Streptococcus equi strain XJMSY16-1 and application thereof in streptococcus equi vaccine
A Streptococcus zooepidemicus and vaccine technology, applied to a strain of Streptococcus zooepidemicus strain XJMSY16-1 from horses and its application in equine streptococcal disease vaccines, can solve the needs of the rapid development of the horse industry, which is difficult to achieve Effective control, mutual immunity differences and other issues, to achieve the effect of high added value of products, high market demand, and no risk of poisoning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: Culture and biological characteristics of Streptococcus zooepidemicus strain XJMSY16-1 CGMCC No.12428.
[0039] Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus XJMSY16-1 CGMCC No.12428 was isolated from the pus of Streptococcus equi diseased horses, inoculated in blood-based medium, and cultured at 37°C for 12-15 hours. The bacteria has the following characteristics: (1) Colony characteristics: the diameter of the colony cultured on the blood agar plate for 1 day is 0.3-1.2 mm, the colony is round, the surface is smooth, the edges are neat, raised, off-white. (2) Morphological characteristics of bacteria: the bacteria are round or oval; Gram staining is positive; the diameter of the bacteria is 1.1-2.1 μm. (3) Physiological and biochemical characteristics: facultative anaerobic growth; growth temperature ranges from 27°C to 39°C, optimum growth temperature is 37°C; pH growth range is 6-8, optimum growth pH is 7.3-7.6; can ferment glucose, sucrose , does not hydrolyz...
Embodiment 2
[0041]Embodiment 2: PCR amplification and sequence determination of the 16S rRNA gene of Streptococcus zooepidemicus strain XJMSY16-1 CGMCC No.12428
