Method for preparing bacterial cellulose from tofu yellow seriflux
A technology of bacterial cellulose and yellow pulp water, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve problems such as environmental pollution and resource waste, reduce enterprise investment, reduce enterprise production costs, and alleviate pollution effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
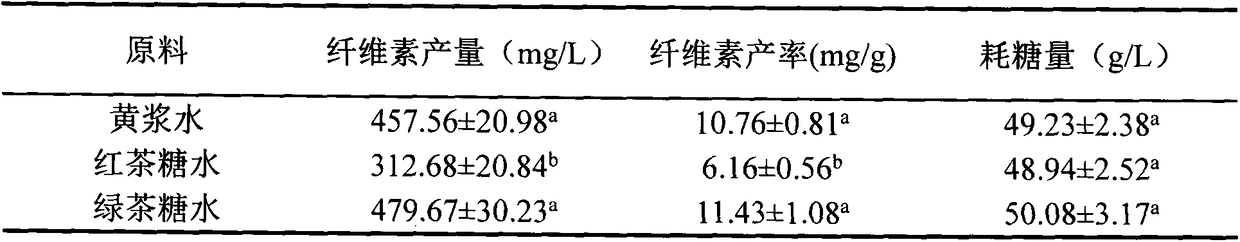
[0022] Collect the yellow pulp water produced in the tofu production process, pasteurize it after adding 6% sucrose by mass fraction; insert freshly activated Acetobacter xylinus (Gluconacetobacter xylinus, the strains were purchased from China General Microorganism Culture Preservation Management Co., Ltd. Center, the strain preservation number is CGMCC 1.1812) up to 10 8 CFU / mL yellow pulp water seed liquid, fermented at 30°C for 3 days to obtain bacterial cellulose; take out the bacterial cellulose, leave 30% of the fermentation liquid in the fermentation device, add 3 times the volume of the fermentation liquid after pasteurization The sugary yellow pulp water is used for the next round of bacterial cellulose production.
[0023] The preparation method of black tea and green tea sugar water in Table 1 is to add 0.5% black tea or green tea and 6% sucrose to the water, boil for 5 minutes, and filter the tea leaves with gauze after cooling. The total amount of Acetobacter xy...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Collect the yellow slurry water produced in the tofu production process, add mass fractions of 1% fructose, 1% maltose, and 4% sucrose and pasteurize it; the ratio of the number of freshly activated bacteria is 10:3:5 Acetobacter xylinus (Gluconacetobacter xylinus, strains purchased from China General Microorganism Culture Collection Management Center, strain preservation number is CGMCC 1.1812), Gluconacetobacter sp. (Gluconacetobacter sp., purchased from China Industrial Microbiology Culture Collection Management Center , the strain preservation number is CICC 10773) and Acetobacter pasteurianus (Acetobacter pasteurianus, the strain was purchased from the China General Microorganism Culture Collection Management Center, the strain preservation number is CGMCC 1.2269), and the total number of colonies reached 10 8 CFU / mL of the yellow pulp water seed solution was fermented at 28°C for 3 days to obtain bacterial cellulose; the bacterial cellulose was taken out, and 20% o...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Collect the yellow pulp water produced in the tofu production process, add mass fractions of 1% fructose, 1% sucrose, 1% maltose and 1% glucose and pasteurize it; the ratio of the number of freshly activated bacteria is 10: 2:3:5 Gluconacetobacter xylinus (Gluconacetobacter xylinus, strains purchased from China General Microorganism Culture Collection Management Center, strain preservation number is CGMCC 1.1812), Gluconacetobacter sp. (Gluconacetobacter sp., purchased from China Industrial Microbiology Culture Collection Management Center, the strain preservation number is CICC 10773), Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strains were purchased from the China General Microorganism Culture Collection Management Center, strain preservation number is CGMCC 2.3888), Debariae hansenii ( Debaryomyces hansenii, the strains were purchased from China General Microorganism Culture Collection Management Center, the strain preservation number is CGMCC 2.3948), and the total number of colonies...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com