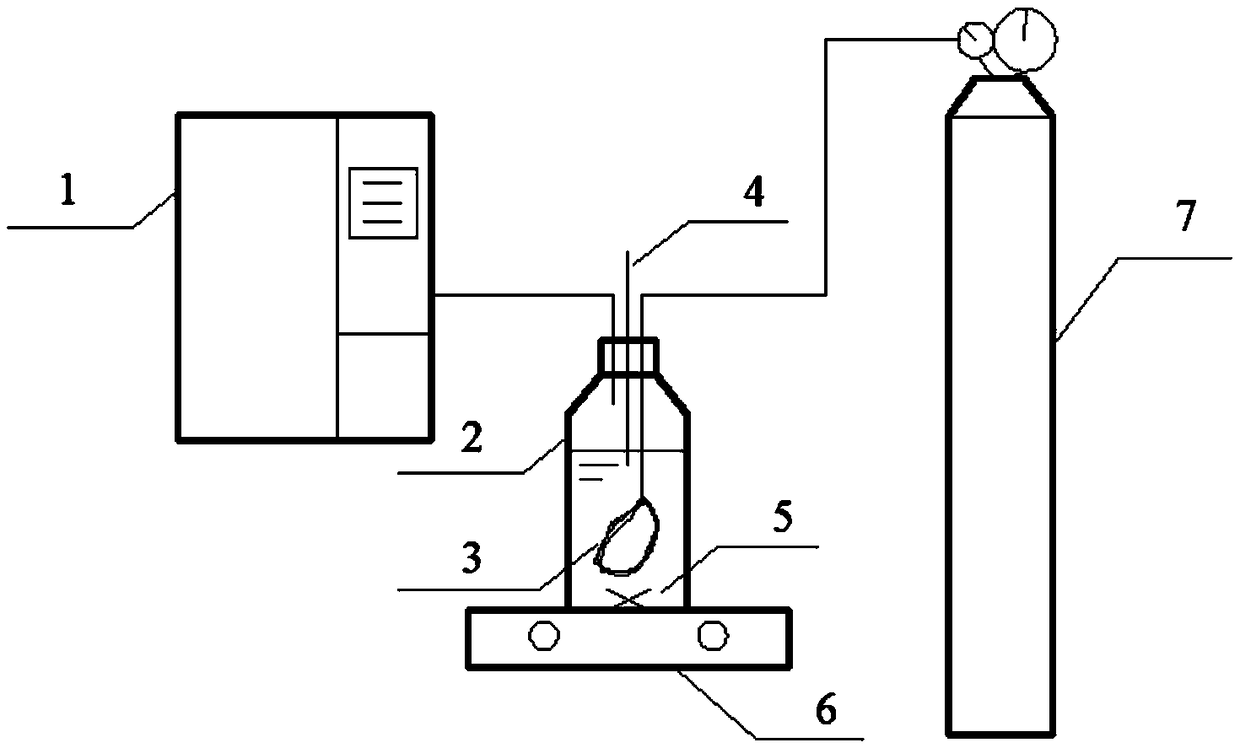
Method or culturing microalgae through membrane aeration
A membrane aeration, microalgae technology, applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, chemical instruments and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., to achieve the effects of being beneficial to the growth of microalgae, increasing the degree of photosynthesis, and increasing the utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] A method utilizing membrane aeration to cultivate microalgae, said method comprising the steps of:
[0032] Source of algae species: select chlorella that has been transformed into algae for 5 days in a constant temperature light incubator, and add 10mL of algae per 100mL of culture solution;
