A kind of preparation method of tungsten disulfide nanosheet
A technology of tungsten disulfide and nanosheets, which is applied in the field of preparing tungsten disulfide nanosheets, to achieve the effects of improved stability and safety, optimized process parameters, and easy availability of raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0040] A method for preparing stable tungsten disulfide nanosheets, comprising the steps of:
[0041] (1) After mixing and stirring tungsten disulfide and strong acid, after fully infiltrating, add ferrate or metal peroxide to react;
[0042] (2) The product after the reaction of step (1) is slowly added dropwise to deionized water for dilution;
[0043] (3) ultrasonically treating the diluted liquid in step (2) in an ultrasonic dispersion device;
[0044] (4) The liquid after the ultrasonic treatment in step (3) is left to stand, and the tungsten disulfide that has not been stripped or has a low stripping degree in the sediment is removed;
[0045] (5) Suction filtration is performed on the upper layer liquid after step (4) treatment, and the obtained substance is washed with hydrochloric acid first, and then washed to neutrality with deionized water;
[0046] (6) Drying the product obtained in step (5) to obtain tungsten disulfide nanosheets.
[0047] The possible princip...
Embodiment 1
[0063] (1) Weigh 1g of tungsten disulfide powder, stir and mix with 60ml of 98.3% concentrated sulfuric acid in a water bath at 20°C for 4 hours, then slowly add 3g of potassium ferrate, and continue to stir for 10 hours to fully react;
[0064] (2) The reactant is slowly added dropwise to deionized water for dilution;
[0065] (3) ultrasonically treat the diluted liquid at 300W for 8h;
[0066] (4) Leave the liquid after ultrasonic treatment for 12 hours to remove tungsten disulfide that has not been stripped or has a low stripping degree in the sediment;
[0067] (5) The treated upper layer liquid is subjected to suction filtration, and the obtained substance is first washed with hydrochloric acid for 2-3 times, and then washed with deionized water to neutrality;
[0068] (6) drying the obtained product at 60° C. for 10 h to obtain tungsten disulfide nanosheets.
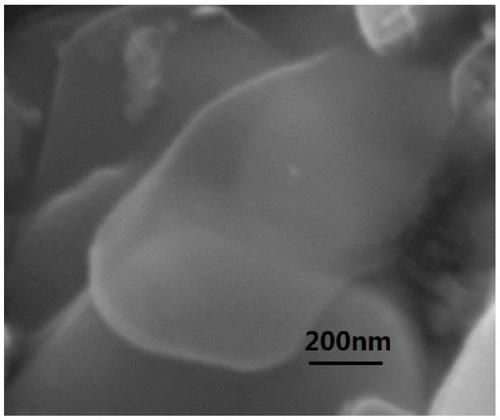
[0069] The scanning electron micrograph of the tungsten disulfide nanosheet prepared in the present embodiment...
Embodiment 2
[0071] (1) Weigh 1g of tungsten disulfide powder, stir and mix with 80ml of 68% concentrated nitric acid in a water bath at 20°C for 4 hours, then slowly add 6g of potassium ferrate, and continue to stir for 10 hours to fully react;
[0072] (2) The reactant is slowly added dropwise to deionized water for dilution;
[0073] (3) ultrasonically treat the diluted liquid at 300W for 8h;
[0074] (4) Leave the liquid after ultrasonic treatment for 12 hours to remove tungsten disulfide that has not been stripped or has a low stripping degree in the sediment;
[0075] (5) The treated upper layer liquid is subjected to suction filtration, and the obtained substance is first washed with hydrochloric acid for 2-3 times, and then washed with deionized water to neutrality;
[0076] (6) drying the obtained product at 60° C. for 10 h to obtain tungsten disulfide nanosheets.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com