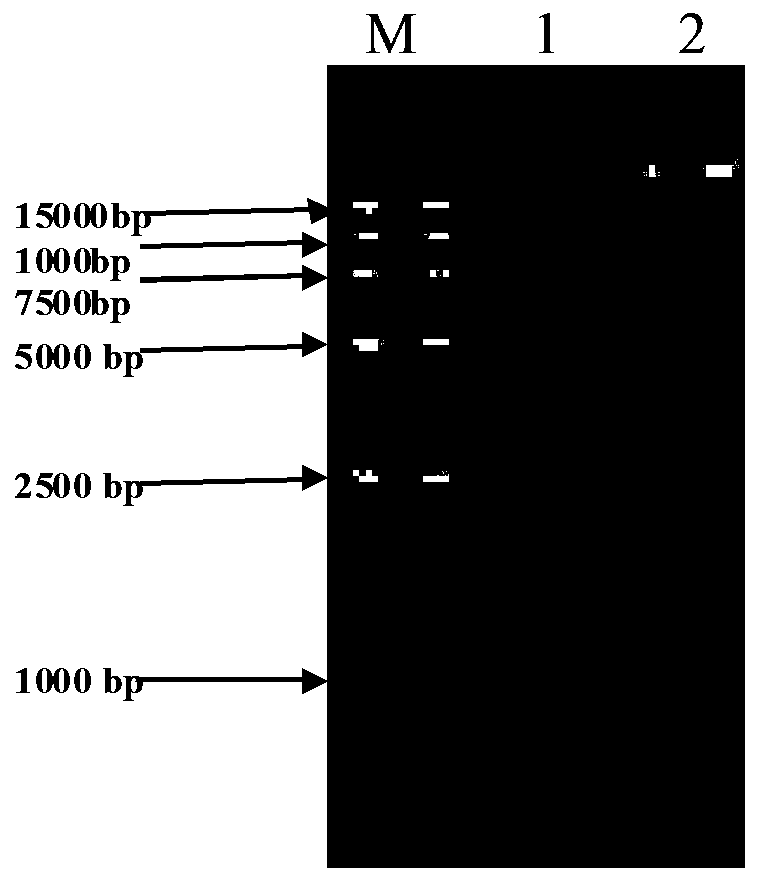
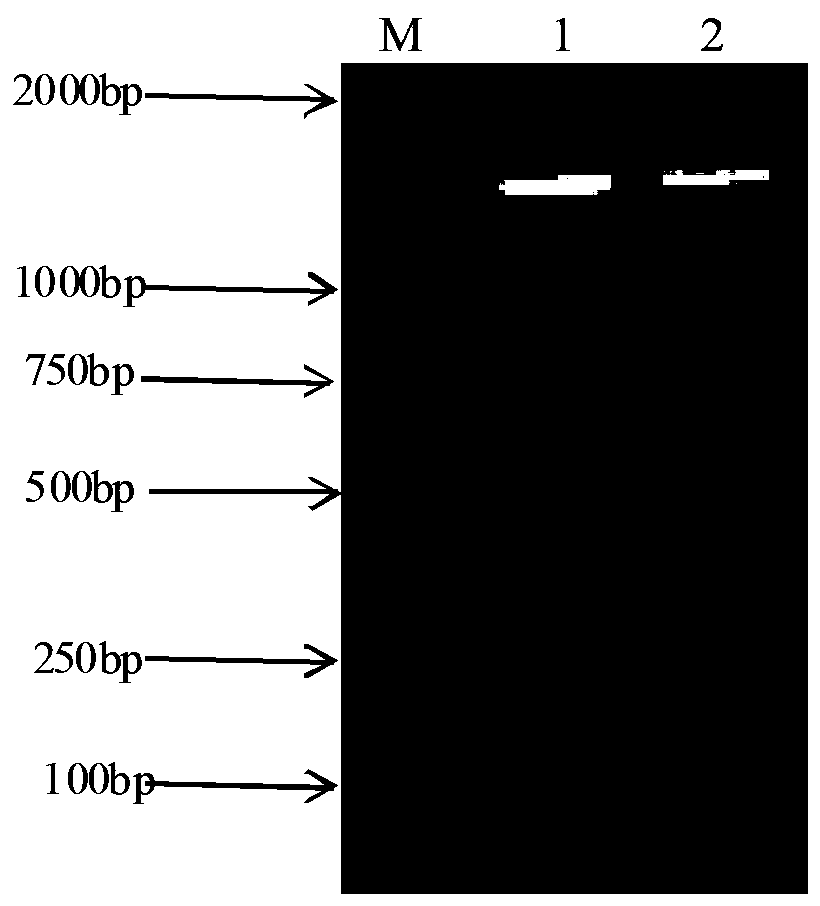
[0042] Streptococcus zooepidemicus strain XJMSY16-1 CGMCC No.12428 was inoculated in liquid medium, and the fermentation broth grown to the late logarithmic period was centrifuged (4500 rpm, 5 minutes) to remove the supernatant, and TE (50 mM Tris, 50 mM EDTA-Na 2 ) solution for 2 times; mix the cells with 0.5 mL TES solution, add appropriate amount of lysozyme, and incubate at 37 ℃ for 2 hours; add 0.2 mL 20 % SDS, and incubate at 60 ℃ for 10 minutes; add 0.3 mL 5M NaClO 4 , mix well; add an equal volume of phenol-chloroform-isoamyl alcohol (25: 24: 1), shake gently for about 5 minutes, centrifuge (5000 rpm, 5 minutes), absorb the supernatant, and then use phenol- Chloroform-isoamyl alcohol (25: 24: 1) was treated once; then chloroform-isoamyl alcohol (24: 1, v / v) was treated twice until no protein film appeared; supernatant w...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Embodiment 3: Preparation of inactivated antigen
[0048] The isolates were inoculated in TM medium supplemented with 2% horse serum, cultured at 37°C and 180r / min for 18-24 hours, and inactivated with 0.4% formaldehyde for 36-48 hours. After complete inactivation, centrifuge at 7000rpm / min for 15min to remove the supernatant. The bacterial pellet was diluted to 1×10 with sterilized PBS (pH7.2, 10mmol) 7 CFU / mL. Immunize rabbits after emulsification with the same amount of complete Freund's adjuvant, emulsify with the same concentration of bacteria and the same amount of incomplete Freund's adjuvant 3 weeks later, sterility test and safety test are carried out after the vaccine is fully shaken and mixed.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com