Method for improving connection strength of thermoplastic composite and metal
A composite material and metal connection technology, applied in the field of welding, can solve the problems of small heat-affected zone, insufficient connection, high cost of implanted materials, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing the contact area and improving the connection strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
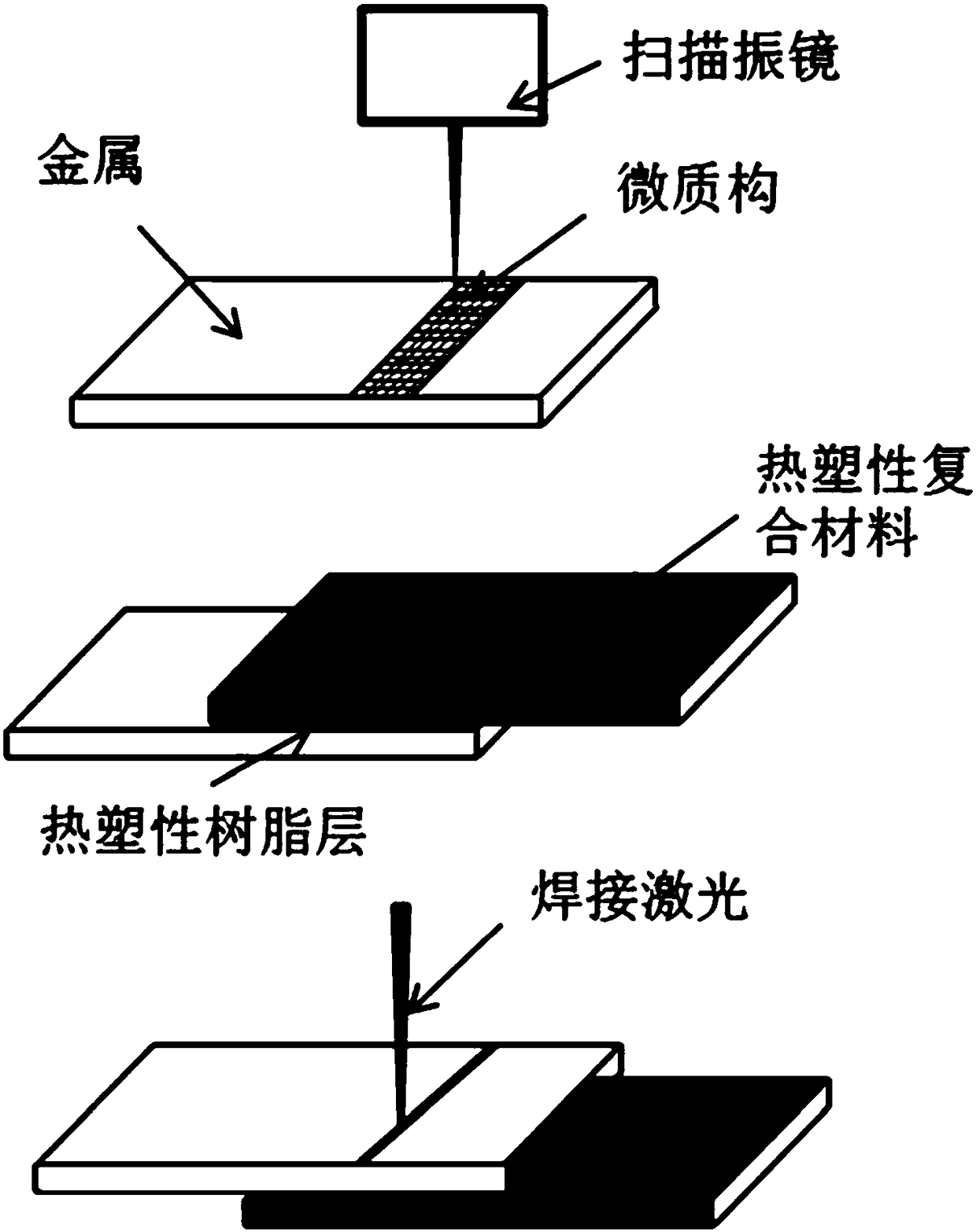
[0032] Such as figure 1 As shown, follow the steps below to laser weld thermoplastic composites to metals:
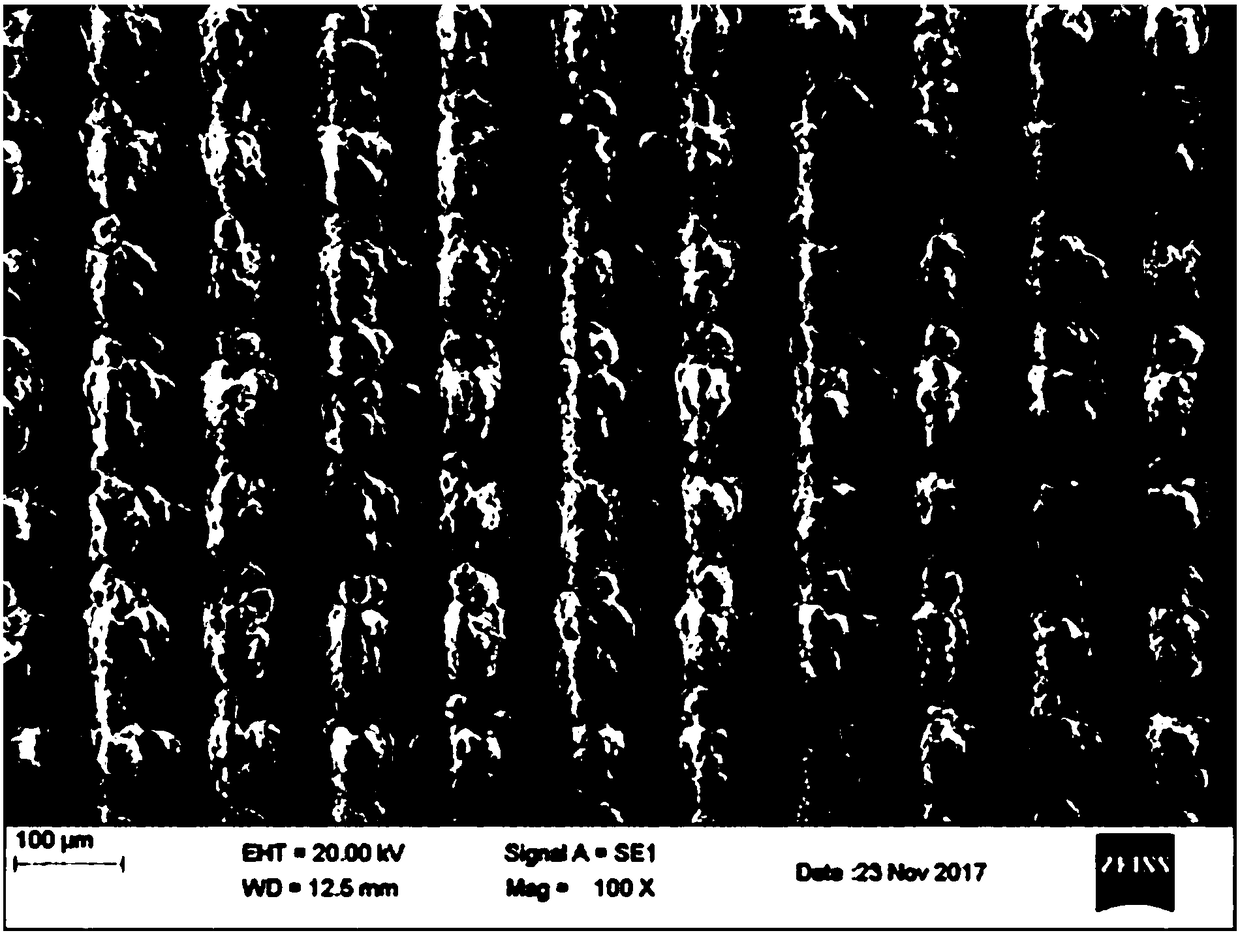
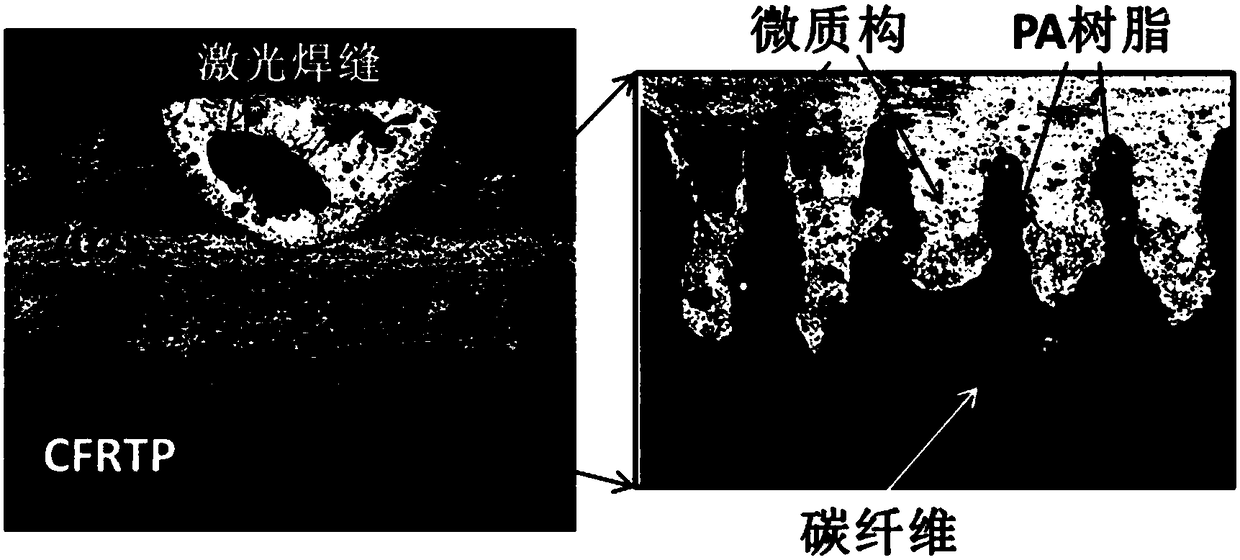
[0033] 1. Using a nanosecond laser (wavelength 532nm, pulse width 20ns, power 30W, frequency 5KHz) and a scanning galvanometer (scanning speed 5m / s) to micro-texture the surface of aluminum alloy (7075), the micro-texture is a grid shape structure, the scanning line spacing is d=0.1mm; the scanning electron microscope image of the prepared microtexture is as follows figure 2 As shown, the text in the figure has no other meaning except for the necessary information such as magnification and length; it can be seen that regular dimples and protrusions