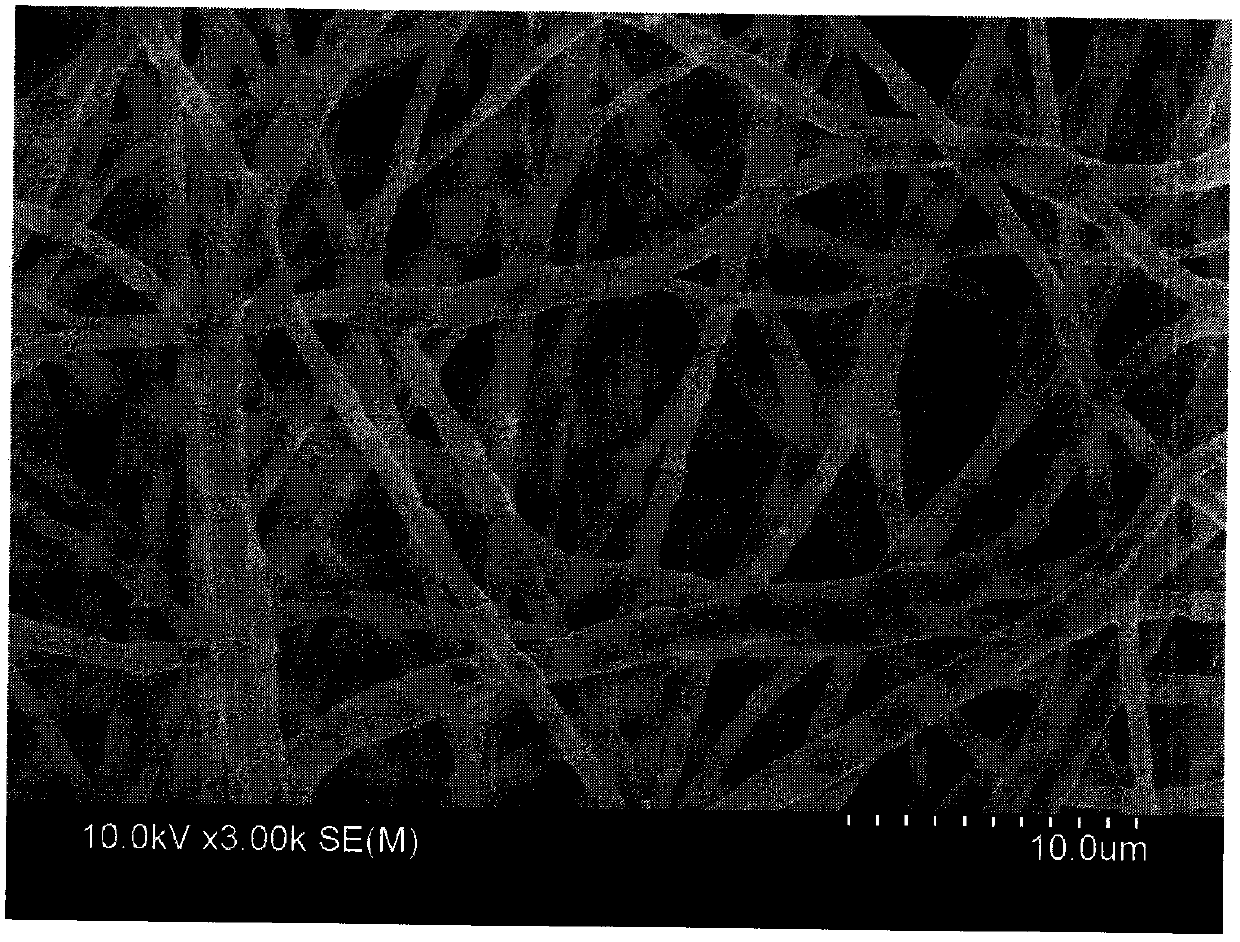
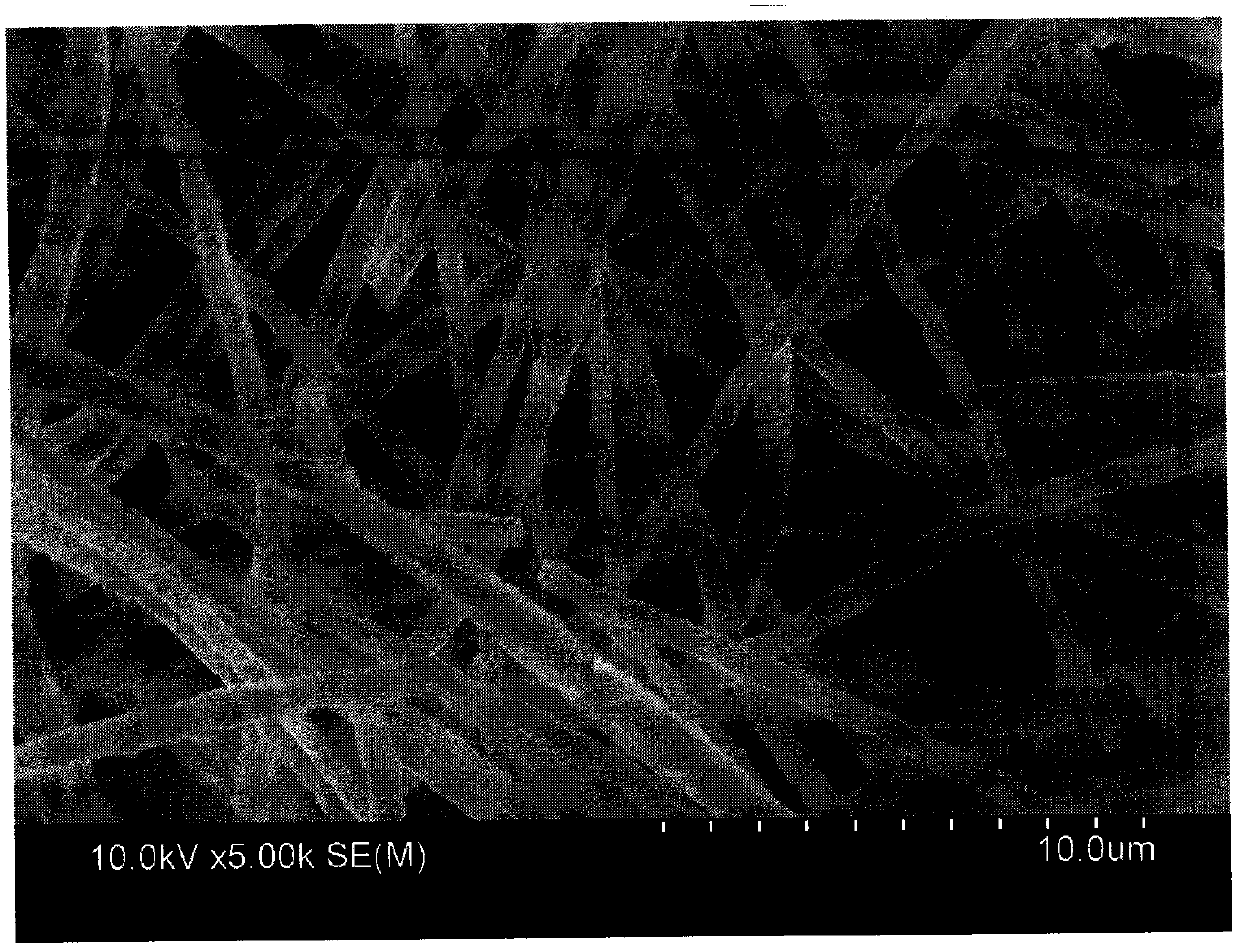
Magnetic cellular porous carbon nanometer fiber@carbon nanotube composite material prepared by carbonization & magnetization & vapor deposition
A nanofiber, carbon nanotube technology, applied in nanotechnology, nanotechnology, nanotechnology for materials and surface science, etc., can solve the problem that the uniformity of physical doping cannot be guaranteed, the specific surface area and activity cannot be provided, and the operation is difficult. And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Add 1 g of polyvinyl alcohol into 9 mL of distilled water, and keep stirring to make it fully swell, then put it into a constant temperature oil bath at 90°C, and stir while heating to obtain a polyvinyl alcohol solution. Dissolve 0.4g of boric acid in 10g of water at room temperature. Take 30 μL of boric acid with a micro-syringe and add it to 10 g of tetrafluoroethylene aqueous emulsion, mix evenly, and then blend with polyvinyl alcohol solution reduced to room temperature to prepare a solution with a mass ratio of polyvinyl alcohol polyvinyl alcohol to tetrafluoroethylene of 1:6, and finally Add 3g of ferric chloride and continue stirring for 12h to obtain spinning solution 1.
[0027]The above-mentioned spinning solution is added to the spinning device, and the spinning process parameters are: air flow rate 0.1MPa, spinning voltage 40kV, receiving distance 50cm, extrusion rate 20mL / h, spinning for a certain period of time to obtain ferric chloride / polyethylene Alco...