Method of producing environment-friendly soap and slow release fertilizer by means of kitchen waste
A kitchen waste, slow-release technology, applied in the preparation of organic fertilizers, chemical instruments and methods, soap detergents and other compounding agents, etc., can solve the problem that plants are difficult to absorb nutrients, large-scale production and application, and difficult to decompose oil and other problems, to shorten the fermentation time, improve the ability to resist pests, and reduce the loss of nitrogen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
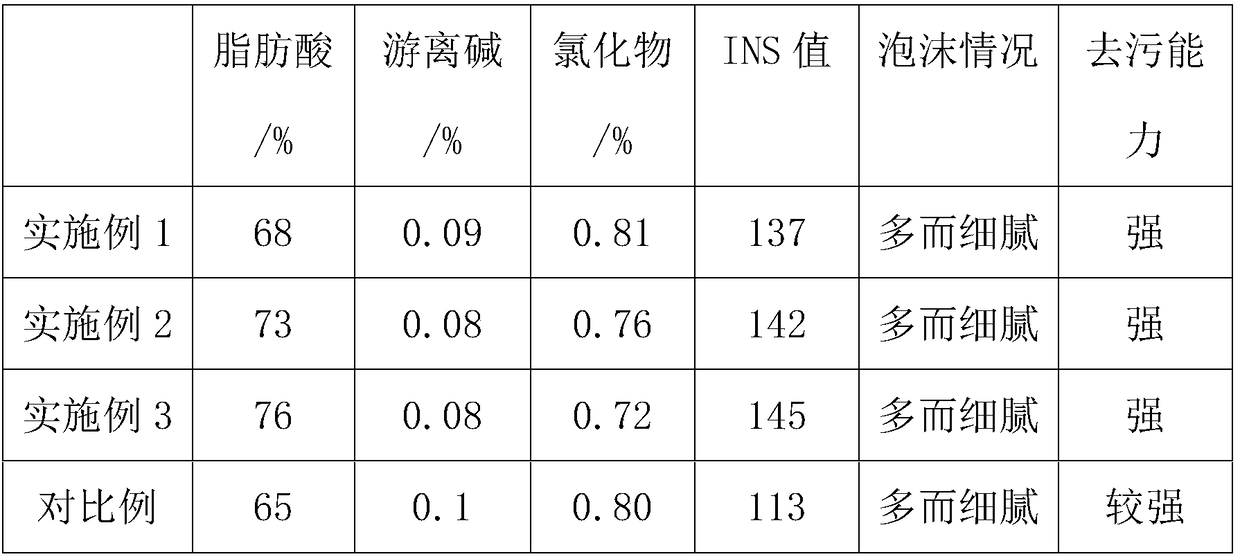
[0029] Step 1: Heat the kitchen waste to 100°C, stir continuously until no bubbles are generated, filter the kitchen waste oil and solid residue, add 5% concentrated H2O with a mass fraction of 75% to the kitchen waste oil 2 SO 4 and 20% sodium dodecylbenzenesulfonate, react until the oil and water layers are completely separated, remove the liquid in the water layer, and obtain crude oil;
[0030] Step 2: Add 3% H to the crude oil extracted in Step 1 2 o 2 and 3.5% activated clay, stirred at 60°C for 20 minutes to obtain decolorized oil;
[0031] Step 3: Add NaOH to the decolorized oil in Step 2, stir and saponify for 2 hours, until the pH is stable at 7.5, then add 10% NaCl to obtain soap gum;
[0032] Step 4: At 40°C, uniformly mix the soap gum in Step 3 with 0.5% methyl ethyl ketone peroxide and 13% polyacrylic acid, let it settle for 1 day, solidify, press, and dry to obtain the environmentally friendly soap;
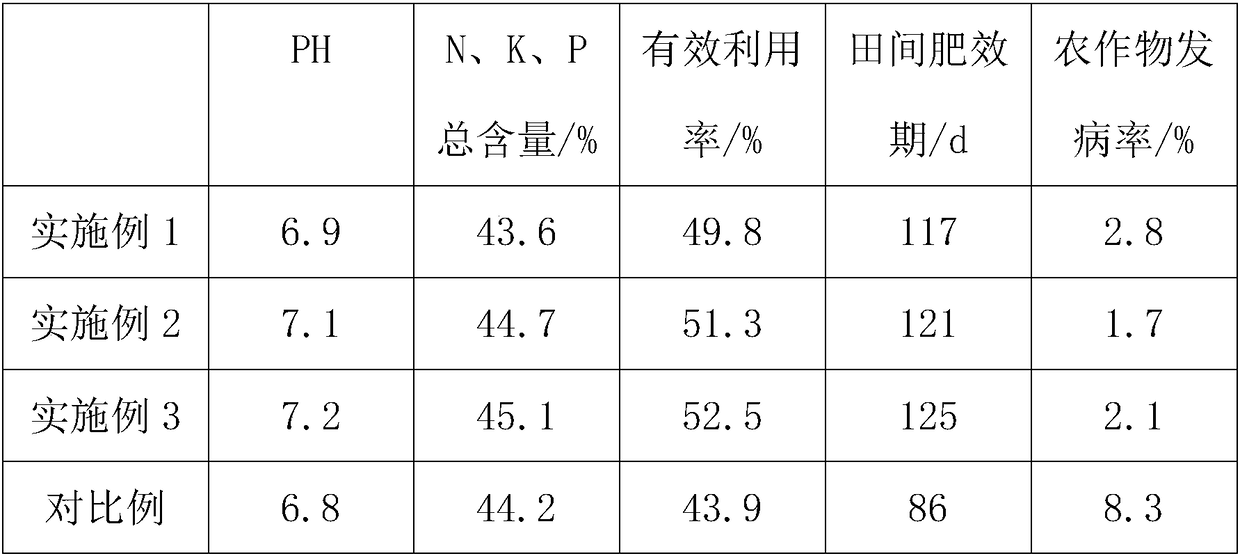
[0033] Step 5: According to the weight ratio of 1.5:1:0.8...
