Preparation method of heterojunction photocatalyst for NADH regeneration
A photocatalyst and heterojunction technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of nano-photocatalytic materials, can solve the problems of difficulty in preparing black phosphorus, and achieve the effect of simple and easy preparation process and cheap preparation of raw materials.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1: g-C supported by red phosphorus quantum dots 3 N 4 The preparation of nanotubes, the steps are as follows:
[0026] Step 1, g-C 3 N 4 The preparation of -NTs is the same as the preparation process of the comparative example;
[0027] Step 2, the red phosphorus of equal quality and the g-C that step 1 makes 3 N 4 -NTs were placed on both ends of a quartz boat, sealed with tin foil, placed in a tube furnace and filled with argon for 20 minutes, the airtight air pressure was 0.04 bar, and the heating program was set to increase the temperature from room temperature at a rate of 5°C / min. to 460°C and maintained for 3 hours, then lowered to 300°C for 30 minutes and maintained for 1 hour, and finally lowered to room temperature. During the vapor deposition process, red phosphorus was deposited into the hollow g-C 3 N 4 On the surface of nanotubes, the obtained red phosphorus quantum dots supported g-C 3 N 4 Nanotubes are heterojunction photocatalysts for NAD...
Embodiment 2
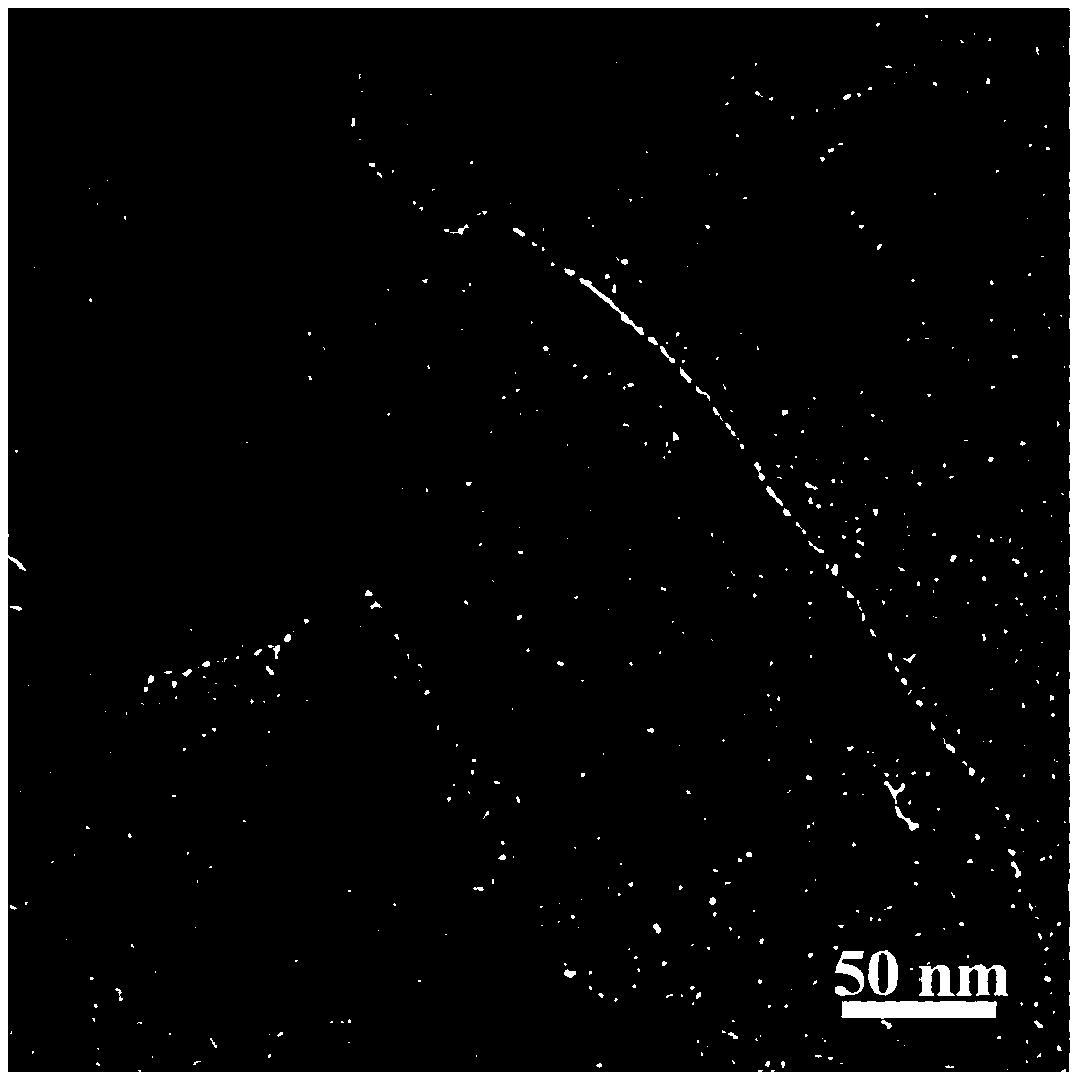
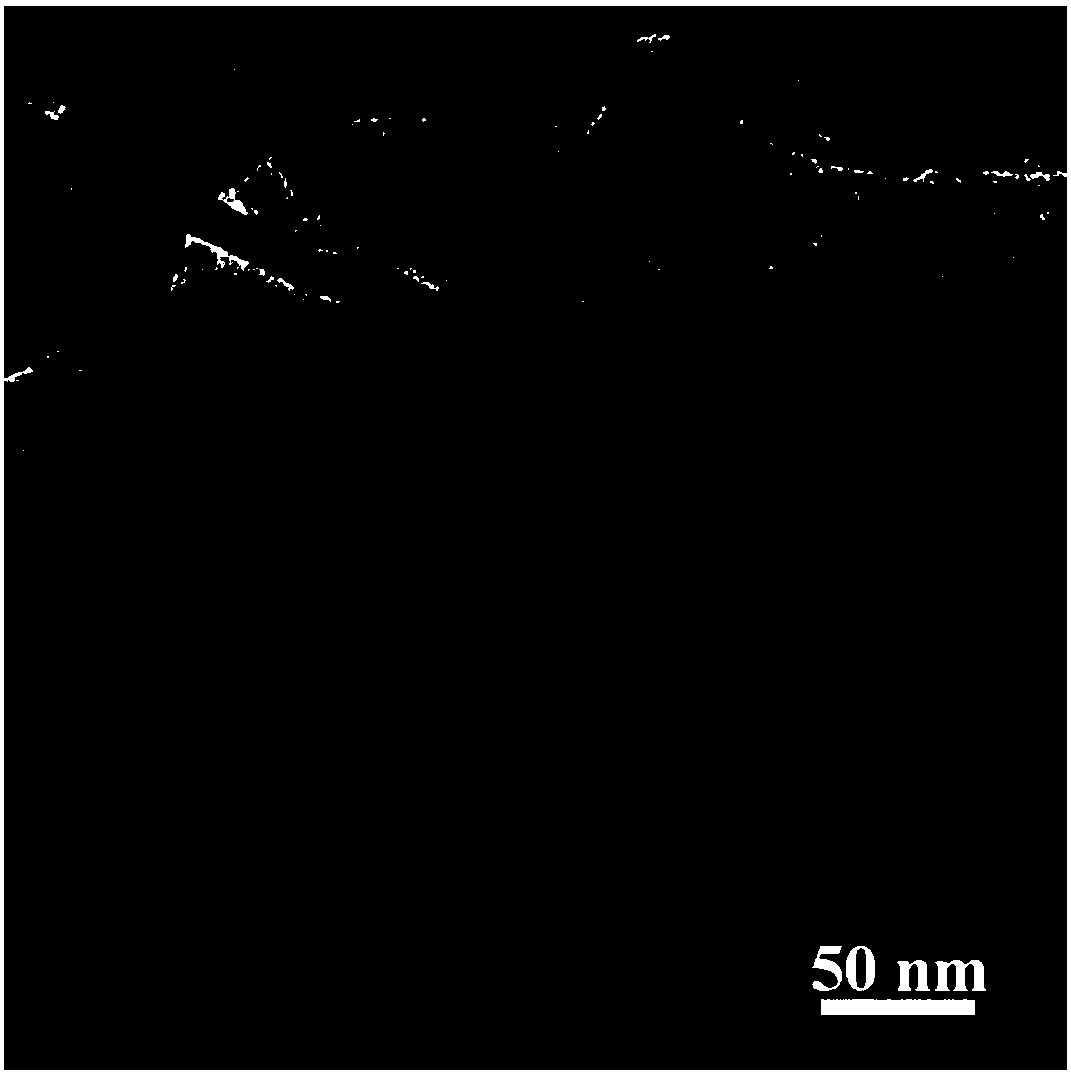
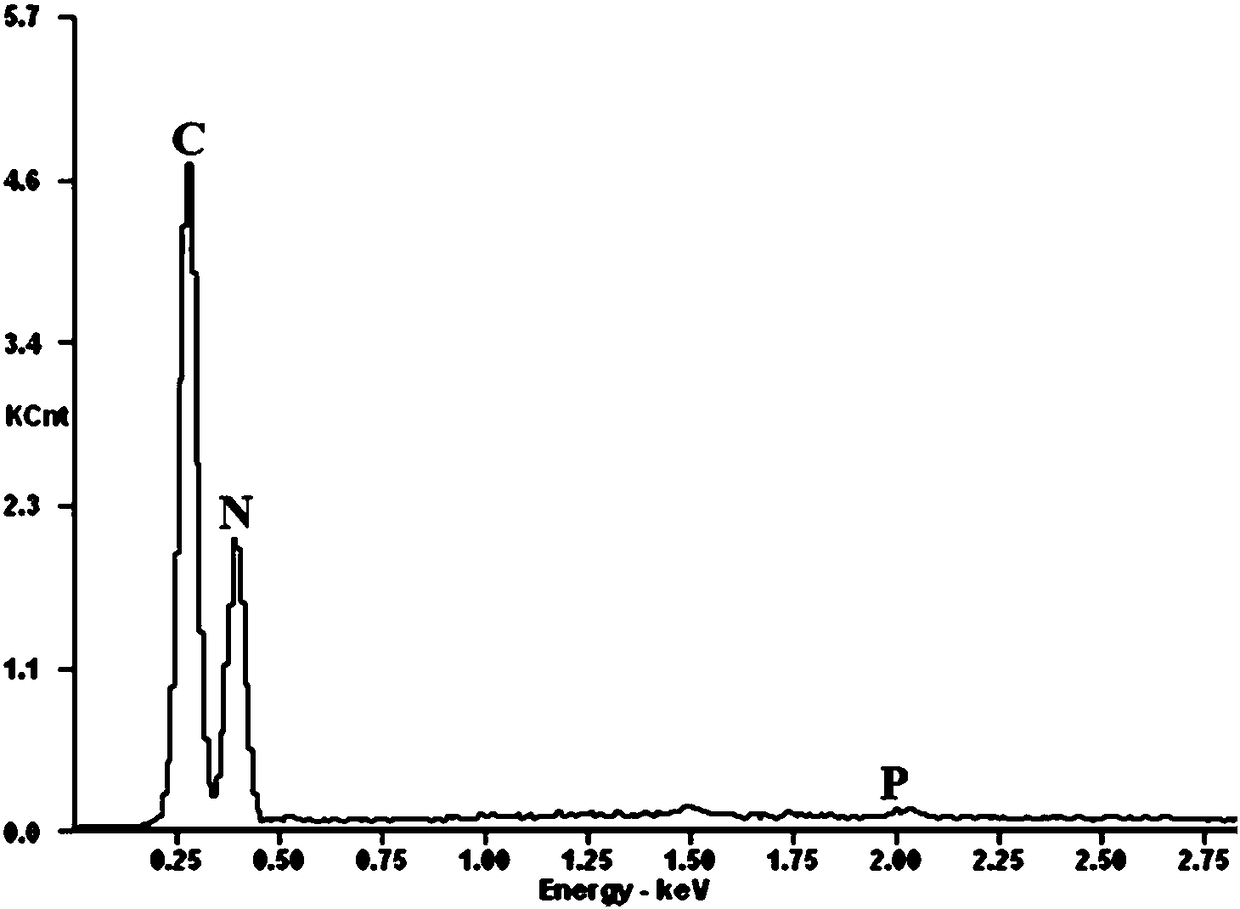
[0031] Example 2: g-C supported by red phosphorus quantum dots 3 N 4 The preparation of nanotubes, the steps of this embodiment and embodiment 1 are basically the same, the difference is: in step 2, red phosphorus and g-C 3 N 4 The mass ratio was changed from 1:1 to 0.5:1. Fig. 2 (a) and Fig. 2 (b) are the g-C that embodiment 2 prepares 3 N 4 - Transmission electron microscope (TEM) images of NTs@rP-QDs and corresponding EDS analysis. Table 2 is g-C prepared by embodiment 2 3 N 4 - Elemental analysis of NTs@rP-QDs. The g-C that embodiment 2 prepares 3 N 4 The NADH regeneration reaction of -NTs@rP-QDs had a conversion rate of 75.83±3.79% at 6 min equilibrium.
[0032] Table 2
[0033] element
Embodiment 3
[0034] Example 3: g-C supported by red phosphorus quantum dots 3 N 4 the preparation of nanotubes,
[0035] The steps of this embodiment are basically the same as in Example 1, the difference is that red phosphorus and g-C 3 N 4 The mass ratio was changed from 1:1 to 2:1. Fig. 3 (a) and Fig. 3 (b) are the g-C that embodiment 3 prepares 3 N 4 - Transmission electron microscope (TEM) images of NTs@rP-QDs and corresponding EDS analysis. Table 3 is g-C prepared by embodiment 3 3 N 4 - Elemental analysis of NTs@rP-QDs. The g-C that embodiment 3 prepares 3 N 4 The NADH regeneration reaction of -NTs@rP-QDs had a conversion rate of 80.45±4.02% at 6 min equilibrium.
[0036] table 3
[0037] element
[0038] Table 4
[0039] experiment
[0040] In summary, through the experiments of the above examples and their corresponding TEM images and EDS energy spectra, it was found that a g-C loaded with red phosphorus quantum dots synthesized by the preparation ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com