Nanomedicine based on lipoyl-terminated star polymers
A lipoyl star and star-shaped polymer technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve the problems of lack of toxic and side effects, low-efficiency nano-medicines, etc., and achieve the effects of excellent biodegradability, good stability, and high loading efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
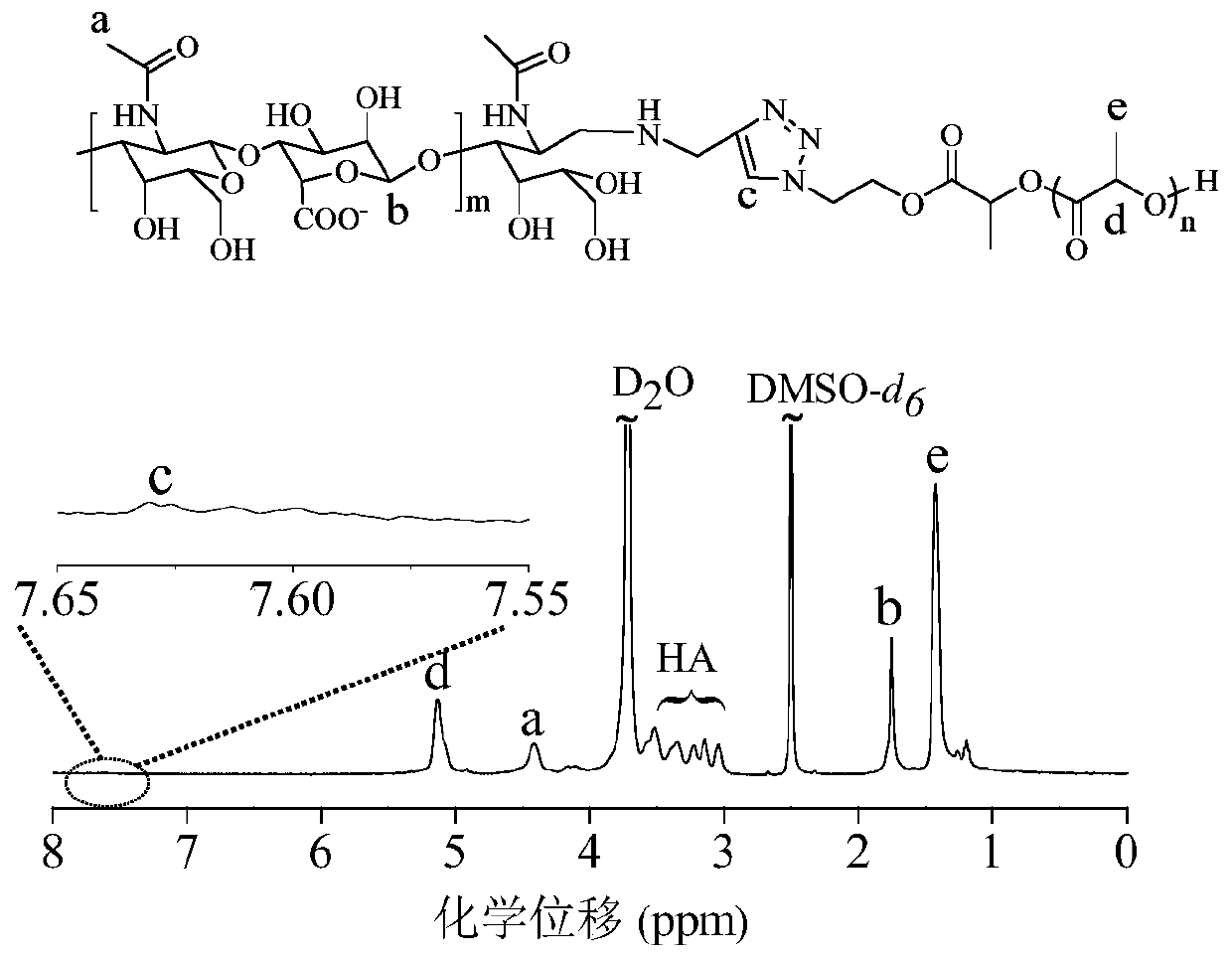
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
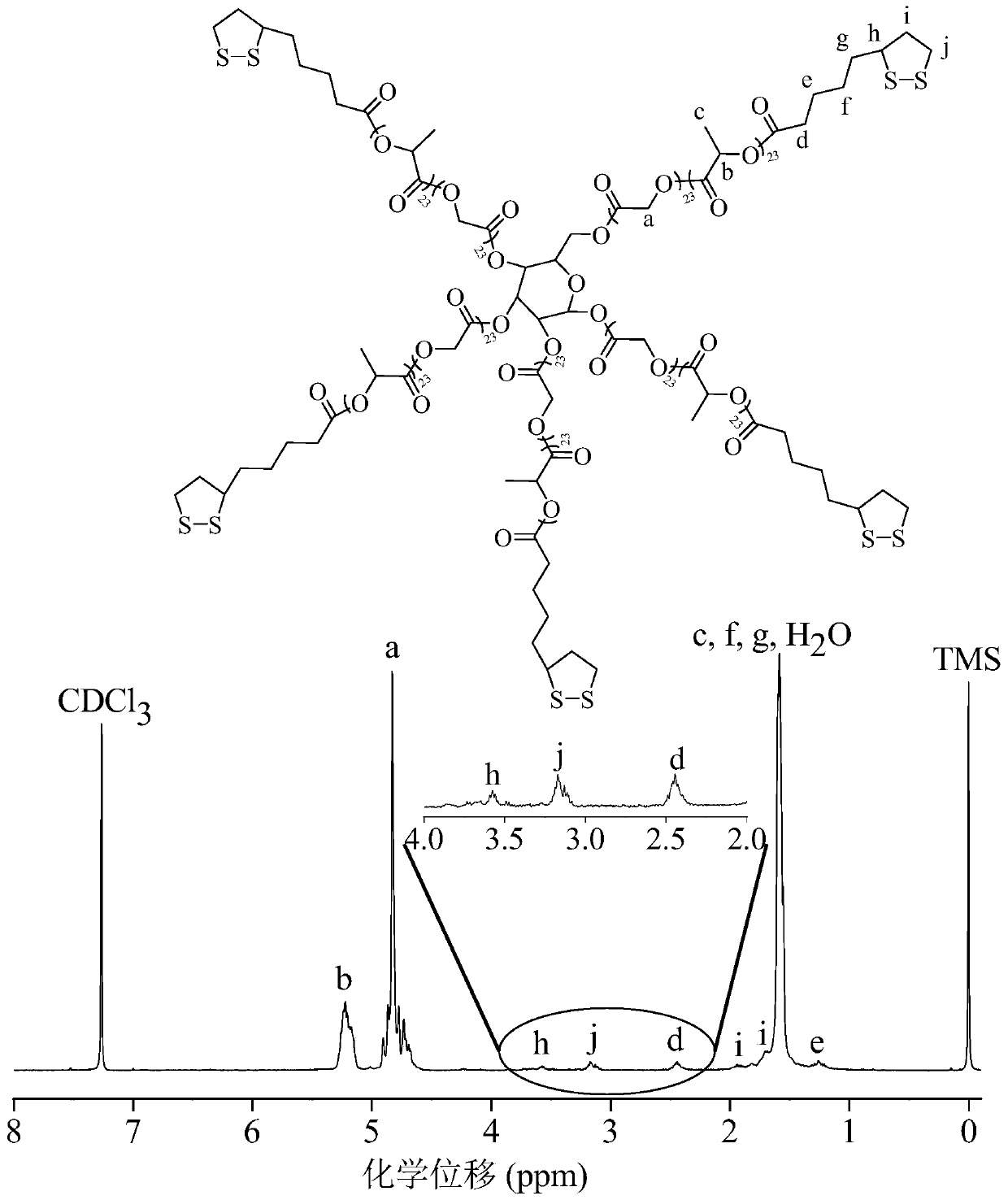
[0052] Example 1 Synthesis of star-shaped polymers containing lipoyl groups in side chains
[0053] Synthesis of star and linear polymers
[0054] The star-shaped polymer can be synthesized by using polyhydroxyglucose as an initiator to initiate ring-opening polymerization of lactide and glycolide under the catalysis of stannous octoate. in N 2 Under ambient conditions, 0.18 g (1 mmol) polyhydroxyglucose, 7.5 g (52 mmol) lactide and 7.5 g (65 mmol) glycolide were added to a closed reaction bottle, followed by adding 4.73 mg catalyst stannous octoate to react bottle and mix all ingredients well. The reaction flask was then evacuated-displacing the N 2 Three times, and