Embodiment 2
[0036] The operation is the same as in Example 1, wherein the heating temperature in step 1: 105°C, concentrated H 2 SO 4 Dosage and mass fraction: 7%, 80%, surfactant: 25%, sodium cetyl sulfate; H in step two 2 o 2 : 3.5%, activated clay: 5%, stirring: 65 ℃, 25min; lye in step 3: Na 2 CO 3 , saponification: 2.5h, PH: 7.6, NaCl: 15%; temperature in step 4: 45°C, hardener: 1.25%, cyclohexanone peroxide, viscous agent: 15%, methyl hydroxyethyl cellulose, Precipitation: 1.5 days; Municipal garbage in step five: pericarp, weight ratio of each component of substrate: 2:1.5:1, mesh number: 55; The parts by weight of each component of slow-release agent in step six: 17,14,27, 46; dosage of sustained release agent: 13%, YM bacteria: 2%, temperature: 85°C, fermentation: 5 days.
Embodiment 3
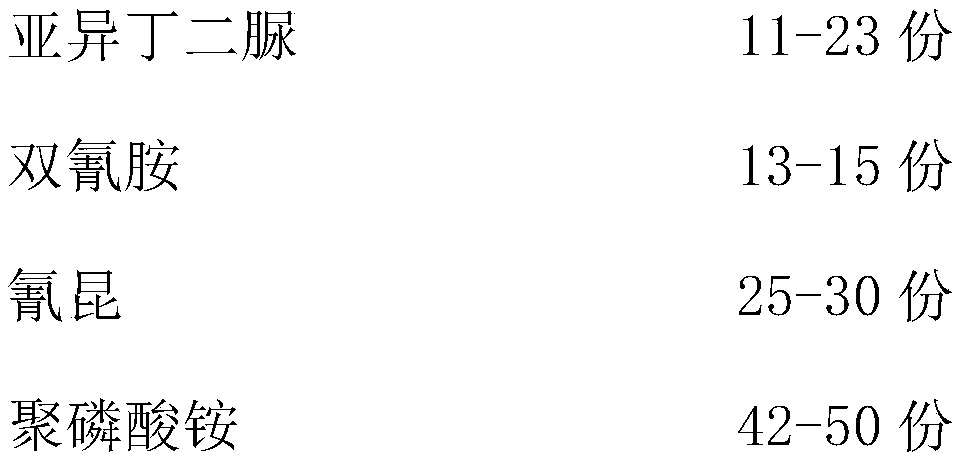
[0038] The operation is the same as in Example 1, wherein the heating temperature in step 1: 110°C, concentrated H 2 SO 4 Dosage and mass fraction: 10%, 85%, surfactant: 30%, fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate; in step 2, H 2 o 2 : 4%, activated clay: 6.5%, stirring: 70°C, 30min; step 3 in lye: KOH, saponification: 3h, PH: 7.8, NaCl: 30%; step 4 in temperature: 50°C, hardener: 1.25 %, cyclohexanone peroxide, viscous agent: 17%, associative polyurethane, precipitation: 2 days; urban garbage in step 5: waste paper, weight ratio of each component of the substrate: 2.5:2:1.2, mesh number : 80; in step 6, the parts by weight of the components of the slow-release agent: 23, 15, 30, 50; the dosage of the slow-release agent: 15%, YM bacteria: 3%, temperature: 90° C., fermentation: 6 days.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com