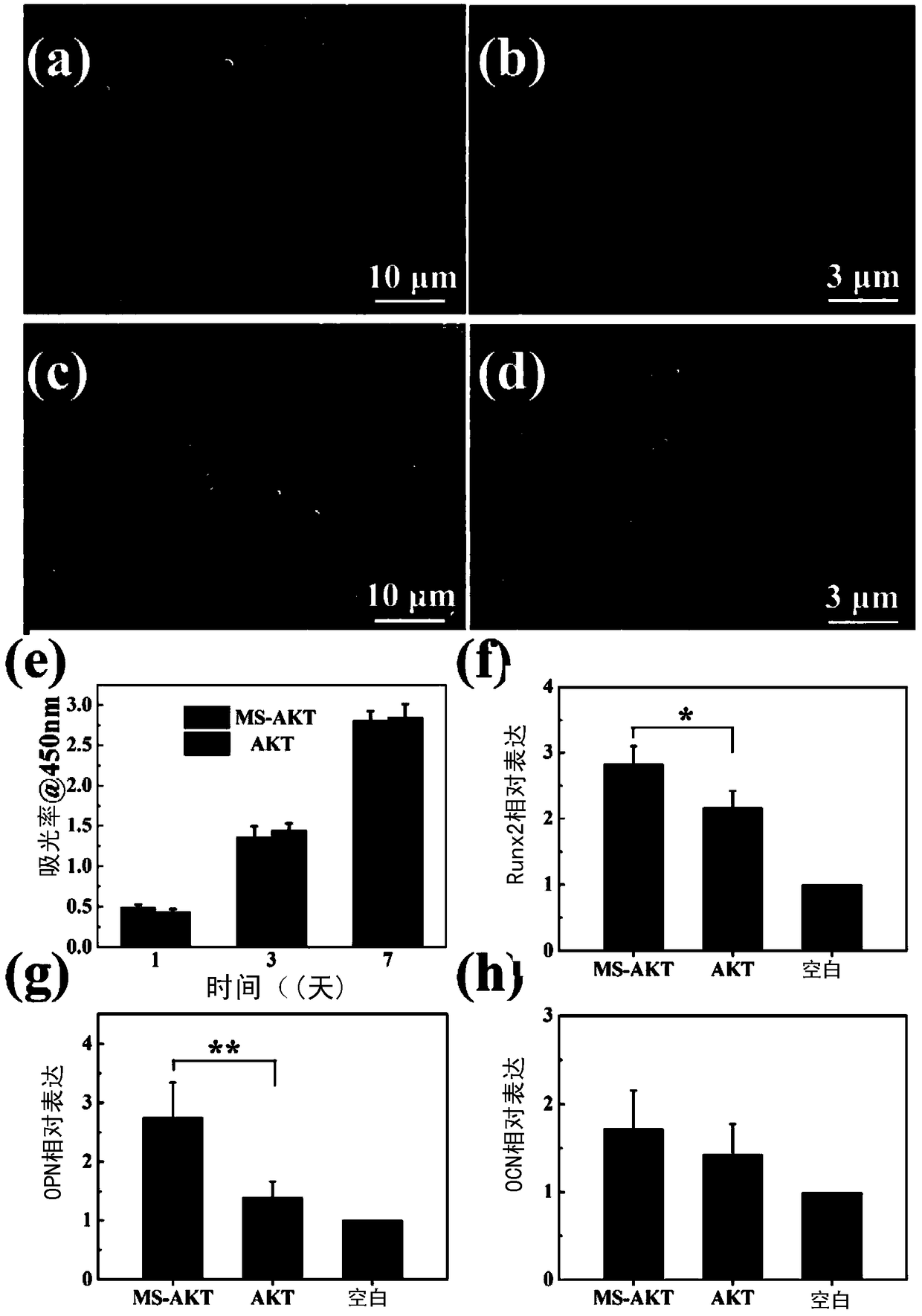
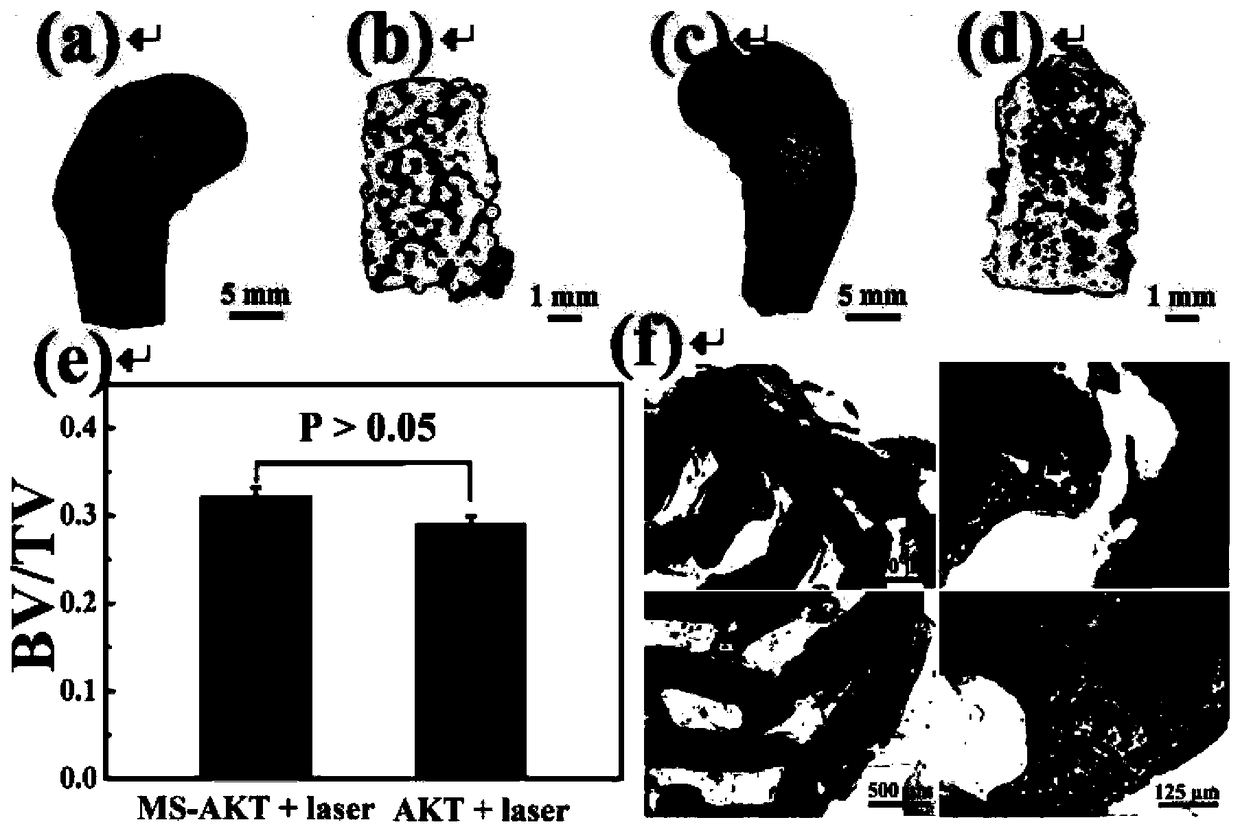
Molybdenum disulfide nano-sheet in-situ modified biological ceramic stent, preparation method and applications thereof
A molybdenum disulfide, in-situ modification technology, used in pharmaceutical formulations, tissue regeneration, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve problems such as difficult self-healing of the body and tissue defects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0069] (1) After taking 5g of pure feldspar powder (Kunshan Huaqiao Technology New Material Co., Ltd.), 0.32g of sodium alginate powder and 2.5g of F127 aqueous solution with a mass fraction of 20%, the scaffold material was prepared by using three-dimensional printing technology;
[0070] (2) Calcinate the printed support at 1350°C for 3 hours to obtain a pure feldspar ceramic support AKT, the size of which is Ф11mmⅹ3mm;
[0071] (3) Add 1mmol ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate and 30mmol thiourea into 35mL deionized water to obtain a solution with a molar concentration of molybdenum atoms of 0.2mol / L. After stirring for 1 hour, pour it into the polytetrafluoroethylene 4g feldspar ceramic support. In the lining of the ethylene hydrothermal kettle, a black bracket was obtained after a 180°C hydrothermal reaction for 24 hours;
[0072] (4) After washing several times with ethanol and water, and drying in a vacuum oven at 60°C, a molybdenum disulfide-modified feldspar scaffold 0.2M...
Embodiment 2
[0086] (1) After fully mixing 5g of pure feldspar powder, 0.32g of sodium alginate powder and 2.5g of F127 aqueous solution with a mass fraction of 20%, the scaffold material was prepared by three-dimensional printing technology;
[0087] (2) Calcinate the printed support at 1350°C for 3 hours to obtain a pure feldspar ceramic support AKT, the size of which is Ф11mmⅹ3mm;
