High-reliability inorganic all-solid-state electrochromic film device and preparing method thereof
An electrochromic, thin-film device technology, applied in instruments, nonlinear optics, optics, etc., can solve the problems of low yield of film forming and high production cost, achieve precise control of light passing rate, prolong life, and improve response time. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
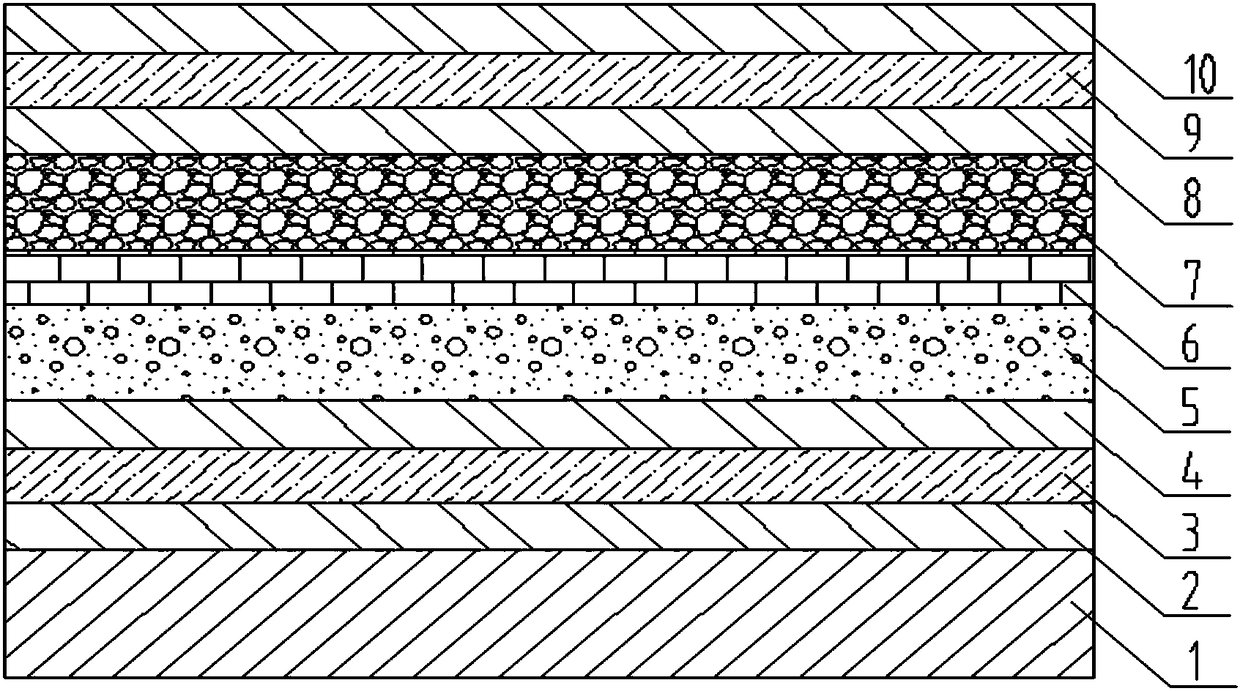
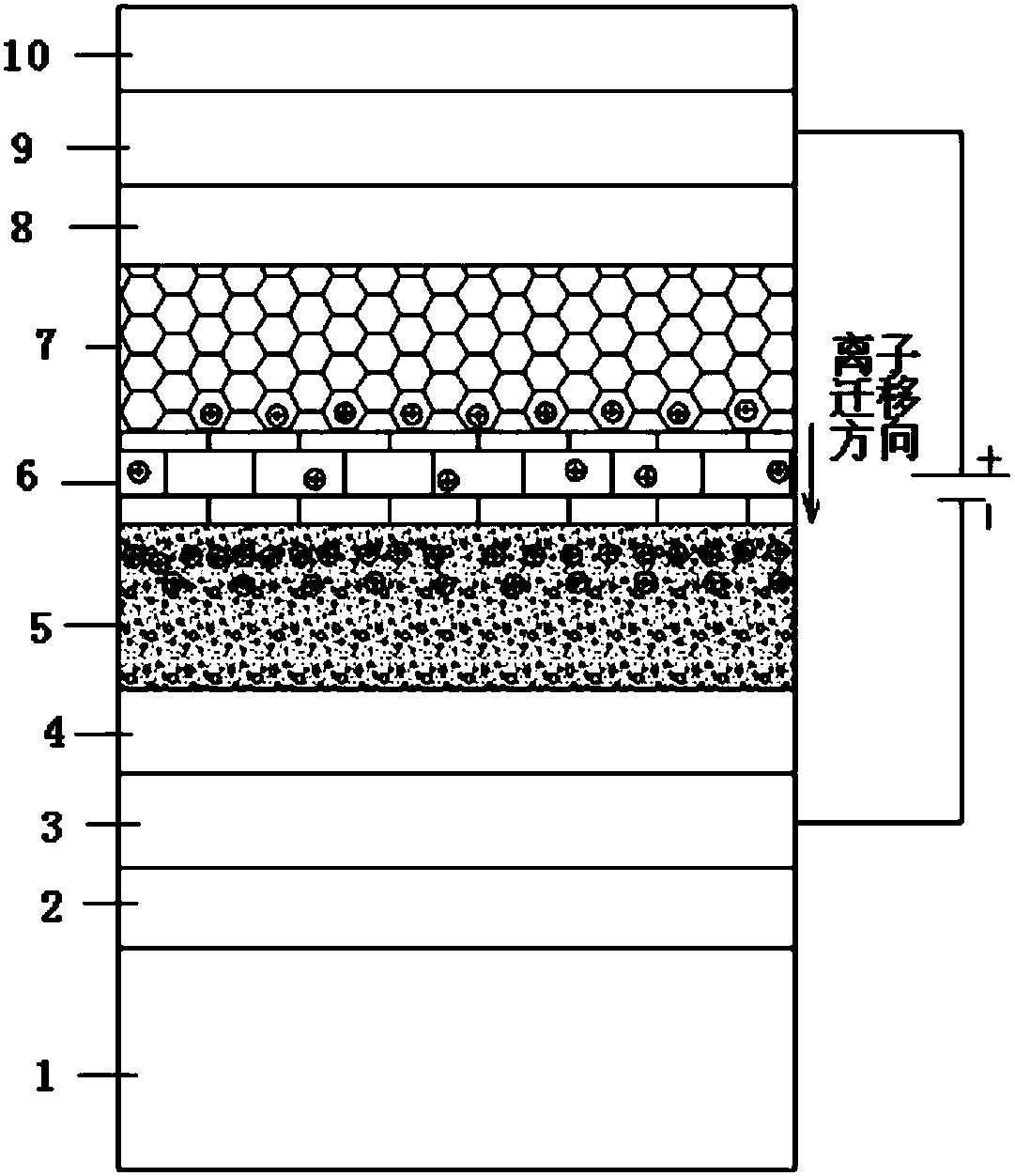
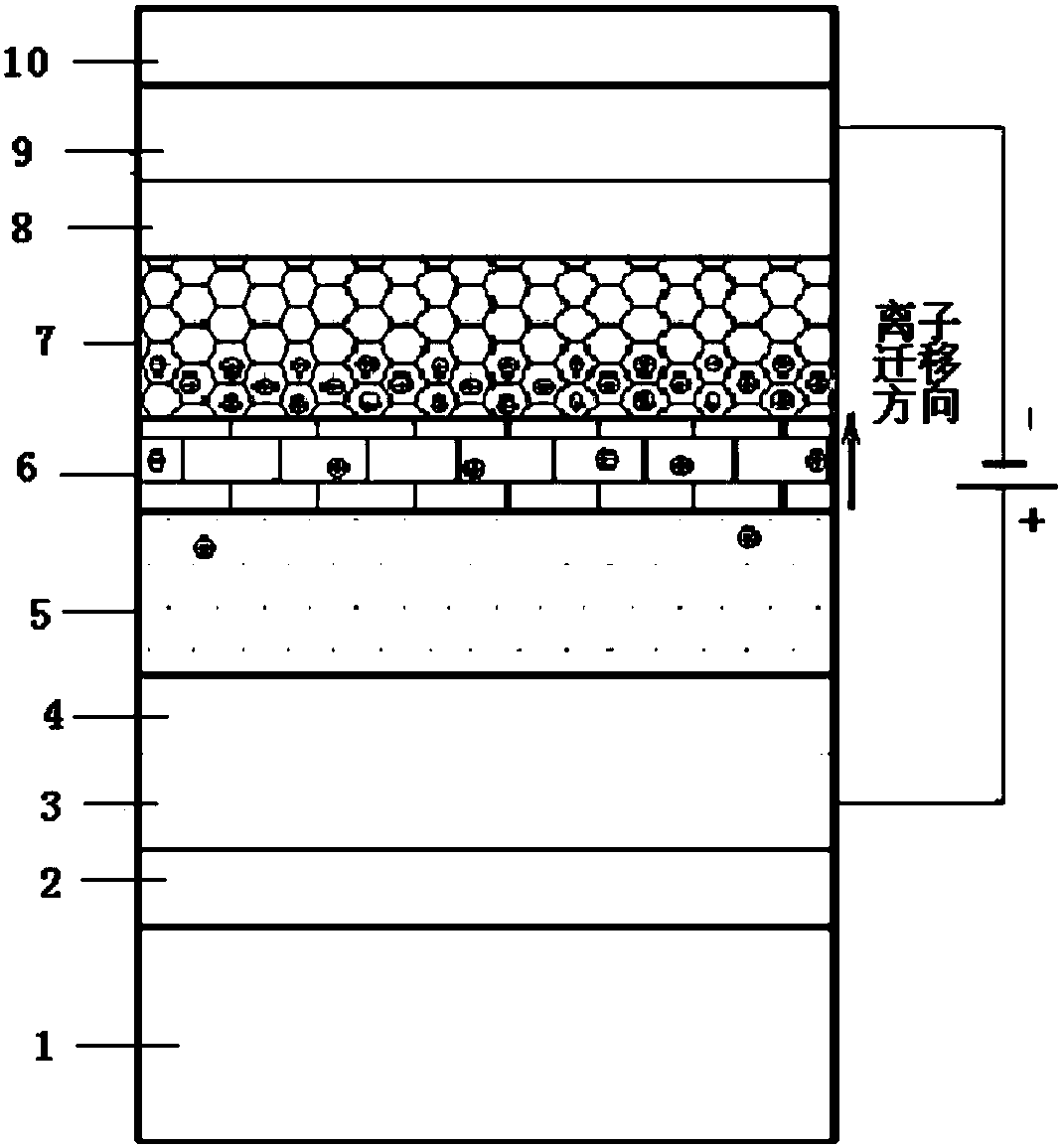
[0056] An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for preparing an inorganic all-solid-state electrochromic thin film device, comprising the following steps: forming a first protective layer, a first transparent conductor layer, and a second protective layer on a substrate in sequence by vapor deposition. layer, an inorganic color-changing layer, an inorganic ion-conducting layer, an inorganic ion storage layer, a third protective layer, a second transparent conductor layer and a fourth protective layer to obtain an inorganic all-solid-state electrochromic thin film device.