finally the reaction vial was evacuated for 30 minutes, and the reaction vial was sealed. The polymerization reaction was carried out in a vacuum box at 160° C. for 8 hours. The crude product was dissolved in dichloromethane, subsequently precipitated in ice methanol, filtered off with suction and dried in v...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2 Synthesis of amphiphilic polymer PEG-PDLLA
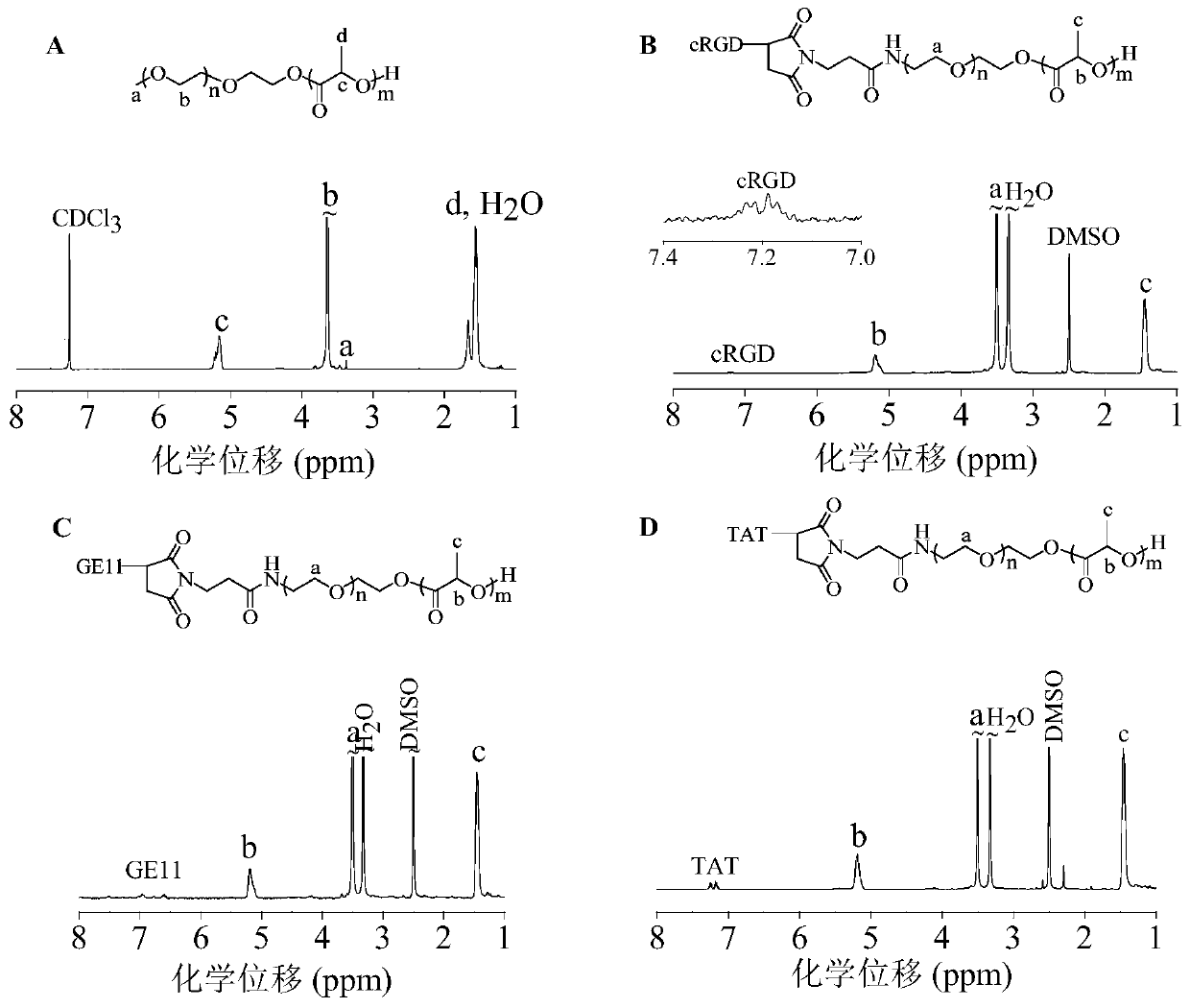
[0059] The amphiphilic polymer PEG-PDLLA can be prepared by ring-opening polymerization of D,L-lactide initiated by macroinitiator PEG. in N 2 environment, add 2.5 mL PEG ( M n =5.0 kg / mol, 0.5 g, 0.1 mmol) and D,L-lactide (0.4g, 2.8 mmol) in anhydrous toluene solution, quickly add 0.5 mL (0.2 mol / L) of stannous octoate toluene stock liquid. After reacting in a constant temperature oil bath at 110 °C for 48 h, glacial acetic acid was added to terminate the reaction. Subsequently, the product was precipitated in glacial ether, filtered with suction and dried in vacuo to obtain PEG-PDLLA with a yield of 88.9%. 1 H NMR (600 MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ 5.16 (-C H (CH 3 )O- ), 3.65 (-C H 2 C H 2 O-), 3.38 (C H 3 O-), 1.56 (-CH(C H 3 )O-), see figure 2 (A). M n ( 1 HNMR) = 8.9 kg / mol, M n (GPC) = 15.9 kg / mol, M w / M n (GPC) = 1.3.
Embodiment 3
[0060] Example 3 Synthesis of amphiphilic targeting polymer cRGD-PEG-PDLLA
[0061] The targeting polymer cRGD-PEG-PDLLA was obtained through a two-step reaction. First, the maleimide-functionalized amphiphilic polymer MAL-PEG-PDLLA was synthesized, and then the cRGD polypeptide-modified amphiphilic polymer cRGD-PEG- PDLLA. Maleimide-functionalized MAL-PEG-PDLLA was prepared by ring-opening polymerization of D,L-lactide initiated by MAL-PEG. in N 2 environment, add 2.5 mL MAL-PEG ( M n =5.0 kg / mol, 0.5 g, 0.1 mmol) and D,L-lactide (0.4 g, 2.8 mmol) in anhydrous toluene solution, quickly add 0.5mL (0.2 mol / L) of stannous octoate toluene stock liquid. After reacting in a constant temperature oil bath at 110 °C for 48 h, glacial acetic acid was added to terminate the reaction. The product was subsequently precipitated in glacial ether, filtered with suction and dried in vacuo to obtain MAL-PEG-PDLLA. Then MAL-PEG-PDLLA and cRGD-SH were dissolved in DMF and reacted at room...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com