[0088] (3) Add 0.5mmol ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate and 15mmol thiourea into 35mL deionized water to obtain a solution with a molar concentration of molybdenum atoms of 0.1mol / L. After stirring for 1 hour, pour it into polytetrafluoroethylene with 4g feldspar ceramic support. In the lining of vinyl fluoride hydrothermal kettle, a black bracket was obtained after 180°C hydrothermal reaction for 24 hours;
[0089] (4) After washing several times with ethanol and water, and drying in a vacuum oven at 60°C, a molybdenum disulfide-modified feldspar scaffold 0.1MS-AKT was obtained;
[0090] (5) Place the stent...
Embodiment 3
[0094] (1) After fully mixing 5g of pure feldspar powder, 0.32g of sodium alginate powder and 2.5g of F127 aqueous solution with a mass fraction of 20%, the scaffold material was prepared by three-dimensional printing technology;
[0095] (2) Calcinate the printed support at 1350°C for 3 hours to obtain a pure feldspar ceramic support AKT, the size of which is Ф11mmⅹ3mm;
[0096] (3) 0.25mmol ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate and 7.5mmol thiourea were added into 35mL deionized water to obtain a molar concentration of molybdenum atom molar solution that was 0.05mol / L. After stirring for 1 hour, pour 4g feldspar ceramic support into the poly In the lining of tetrafluoroethylene hydrothermal kettle, a black bracket was obtained after hydrothermal reaction at 180°C for 24 hours;
[0097](4) After washing several times with ethanol and water, and drying in a vacuum oven at 60°C, a molybdenum disulfide-modified feldspar scaffold 0.05MS-AKT was obtained;
[0098] (5) Place the stent i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Film diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com