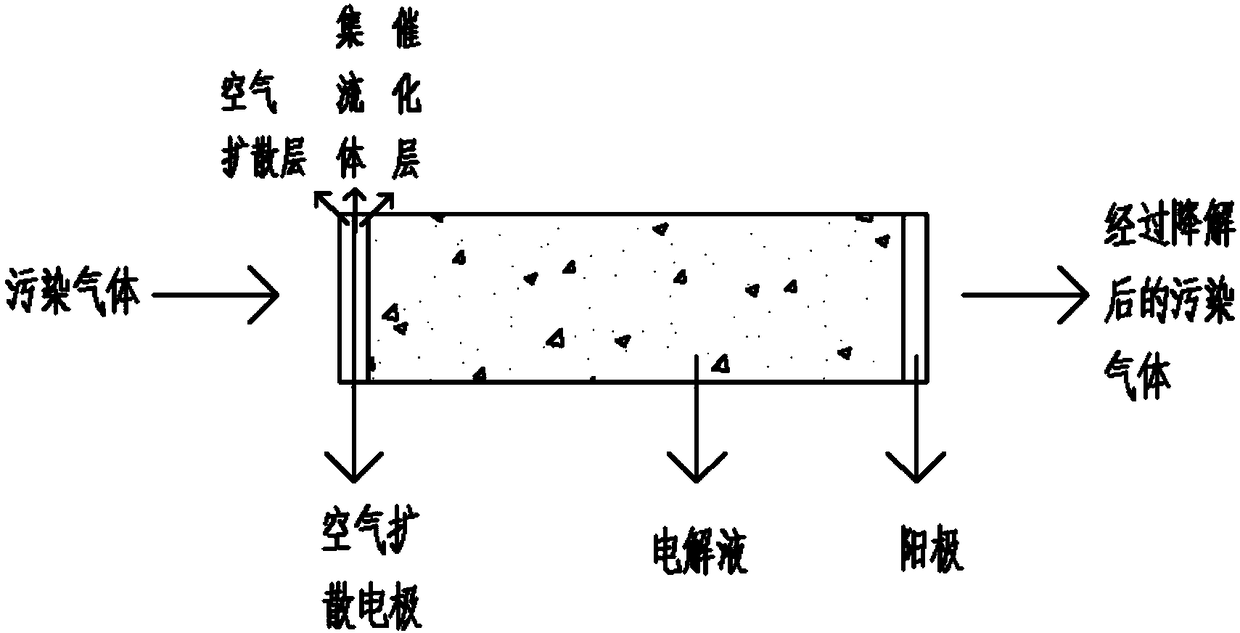
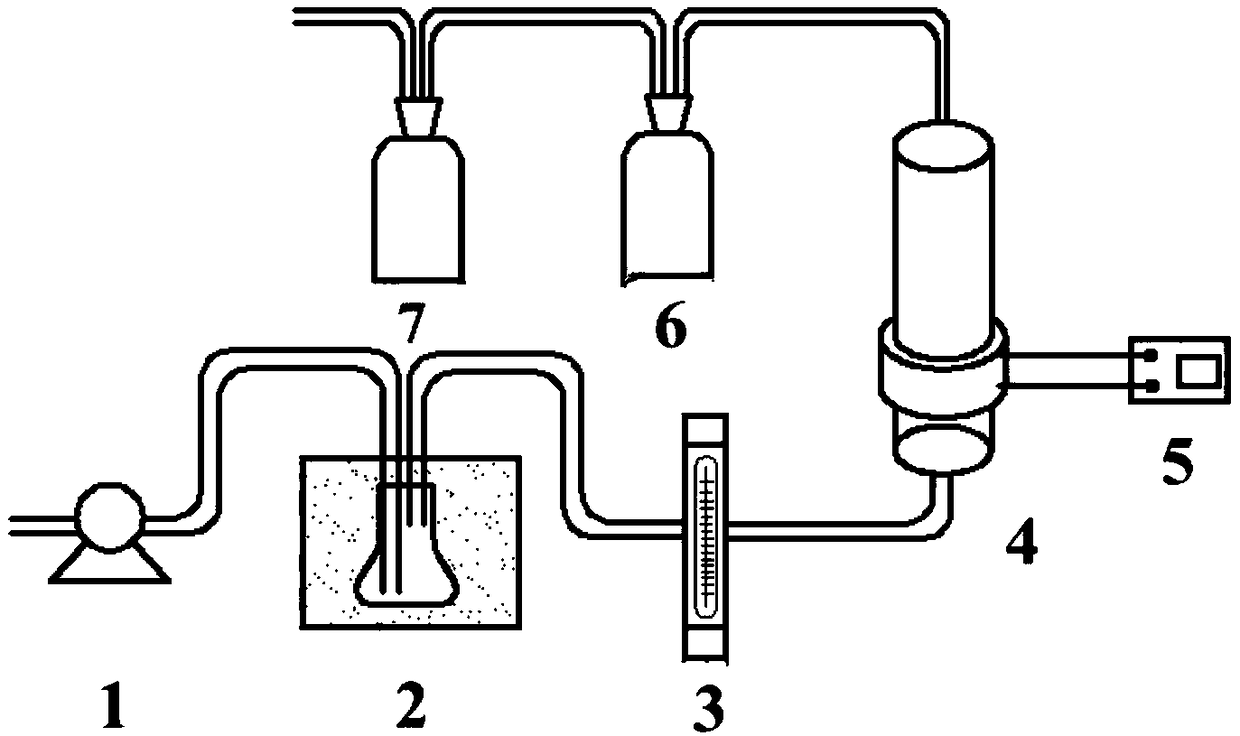
Flow reactor, device and method for electrochemically degrading volatile organic pollutants
A flow reactor, volatile organic technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, gas treatment, etc., can solve the problems of difficult material migration and conversion process, thick electrolyte solution, iron sludge precipitation, etc., to improve electrochemical devices , simple device, high degradation efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
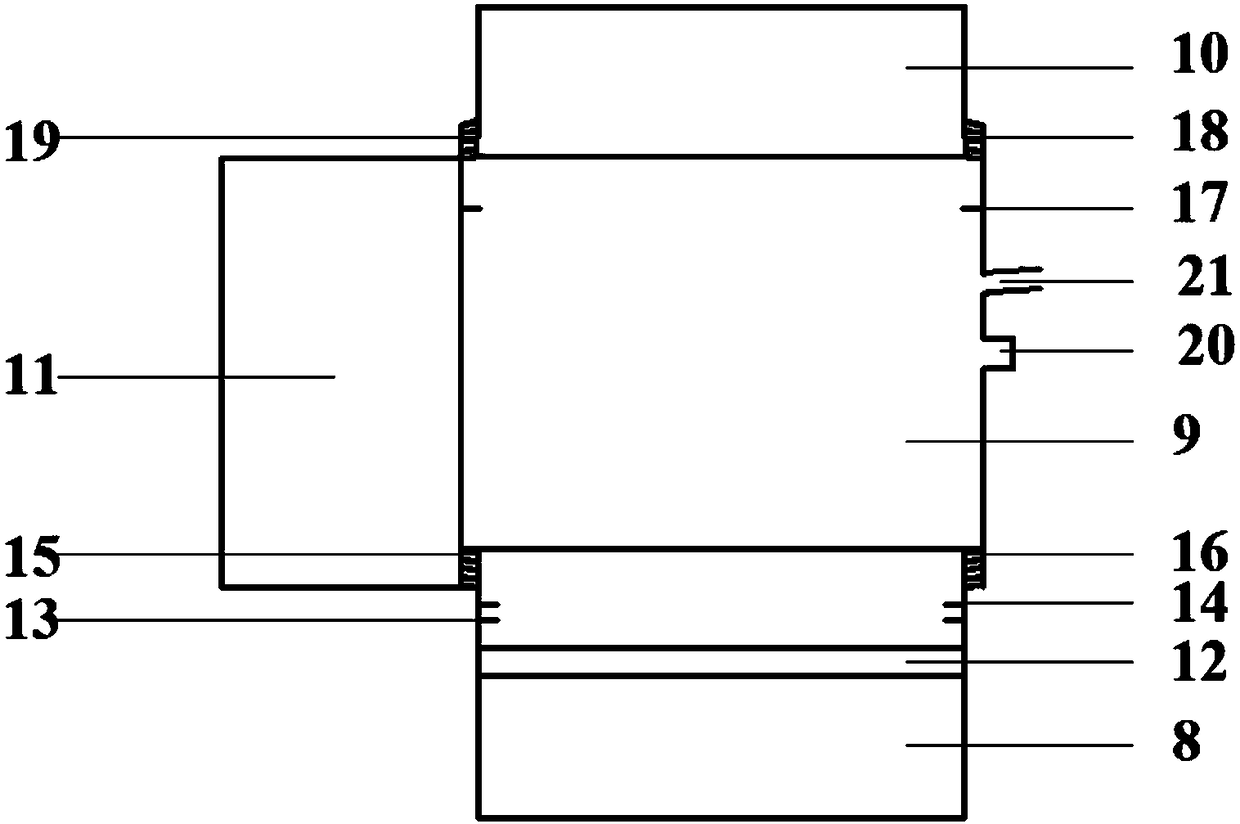
[0040] A flow reactor for the electrochemical degradation of volatile organic pollutants such as image 3 As shown, the flow reactor 4 is a cylindrical plexiglass body composed of four parts: an air inlet tank 8 , a housing 9 , an air outlet tank 10 , and a test tank 11 .
[0041] The air inlet tank 8 has an inner diameter of 3cm, an outer diameter of 4cm, and a height of 6cm. It is located at the bottom of the flow reactor. At 2-3 cm, there is a circle of partitions 13 and 14 with a width of 0.5 cm, the