[0057] In the embodiment of the present invention, the substrate can be washed, dried, and then put into a coating system to form the above-mentioned film layers in sequence. The contents of the substrate and each layer are as described above, and will not be repeated here.
[0058]Physical vapor deposition (Physical Vapor Deposition, PVD) technology refers to the use of physical methods und...
Embodiment 1
[0065] The device structure of the film-layer combination in this embodiment is as follows: using ultra-clear glass with a thickness of 1.8 mm as the substrate, sequentially formed: bottom protective layer: silicon dioxide; bottom transparent conductor layer: indium tin oxide; protective layer: silicon dioxide; color-changing layer : tungsten oxide layer; ion conductor layer: lithium tungsten oxide layer; ion storage layer: lithium-doped tungsten nickel oxide layer; protective layer, silicon oxide; top transparent electrode layer: indium tin oxide; top protective layer, silicon dioxide.
[0066] The specific manufacturing process is as follows:
[0067] (1) The glass substrate is cleaned and dried, and enters the coating system.
[0068] (2) Intermediate frequency reactive sputtering rotating silicon target to prepare silicon dioxide; set power AC 30KW, atmosphere: argon and oxygen mixed, air pressure 3×10 -4 mbar, film thickness 20nm.
[0069] (3) Magnetron sputtering rotat...
Embodiment 2
[0079] The device structure of the film layer combination of this embodiment is the same as that of Embodiment 1;
[0080] The difference in the specific manufacturing process is: using a rotating lithium tungsten oxide target to directly form a lithium tungsten oxide layer; radio frequency 13.56MHz, the atmosphere is mixed with argon and oxygen, and the mixed volume ratio Ar 2 :O 2 =2:3, air pressure 8×10 -4 mbar, forming a lithium tungsten oxide layer with a thickness of 200nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com