Preparation method of antistatic material taking rhamnolipid as antistatic coating
A rhamnolipid and antistatic technology, applied in the field of preparation of antistatic materials, can solve the problems of eutrophication of water body, damage to water body ecosystem, loss of antistatic effect, poor compatibility, etc., achieve wide application value and reduce stability The effect of improving resistance and antistatic performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] (1) Prepare rhamnolipid with a mass concentration of 0.1%;
[0032] (2) Polymer materials: polytetrafluoroethylene, polycarbonate, polystyrene, polymethyl methacrylate, nylon, polyethylene, polypropylene, polydimethylsiloxane, polyvinyl chloride, acrylonitrile -Butadiene-styrene was ultrasonically cleaned with ethanol, then dip-coated in rhamnolipid solution, and shaken for 4 h (rotating speed 200 rpm, temperature 37°C). Take it out slowly, place it at room temperature to dry, wash it twice with ultrapure water, and dry it at room temperature to obtain an antistatic material. The material which was not dipped in rhamnolipid was used as a control.
Embodiment 2
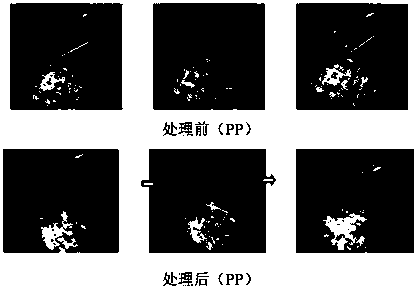
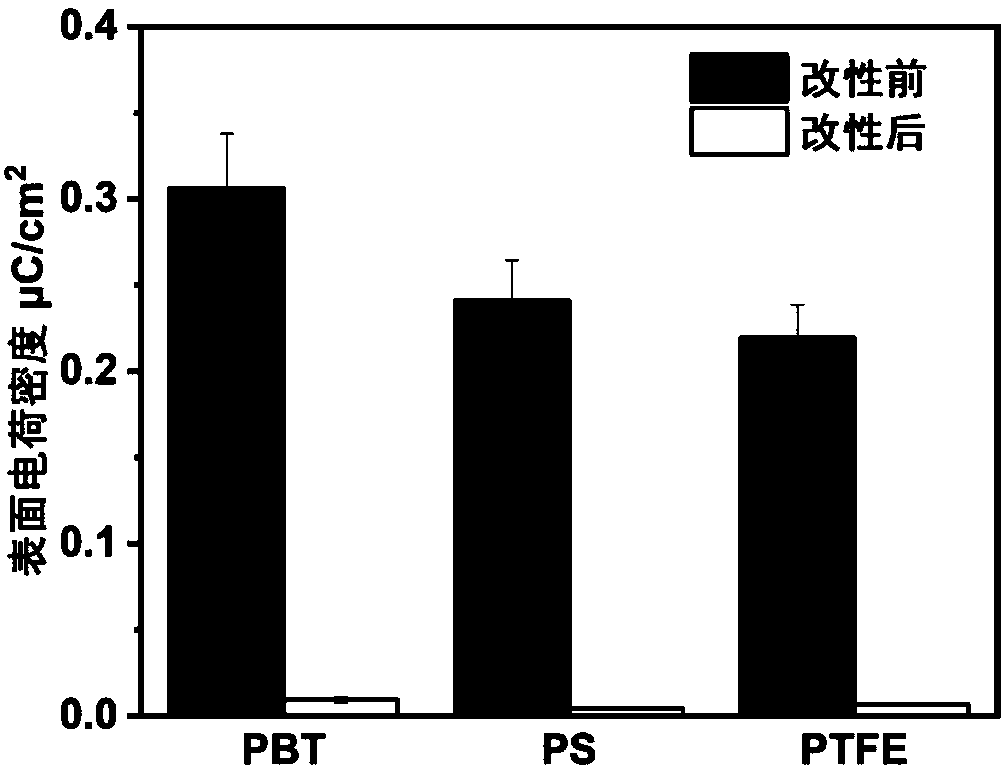
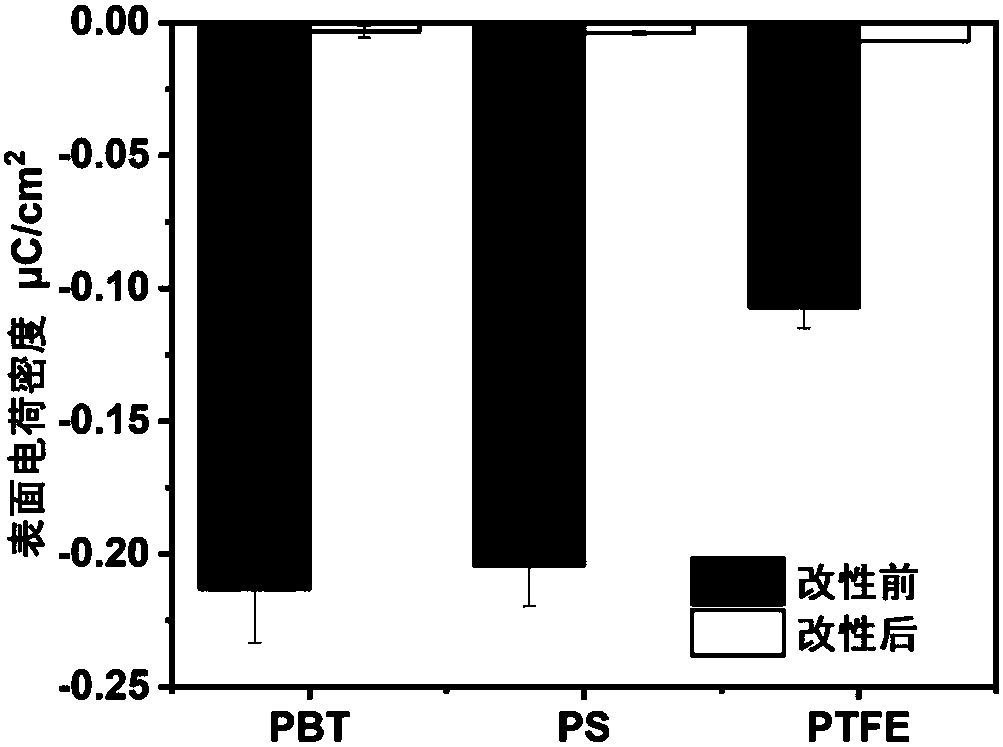
[0034] The antistatic material prepared in the above-mentioned Example 1 was subjected to static charge measurement. The material to be tested is contacted with PTFE several times, and the measured value under 60% humidity is as follows: figure 1 , measured at 15% humidity as image 3 . The material to be tested is contacted with nylon several times, and the measured value under 60% humidity is as follows: figure 2 , measured at 15% humidity as Figure 4 . Experiments show that the surface charge of the material treated with rhamnolipid is significantly reduced, and the antistatic effect is obvious.
Embodiment 3
[0036] With the antistatic material that above-mentioned embodiment 1 makes, carry out measurement contact angle experiment and surface resistivity test, experiment, the result sees Figure 5 , Table 1, Table 2. Experiments show that the hydrophilicity of the material treated with rhamnolipid is greatly improved, and the surface resistivity of the material decreases under different humidity, and the higher the humidity, the greater the decrease, which improves the antistatic performance of the material.
[0037] Table 1. Surface resistivity of materials before and after rhamnolipid surface modification at 60 % humidity
[0038]
[0039] Table 2. Surface resistivity of materials before and after rhamnolipid surface modification at 15 % humidity
[0040]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com