[0033] Experimental vial: the vial is a 1L glass bottle with a blue cap, and the working volume is 660mL (that is, 60mL of algae solution + 600mL of culture solution);
[0034] Vial reaction conditions: control the internal temperature of the incubator at 25°C, the light intensity at 8333 lumens, the initial pH of the culture solution at 7.0, the hollow fiber membrane is polyvinylidene fluoride, the pore size of the hollow fiber membrane is 300nm, and the membrane area of the hollow fiber membrane is 14.57cm 2 , the concentration of carbon dioxide gas is 20%;
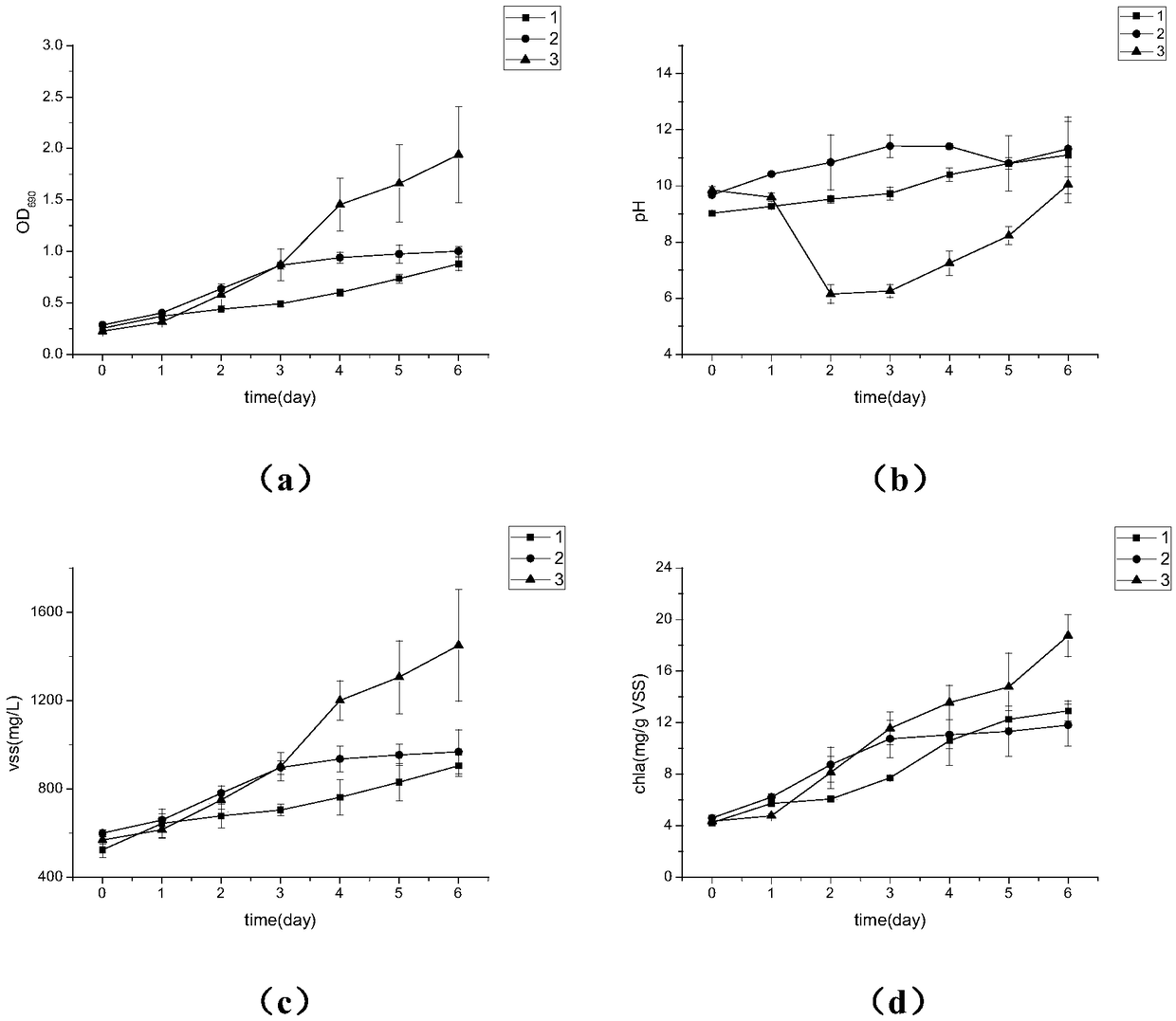