distance between the two partitions is 0.3 cm, and fastening clips are installed on the partitions, and there are external threads 15 at a distance of 1 cm from the top;
[0042] The housing 9 has an inner diameter of 3.4 cm, an outer diameter of 4.4 cm, and a height of 2 cm. It is located in the middle of the flow reactor, has no bottom and no cover, and has an internal thread 16 at a distance of 1 cm from the bottom, and a ring of partitions 17 at a distance of 2 to 3 cm from ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] The platinum sheet was used as the anode, the air diffusion electrode was used as the cathode, the gas blowing rate was 6L / h, and the electrolyte concentration was 0.8mol / L. The xylene removal rate was studied when the electrolysis voltage was 6-10V. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0053] Table 1
[0054]
[0055] It can be seen from Table 1 that the removal rate increases with the increase of voltage, and the removal rate is the largest at 10V. According to Faraday's law, when the current density increases, the output of the cathode and the electricity obtained by the anode also increase, resulting in HO and HO 2 ·、H 2 o 2 The amount of oxidant is more; therefore, the removal rate increases with the increase of current density. However, with the increase of voltage, the degree of polarization of the two poles increases, the energy consumption increases, the temperature of the electrolyte increases, and the decomposition rate of hydrogen peroxide will also acc...
Embodiment 3
[0057] The platinum sheet was used as the anode, the air diffusion electrode was used as the cathode, the electrolysis voltage was 10V, the electrolyte concentration was 0.8mol / L, and the xylene removal rate was studied when the air blowing rate was 4-8L / h. The results are shown in Table 2.
[0058] Table 2
[0059]
[0060] It can be seen from Table 2 that the removal rate increases with the increase of the blowing rate, and the removal rate is the largest when the blowing rate is 8L / h, but the removal rate slows down, mainly because more gaseous Pollutants add to the processing load.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com