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Add 0.8 g of polyvinyl alcohol into 9.2 mL of distilled water, and keep stirring to make it fully swell, then put it into a constant temperature oil bath at 90°C, and stir while heating to obtain a polyvinyl alcohol solution. Dissolve 0.3g of boric acid in 10g of water at room temperature. Take 45 μL of boric acid with a micro-syringe and add it to 12 g of tetrafluoroethylene aqueous emulsion, mix evenly, and then blend with polyvinyl alcohol solution restored to room temperature to prepare a solution with a mass ratio of polyvinyl alcohol to polytetrafluoroethylene of 1:9, and finally Add 2g of pressed ferric chloride and continue to stir for 9h to obtain a spinning solution.
[0032] The above spinning solution is added to the spinning device, and the spinning process parameters are: air flow rate 0.06MPa, spinning voltage 25kV, receiving distance 50cm, extrusion rate 40mL / h, spinning for a certain period of time to obtain ferrous chloride / polyethylene Vinyl alcohol / ...
Embodiment 3
[0036] Add 1.2 g of polyvinyl alcohol into 8.8 mL of distilled water, and keep stirring to make it fully swell, then put it into a constant temperature oil bath at 90°C, and stir while heating to obtain a polyvinyl alcohol solution. Dissolve 0.5g of boric acid in 10g of water at room temperature. Take 15 μL of boric acid with a micro-syringe and add it to 24 g of tetrafluoroethylene aqueous emulsion, mix evenly, and then blend with polyvinyl alcohol solution reduced to room temperature to prepare a spinning solution with a mass ratio of polyvinyl alcohol polyvinyl alcohol to tetrafluoroethylene of 1:3. .
[0037] Add the above spinning solution into the spinning device, the spinning process parameters are: air flow rate 0.14MPa, spinning voltage 45kV, receiving distance 50cm, extrusion rate 30mL / h, spinning for a certain period of time to obtain ferric nitrate / polyvinyl alcohol / PTFE / boric acid composite microfiber.
[0038] The obtained composite microfibers were subject...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com