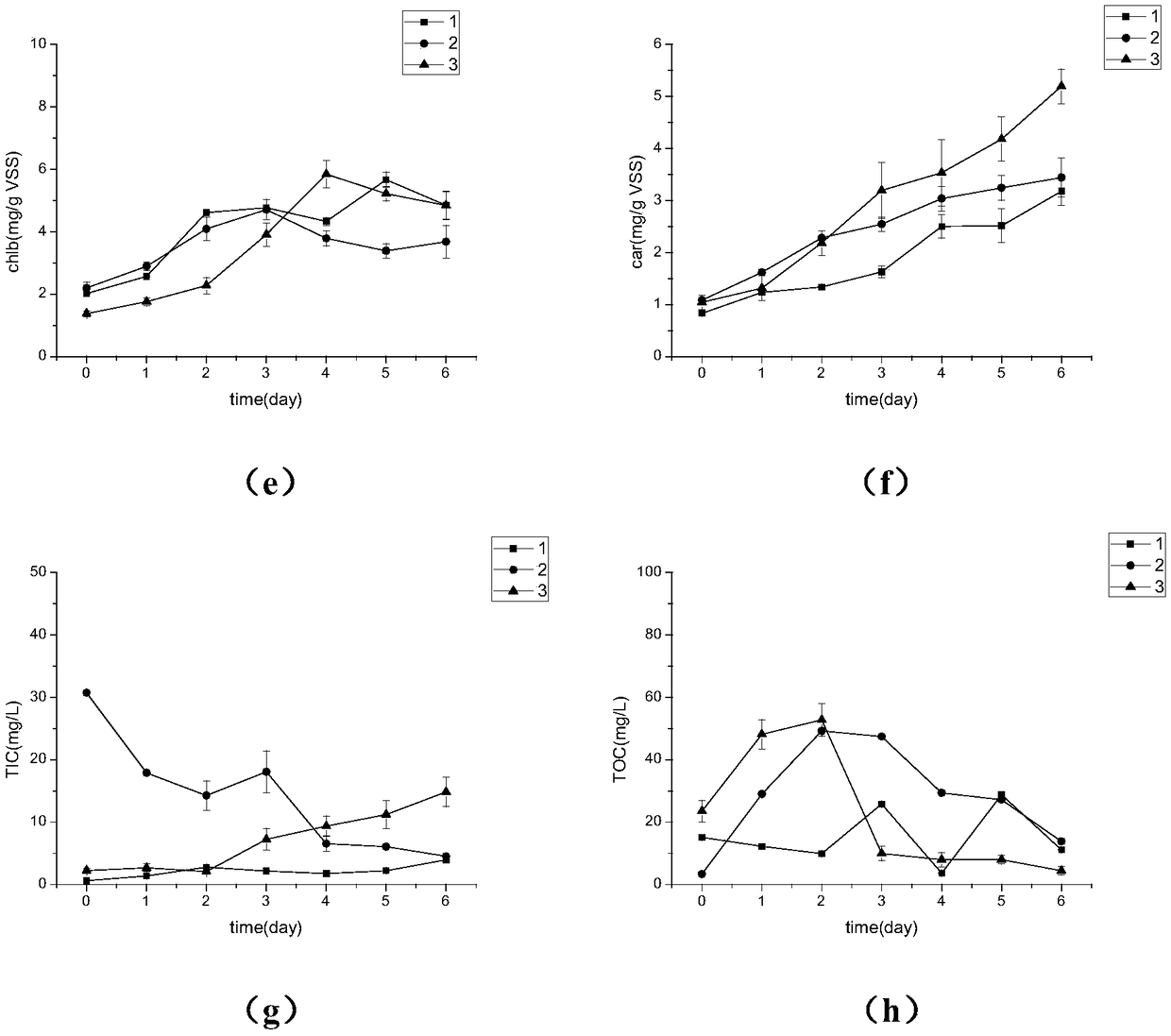
[0035] Batch test operation mode: the reaction time of each batch of vial experiments is 6 days, water samples are t...
Embodiment 2
[0037] A method for cultivating microalgae using membrane aeration, the difference from Example 1 is that the pore diameter of the hollow fiber membrane is 100nm.
Embodiment 3
[0039] A method for cultivating microalgae using membrane aeration, the difference from Example 1 is that the pore diameter of the hollow fiber membrane is 30nm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Membrane area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Aperture | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com