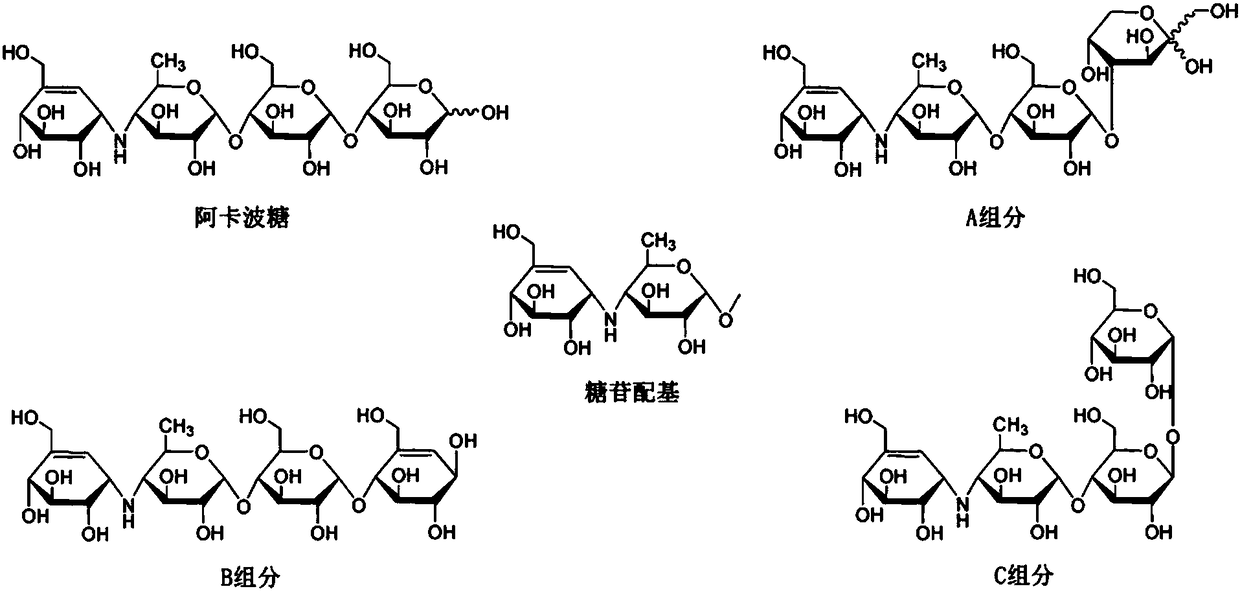
Acarbose-producing engineered bacterial strain, and preparation method and application thereof
An acarbose and engineering bacteria technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of complex process, increased production cost, instability, etc., and achieves the effects of simple purification steps, product quality assurance, and cost reduction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-1
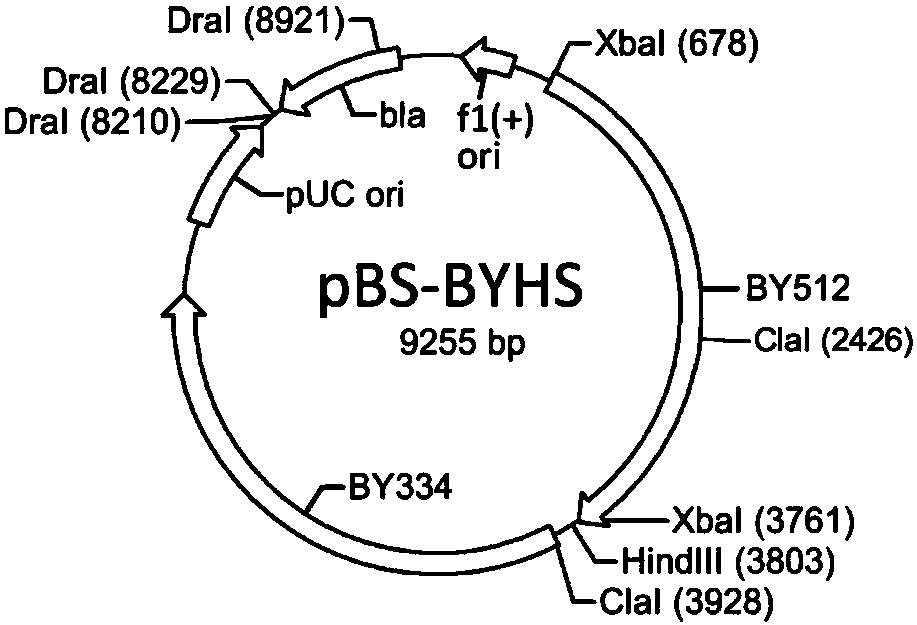
[0047] Example 1-1: Construction of recombinant plasmid pBS-BYHS-AMT for inactivating bglY gene
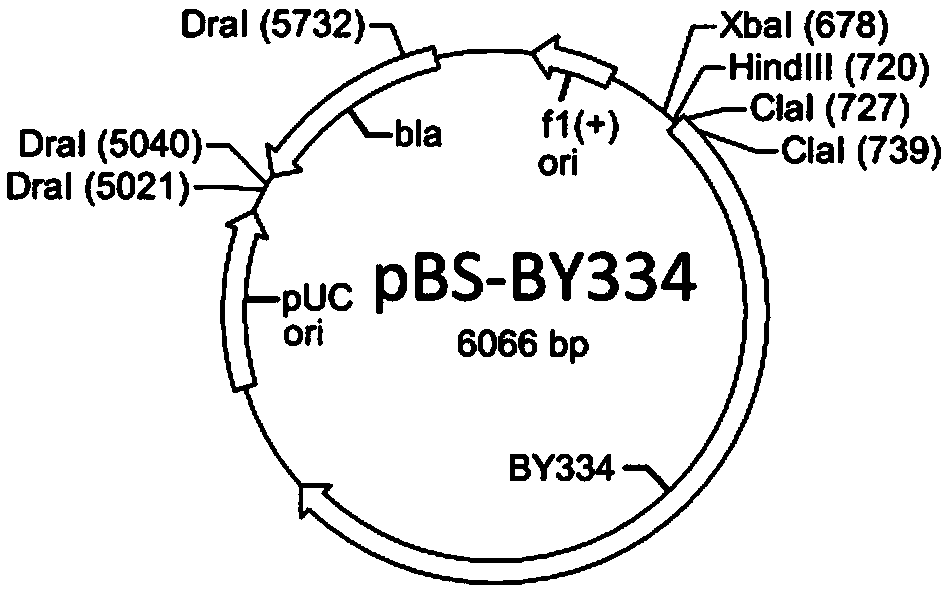
[0048] a) Using primers BY3F53 (SEQ ID NO: 6) / BY3R54 (SEQ ID NO: 7) to amplify from Actinomycetes mobilis 8-22 genomic DNA to obtain a fragment BY334 (SEQ ID NO: 23) of about 3.1 kb, the After the fragment was phosphorylated, it was inserted into the HincII site of the vector pBluKS (Genebank X52331.1) to obtain the plasmid pBS-BY334 (for the insertion direction of the fragment, see figure 2 );
[0049] b) Using HisunHF (SEQ ID NO: 9) / HisunCR (SEQ ID NO: 10) as primers and using the single strand (SEQ ID NO: 8) as a template, amplify the fragment HHCPCR (SEQ ID NO: 24). The plasmid pBS-BY334 was transformed into Escherichia coli JM110 and re-extracted to remove the methylation on base A, so that its ClaI restriction site could be cut by endonuclease ClaI. After the plasmid was digested by HindIII / ClaI, it was ligated with the fragment HHCPCR that had been digested by the same r...
Embodiment 1-2
[0052] Example 1-2: Construction of recombinant plasmid SAT-MGSH for inactivating mpbG gene