are formed on the surface of the aluminum alloy, which increases the contact between the aluminum alloy and the thermoplastic composite material during connection. area, improve connection strength;
[0034] 2. Lay polyamide resin with a thickness of 25 μm on the microstructure, which is just large enough to completely cov...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Follow the steps below to laser weld thermoplastic composites to metals:
[0040] 1. Using a picosecond laser (wavelength 1064nm, pulse width 40ps, power 20W, frequency 30MHz) and a scanning galvanometer (scanning speed 8m / s) to process the microtexture of the stainless steel surface, the microtexture is an inverted cone structure;
[0041] 2. Lay polymethyl methacrylate resin with a thickness of 100 μm on the micro texture, which is just large enough to completely cover the micro texture of the stainless steel surface;
[0042] 3. Place the glass fiber-reinforced polymethyl methacrylate on the stainless steel, with the microstructure and polymethyl methacrylate resin layer between the two, clamp the combined workpiece together by pneumatic tooling, and apply 0.5 The pressure of MPa makes the polymethyl methacrylate composite material and stainless steel stick together;
[0043] 4. Use a 532nm green laser (power 100W) to focus on the stainless steel surface, and scan (...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Follow the steps below to laser weld thermoplastic composites to metals:
[0047] 1. Using a femtosecond laser (pulse width 200fs, power 5W, frequency 100MHz) and a scanning galvanometer (scanning speed 10m / s) to process the microtexture of the titanium alloy surface, the microtexture is a slightly convex structure;
[0048] 2. Lay polyphenylene sulfide resin with a thickness of 50 μm on the microstructure, which is just large enough to completely cover the microstructure on the surface of the titanium alloy;
[0049] 3. Place the aramid fiber-reinforced polyphenylene sulfide on the titanium alloy, with the microstructure and polyphenylene sulfide resin layer in between, clamp the combined workpiece together by pneumatic tooling, and apply 0.4MPa Pressure, so that the polyphenylene sulfide composite material and the titanium alloy are bonded together;
[0050] 4. Use a 266nm ultraviolet laser (power 40W) to focus on the surface of the titanium alloy, and scan the surface...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com