[0053] a) Using primers MG3F63 (SEQ ID NO: 14) / MG3R64 (SEQ ID NO: 15) to amplify the 3.5 kb fragment MG334 (SEQ ID NO: 27) from the genomic DNA of Actinomycetes mobilis 8-22. After the fragment was phosphorylated, it was inserted into the HincII site of the vector pBluKS to obtain the plasmid pBS-MG334 (for the insertion direction of the fragment, see Figure 6 );
[0054] b) Using HisunHF (SEQ ID NO: 9) / HisunCR (SEQ ID NO: 10) as primers and single strand (SEQ ID NO: 8) as a template, amplify the fragment HHCPCR. After the fragment was digested by HindIII / ClaI, it was ligated with the plasmid pBS-MG334 which had been digested by the same enzyme, to obtain the plasmid pBS-MG334HS;
[0055]c) Cut out a 1229bp fragment containing pUCori (SEQ ID NO: 28) from the Cosmid plasmid supcos-1 (Stratagene, Inc.) with HincII+DraI; cut out a 1271bp fragment containing aac3 (IV) from pIJ773 with ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2: Transformation of bglY gene and mpbG gene-deleted recombinant plasmids PBS-BYHS-AMT and SAT-MGSH into host bacterium Actinomyces mobilis 8-22
[0059] a) Transform recombinant plasmids PBS-BYHS-AmT and SAT-MGSH into Escherichia coli ET12567 (pUZ8002) (in literature Gust B, Kieser T and Chater K, F. technology: PCR-targeting system in Streptomyces coelicolor. John Innes Centre.2002 has detailed descriptions): Take 1 μl of the recombinant plasmid and add it to 100 μl Escherichia coli ET12567 (pUZ8002) competent cells (with CaCl 2 (Preparation method), place on ice for 30 minutes, heat shock at 42°C for 90 seconds, then quickly cool on ice for 1 minute, add 900 μl LB for culture, and bathe in water at 37°C for 50 minutes. Take 100 μl and smear it on the solid LB culture containing 25 μg / ml chloramphenicol (Cm), 50 μg / ml kanamycin (Km), 50 μg / ml apramycin (Am), cultivate overnight at 37 ° C, and grow Transformants ET12567(pUZ8002, PBS-BYHS-AmT) and ET12567(pUZ8...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com